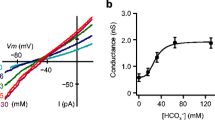
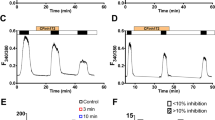
Abstract
Epithelial chloride channels can be blocked by various inhibitors, which show considerable differences in their molecular structure. In the present patch-clamp study, we compared different blockers of one type of epithelial Cl− channel with respect to their inhibitory potency. We applied the blockers to excised inside-out-or outside-out-oriented membrane patches of cultured HT29 colon carcinoma and respiratory epithelial cells (REC) containing the outwardly rectifying intermediate-conductance (ICOR) chloride channel. Four types of inhibitory compounds were tested: stilbene disulphonate derivatives, indanyloxyacetic acid, amidine, and arylaminobenzoates. The concentrations for half-maximal inhibition (IC50) for the different channel blockers were (μmol/l): 4-acetamido-4′-isothiocyanato-stilbene-2,2′-disulphonic acid 100; 4,4′-diisothiocyanato-stilbene-2,2′-disulphonic acid 80; indanyloxyacetic acid 9; 4,4′-dinitrostilbene-2, 2′-disulphonic acid 8; amidine 8 and 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)-benzoate (NPPB) 0.9. All compounds, when applied to the cytosolic side of the channel, induced a flicker-type block of the ICOR Cl− channel at lower concentrations and a complete channel inhibition at higher concentrations. The inhibitory potency of NPPB was much higher when it was added to the external surface of the channel in outside-out-oriented membrane patches. At 1 μmol/l the inhibition was complete. All blocker effects were fully reversible. The probe with the highest affinity (NPPB) and a closely related compound 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylethylamino)-benzoate (NPFB) were used to construct macromolecular probes by linking these blockers to aminopolyethyleneglycol (PEG) or aminoethyl-O-dextran (5 kDa). These macromolecular NPPB and NPEB derivatives inhibited the ICOR Cl− channels only from the outside but had no effect on the cytosolic side. In the case of PEG-NPPB an IC50 of 30 nmol/l was determined in outside-out patches. The data indicate that the interaction site for arylaminobenzoates is accessible from the outer aspects of the Cl− channel facing the extracellular medium. Furthermore, these data show that the macromolecular probes of arylaminobenzoates have affinities to the Cl− channel very similar to those of the respective parent compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridges RJ, Worrel RT, Frizzell RA, Benos DJ (1989) Stilbene disulfonate blockade of colonie secretory Cl− channels in planar lipid bilayers. Am J Physiol 256:C209-C912
Cabantchik ZI, Knauf PA, Rothstein A (1978) The anion transport system of the red blood cell. The role of membrane protein evaluated by use of “probes”. Biochim Biophys Acta 515:239–302
Champigny G, Verrier B, Lazdunski M (1990) Ca2+ channel blockers inhibit secretory Cl− channels in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 171:1022–1028
Cousin JL, Motais R (1982) Inhibition of anion red blood cell by anionic amphiphilic compounds: I. Determination of the flufenamate-binding site by proteolytic dissection of the band 3 protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 687:147–155
Cousin JL, Motais R (1982) Inhibition of anion transport in the red blood cell by anionic amphiphilic compounds: II. Chemical properties of the flufenamate-binding site on the band 3 protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 687:156–164
Cragoe EJ, Gould NP, Woltersdorf OW, Ziegler C, Bourke RS, Nelson LR, Kimelberg HK, Waldman JB, Popp AJ, Sedransk N (1982) Agents for the treatment of brain injury: 1. (Aryloxy)alkanoic acids. J Med Chem 25:567–579
Diener M, Rummel W, Mestres P, Lindemann B (1989) Single chloride channels in colon mucosa and isolated enterocytes of the rat. J Membr Biol 108:21–30
Di Stefano A, Wittner M, Schlatter E, Lang HJ, Englert H, Greger R (1985) Diphenylamine-2-carboxylate, a blocker of the Cl− -conductive pathway in Cl− -transporting epithelia. Pflügers Arch 405 [Suppl 1]:S95-S100
Dreinhöfer J, Gögelein H, Greger R (1988) Blocking kinetics of Cl− channels in colonic carcinoma cells (HT29) as revealed by 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)-benzoic acid (NPPB). Biochim Biophys Acta 956:135–142
Eidelman O, Yanai P, Englert HC, Lang HJ, Greger R, Cabantchik ZI (1991) Macromolecular conjugates of transport inhibitors: new tools for probing the topography of anion transport proteins. Am J Physiol (in press)
Gögelein H, Greger R (1986) Na+ selective channels in the apical membrane of rabbit late proximal tubule (pars recta). Pflügers Arch 406:198–203
Gray MA, Pollard CE, Harris A, Coleman L, Greenwell JR, Argent BE (1990) Anion selectivity and block of the small-conductance chloride channel on pancreatic duct cells. Am J Physiol 259:C752-C761
Greger R (1985) Ion transport mechanisms in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mammalian nephron. Physiol Rev 65:760–797
