Abstract
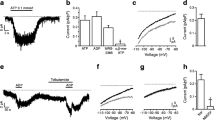
Pretreatment of pancreatic β cells with pertussis toxin resulted in a 30% increase in peak whole-cell Ca2+ currents recorded in the absence of exogenous intracellular guanine nucleotides. Intracellular application of 90 μM GTP[γS], by liberation from a caged precursor, resulted in 40% reduction of the peak Ca2+ current irrespective of whether the current was carried by Ca2+ or Ba2+. Effects on the delayed outward K+ current were small and restricted to a transient Ca2+-dependent K+ current component. Inhibition by GTP[γS] of the Ca2+ current was not mimicked by standard GTP and could not be prevented either by pretreatment with pertussis toxin or by inclusion of GDP[βS] or cyclic AMP in the intracellular medium. The inhibitory effect of GTP[γS] could be counteracted by a prepulse to a large depolarizing voltage. A similar effect of a depolarizing prepulse was observed in control cells with no exogenous guanine nucleotides. These observations indicate that inhibition of β cell Ca2+ current by G protein activation results from direct interaction with the channel and does not involve second-messenger systems. Our findings also suggest that the β cell Ca2+ current is subject to resting inhibition by G proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrén B, Berggren PO, Bokvist, K, Rorsman PO (1989) Does galanin inhibit insulin secretion by opening of the ATP-regulated K+-channel in the β-cell? Peptides 10:453–457
Ämmälä C, Bokvist K, Galt S, Rorsman P (1991) Inhibition of ATP-regulated K+-channels by a photoactivatable ATP-analogue in mouse pancreatic β-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1092:347–349
Ashcroft FM, Rorsman P (1989) Electrophysiology of the pancreatic β-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 54:87–143
Ashcroft FM, Harrison DE, Ashcroft FM (1984) Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic β-cells. Nature 312:446–448
Ashcroft FM, Kelly R, Smith PA (1990) Two types of Ca channel in rat pancreatic β-cells. Pflügers Arch 415:504–506
Bokvist K, Ämmälä C, Berggren PO, Rorsman P, Wåhlander K (1991) Alpha2-adrenoceptor stimulation does not inhibit L-type calcium channels in mouse pancreatic β-cells. Biosci Rep 11:147–157
Cook DL, Hales CN (1984) Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+-channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature 311:269–271
Cook DL, Perara E (1982) Islet electric pacemaker response to alpha adrenergic stimulation. Diabetes 31:985–990
Dolphin AC (1990) G protein modulation of calcium currents in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol 52:243–255
Dolphin AC (1991) Regulation of calcium channel activity by GTP binding proteins and second messengers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1091:68–80
Dolphin AC, Scott RH (1987) Calcium-channel currents and their inhibition by (−)-baclofen in rat sensory neurons: modulation by guanine nucleotides. J Physiol (Lond) 386:1–17
Dolphin AC, Wooton JF, Scott RH, Trentham DR (1988) Photoactivation of intracellular guanosine triphosphate analogues reduces and slows the kinetics of voltage-activated calcium channel currents in sensory neurons. Pflügers Arch 411:628–636
Drews G, Debuyser A, Nenquin N, Henquin JC (1990) Galanin and epinephrine act on distinct receptors to inhibit insulin release by the same mechanisms including an increase in K+ -permeability of the β-cell membrane. Endocrinology 126:1646–1653
Dunne MJ, Bullett MJ, Li GD, Wollheim CB, Petersen OH (1989) Galanin activates nucleotide-dependent K+-channels in insulin-secreting cells via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein. EMBO J 8:413–420
Grassi F, Lux HD (1989) Voltage-dependent GABA-induced modulation of calcium currents in chick sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett 105:113–119
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high resolution recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hescheler J, Rosenthal W, Wulfern M, Tang M, Yajima M, Trautwein W, Schultz G (1988) Involvement of the guanine nucleotide-binding protein N0, in the inhibitory regulation of neuronal calcium channels. Adv 2nd Messenger Phosphoprotein Res 21:165–174
