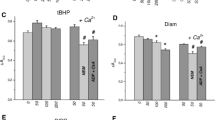
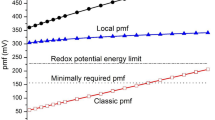
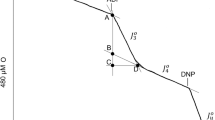
Abstract
A study is presented of the effect of acidic uncouplers and oligomycin on energy-linked and passive proton translocation, oxidative phosphorylation, and energy-linked nicotinamide-adenine-nucleotide transhydrogenase in EDTA submitochondrial particles from beef-heart. A flow potentiometric technique has been applied to resolve the kinetics of the initial rapid phase of the redox proton pump. Rapid kinetics analysis shows that carbonyl-cyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-hydrazone (FCCP) does not exert any direct effect on redox-linked active proton transport. The uncoupling action of FCCP on oxidative phosphorylation and energy-linked transhydrogenase is shown to be quantitatively accounted for by its promoting effect of passive proton-diffusion across the mitochondrial membrane. Oligomycin depresses passive proton diffusion in EDTA sonic particles and this effect accounts for the coupling action exerted by the antibiotic on oxidative phosphorylation and energy-linked transhydrogenase. In fact, rapid kinetic analysis demonstrates that oligomycin does not directly affect the redox-linked proton pump. The present results show that there does not exist any labile intermediate in the redox-linked proton pump which is sensitive to acidic uncouplers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Papa, in:Energy Transduction in Respiration and Photosynthesis, E. Quagliariello, S. Papa and C.S. Rossi (Eds.), Adriatica Editrice, Bari (1971) p. 173.
S. Papa, F. Guerrieri, S. Simone, M. Lorusso and D. Larosa,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,292 (1973) 20.
S. Papa, F. Guerrieri, S. Simone and M. Lorusso, in:Mechanisms in Bioenergetics, G.F. Azzone, L. Ernster, S. Papa, E. Quagliariello and N. Siliprandi (Eds.), Academic Press, New York and London (1973) p. 451.
S. Papa, A. Scarpa, C.P. Lee and B. Chance,Biochemistry,11 (1972) 3091.
S. Papa, F. Guerrieri, M. Lorusso and S. Simone,Biochimie,55 (1973) 703.
P. Mitchell and J. Moyle,Eur. J. Biochem.,7 (1969) 471.
V.P. Skulachev, in:Current Topics in Bioenergetics, D.R. Sanadi (Ed.), Academic Press, New York and London, Vol. 4 (1971) p. 127.
E.J. Harris and B.C. Pressman,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,172 (1969) 66.
S. Massari and G.F. Azzone,Eur. J. Biochem.,12 (1970) 310.
F. Guerrieri, M. Lorusso and S. Papa, 9th Int. Congr. Biochem., Stockholm, 1973, Abstract no. 4j 8.
H. Löw and I. Vallin,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,69 (1963) 361.
C.P. Lee and L. Ernster,Eur. J. Biochem.,3 (1968) 391.
H.J. Hohorst, in:Methods in Enzymatic Analysis, H.U. Bergmeyer (Ed.), Academic Press, New York (1963) p. 134.
M. Klingenberg, in:Methods in Enzymatic Analysis, H.U. Bergmeyer (Ed.), Academic Press, New York (1963) p. 535.
L. Rossi Bernardi and R.L. Berger,J. Biol. Chem.,243 (1968) 1297.
S. Papa, F. Guerrieri and M. Lorusso,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,357 (1974) 181.
J.T. Penniston,Biochemistry,12 (1973) 650.
S. Papa, F. Guerrieri and M. Lorusso, in:Membrane Proteins in Transport and Phosphorylation, M. Klingenberg and G.F. Azzone (Eds.), North-Holland, Amsterdam (1974) p. 177.
S. Papa, M. Lorusso and F. Guerrieri,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,376 (1975) 231.
P. Mitchell and J. Moyle,Biochemical J.,105 (1967) 1147.
S. Papa, F. Guerrieri, L. Rossi Bernardi and J.M. Tager,Biochim. Biophys. Acta,197 (1970) 100.
P.C. Hinkle and L.L. Horstman,J. Biol. Chem.,246 (1971) 6024.
C.P. Lee and L. Ernster, in:Regulation of Metabolic Processes in Mitochondria, J.M. Tager, S. Papa, E. Quagliariello and E.C. Slater (Eds.), Elsevier, Amsterdam (1966) p. 218.
S. Papa, F. Guerrieri, S. Simone and M. Lorusso, in:Mechanisms in Bioenergetics, G.F. Azzone, L. Ernster, S. Papa, E. Quagliariello and N. Siliprandi (Eds.), Academic Press, New York and London (1973) p. 451.
P. Mitchell,FEBS Letters,33 (1973) 267.
P.L. Pedersen,J. Bioenergetics,6 (1975) 243.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerrieri, F., Lorusso, M., Pansini, A. et al. On the mechanism of action of oligomycin and acidic uncouplers on proton translocation and energy transfer in “sonic” submitochondrial particles. J Bioenerg Biomembr 8, 131–142 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00748959
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00748959