Greger R (1991) Chloride channel blockers. Methods Enzymol 191:793–810
Greger R, Gögelein H, Schlatter E (1987) Potassium channels in the basolateral membrane of the rectal gland of the dogfish (Squalus acanthias). Pflügers Arch 409:100–106
Greger R, Kunzelmann K, Gerlach L (1989) Mechanism of chloride transport in secretory epithelia. Ann NY Acad Sci 574:404–415
Greger R, Lang HJ, Englert HC, Wangemann P (1987) Blockers of the Na+ 2 Cl− K+ carrier and of chloride channels in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. In: Puschett JB (ed) Diuretics II. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 33–38
Greger R, Nitschke RB, Lohrmann E, Burhoff I, Hropot M, Englert HC, Lang HJ (1991) Effects of chloride channel blockers on equivalent short circuit current in rabbit colon. Pflügers Arch (in press)
Greger R, Schlatter E, Gögelein H (1987) Chloride channels in the luminal membrane of the rectal gland of the dogfish (Squalus acanthias). Properties of the “larger” conductance channel. Pflügers Arch 409:114–121
Greger R, Wangemann P, Wittner M, Di Stefano A, Lang HJ, Englert HC (1987) Blockers of active transport in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. In: Andreucci VE, Dal Canton A (eds) Diuretics: basic, pharmacological, and clinical aspects. Nijhoff, Boston, pp 33–38
Halm DR, Rechkemmer GR, Schoumacher RA, Frizzell RA (1988) Apical membrane chloride channels in a colonie cell line activated by secretory agonists. Am J Physiol 254: C505-C511
Halm DR, Rechkemmer G, Schoumacher RA, Frizzell RA (1989) Biophysical properties of a chloride channel in the apical membrane of a secretory epithelial cell. Comp Biochem Physiol 90A:597–601
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hanrahan JW. Tabcharani JA (1990) Inhibition of an outwardly rectifying anion channel by HEPES and related buffers. J Membr Biol 116:65–77
Hayslett JP, Gögelein H, Kunzelmann K, Greger R (1987) Characteristics of apical chloride channels in human colon cells (HT29). Pflügers Arch 410:487–494
Jorissen M, Vereecke J, Carmeliet E, Van den Berghe H, Cassiman JJ (1990) Outward-rectifying chloride channels in cultured adult and fetal human nasal epithelial cells. J Membr Biol 117:123–130
Kunzelmann K, Pavenstädt H, Beck C, Uenal O, Emmrich P, Arndt HJ, Greger R (1989) Characterization of potassium channels in respiratory cells: I. General properties. Pflügers Arch 414:291–296
Kunzelmann K, Pavenstädt H, Greger R (1989) Properties and regulation of chloride channels in cystic fibrosis and normal airway cells. Pflügers Arch 415:172–182
Landry DW, Reitman M, Cragoe EJ, Al-Awqati Q (1987) Epithelial chloride channel. J Gen Physiol 90:779–798
Landry DW, Akabas MH, Rehead C, Edelman A, Cragoe EJ, Al-Awqati Q (1989) Purification and reconstitution of chloride channels from kidney and trachea. Science 244:1469–1472
Li M, McCann JD, Welsh MJ (1990) Apical membrane Cl− channels in airway epithelia: anion selectivity and effect of an inhibitor. Am J Physiol 259:C295-C301
Nitschke R, Schlatter E, Eidelman O, Lang HJ, Englert HC, Cabantchik ZI, Greger R (1989) Piretanide-dextran and piretanide-polyethylene glycol interact with high affinity with the Na+ 2 Cl− K+ cotransporter in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. Pflügers Arch 413:559–561
Novak I, Greger R (1988) Properties of the luminal membrane of isolated perfused rat pancreatic ducts. Pflügers Arch 411:546–553
Passow H (1986) Molecular aspects of band 3 protein-mediated anion transport across the red blood cell membrane. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 103:62–123
Reinach PS, Schoen HF (1990) NPPB inhibits the basolateral membrane K+ conductance in the isolated bullfrog cornea. Biochim Biophys Acta 1026:13–20
Rohlicek V, Fröbe U, Gögelein H, Greger R (1989) Versatile supplement device with remote control for the control of patch clamp experiments. Pflügers Arch 413:444–446
Siemer C, Gögelein H (1990) Activation of nonselective cation channels during stimulation of secretion in rat distal colon cells. In: Wong PYD, Young JA (eds) Exocrine secretion II. United League Graphic and Printing Co., Hongkong, pp 123–124
Wangemann P, Wittner M, Di Stefano A, Englert HC, Lang HJ, Schlatter E, Greger R (1986) Cl−-channel blockers in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. Structure activity relationship. Pflügers Arch 407 [Suppl 2]:S128-S141
Welsh MJ (1986) Single apical membrane anion channels in primary cultures of canine tracheal epithelium. Pflügers Arch 407:S116-S122
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tilmann, M., Kunzelmann, K., Fröbe, U. et al. Different types of blockers of the intermediate-conductance outwardly rectifying chloride channel in epithelia. Pflügers Arch 418, 556–563 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00370571
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00370571