Hildebrandt JD, Sekura RD, Codina J, Iyengar R, Manclark CR, Birnbaumer L (1983) Stimulation and inhibition of adenylyl cyclases mediated by distinct regulatory proteins. Nature 302:706–709
Hiriart M, Matteson DR (1988) Na channels and two types of Ca-channels in rat pancreatic β-cells identified with the reverse hemolytic plaque assays. J Gen Physiol 91:617–639
Hoenig M, Matschinsky FM (1987) HPLC analysis of nucleotide profiles in glucose-stimulated rat islets. Metabolism 36:295–301
Hopkins WF, Satin LS, Cook DL (1991) Inactivation kinetics and pharmacology distinguish two calcium currents in mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Membr Biol 119:229–239
Hsu WH, Xiang, H, Rajan AS, Kunze DL, Boyd AE (1991) Somatostatin inhibits insulin secretion by a G-protein-mediated decrease in Ca2+ entry through voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in the beta cell. J Biol Chem 266:837–843
Jakobs KH, Aktories K, Schultz G (1984) Mechanisms of pertussis toxin action on the adenylate cyclase system. Eur J Biochem 140:177–181
Keahey HH, Boyd AE III, Kunze DL (1989) Catecholamine modulation of calcium currents in clonal pancreatic β-cells. Am J Physiol 257:C1171-C1176
Lewis DL, Luini A, Weight FF (1986) A guanine nucleotidebinding protein mediates the inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:9035–9039
Nilsson T, Arkhammar P, Rorsman P, Berggren PO (1989) Suppression of insulin release by galanin and somatostatin is mediated by G-protein. An effect involving repolarisation and reduction in cytoplasmic free Ca2+-concentration. J Biol Chem 264:973–980
Plant TD (1988) Properties and calcium-dependent inactivation of calcium currents in cultured mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol (Lond) 404:731–747
Prentki M, Matschinsky FM (1987) Ca2+, cAMP and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol Rev 67:1185–1249
Robertson RP, Seaquist ER, Walseth TF (1991) G proteins and modulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes 40:1–6
Rorsman P, Trube G (1986) Calcium and delayed potassium currents in mouse pancreatic β-cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol (Lond) 374:531–550
Rorsman P, Ashcroft FM, Trube G (1988) Single Ca channel currents in mouse pancreatic B-cells. Pflügers Arch 412:597–603
Rorsman P, Bokvist K, Ämmälä C, Arkhammar P, Berggren P-O, Larsson O. Wåhlander K (1991) Activation by adrenaline of a low-conductance G protein-dependent K+-channel in mouse pancreatic B-cells. Nature 349:77–79
Satin LS, Cook DL (1989) Calcium current inactivation in insulin-secreting cells is mediated by calcium influx and membrane depolarization. Pflügers Arch 414:1–10
Schultz G, Rosenthal W, Hescheler J, Trautwein W (1990) Role of G-proteins in calcium channel modulation. Annu Rev Physiol 52:275–292
Scott RH, Dolphin AC (1990) Voltage-dependent modulation of rat sensory neurone calcium channel currents by G protein activation-effect of a dihydropyridine antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 99:629–630
Smith PA, Rorsman P, Ashcroft FM (1989) Modulation of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ -channels by glucose metabolism in pancreatic β-cells. Nature 342:550–553
Smith PA, Bokvist K, Arkhammar P, Berggren PO, Rorsman P (1990) Delayed rectifying and calcium-activated K+-channels and their significance for action potential repolarization in mouse pancreatic β-cells. J Gen Physiol 95:1041–1059
Toselli M, Lang J, Costa T, Lux HD (1989) Direct modulation of voltage-dependent calcium channels by muscarinic activation of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein in hippocampal neurons. Pflügers Arch 415:255–261
Velasco JM, Petersen JUH, Peterson OH (1988) Single channel Ba2+ currents in insulin-secreting cells are activated by glyceraldehyde stimulation. FEBS Lett 213:366–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ämmälä, C., Berggren, PO., Bokvist, K. et al. Inhibition of L-type calcium channels by internal GTP [γS] in mouse pancreatic β cells. Pflugers Arch. 420, 72–77 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378643
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378643