Summary
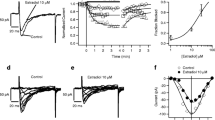
Extracellular calcium concentration is an important regulator of calcitonin secretion. We used primary cell cultures of human medullary thyroid carcinoma to study the role of voltage dependent calcium channels for stimulus secretion coupling. Increasing extracellular calcium concentration (1.6–5.0 mM) in the medium caused a dose dependent release of calcitonin. The calcium channel activator BAY K 8644, a dihydropyridine, stimulated calcitonin secretion in a dose dependent manner (10−7−10−5 M). This effect was completely inhibited by equimolar concentrations of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine and abolished in the absence of extracellular calcium. Similarly, nifedipine suppressed the stimulatory action of extracellular calcium. The effects of calcium and BAY K 8644 with and without nifedipine suggest that calcium influx via voltage dependent calcium channels plays an important role in calcitonin secretion. The primary cell culture of human medullary thyroid carcinoma is a good model for the study of stimulus secretion coupling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
calcitonin
- [Ca2+]e :
-
extracellular calcium concentration
- [Ca2+]i :
-
intracellular calcium concentration=cytosolic free calcium concentration
- MTC:
-
medullary thyroid carcinoma
References
Austin LA, Health III H (1981) Calcitonin, physiology and pathophysiology. N Engl J Med 304:269–278
Cooper CW, Borosky SA, Farrell PE, Steinsland OS (1986) Effects of the calcium channel activator BAY K 8644 on in vitro secretion of calcitonin and parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology 118:545–549
Fried RM, Tashjian AH (1986) Unusual sensitivity of cytosolic free Ca2+ to changes in extracellular Ca2+ in rat C-cells. J Biol Chem 261:7669–7674
Fried RM, Tashjian AH (1987) Action of rat growth hormone-releasing factor and norepinephrine on cytosolic free calcium and inositol triphosphate in rat C-cells. J Bone Mineral Res 2:579–585
Haller-Brem S, Muff R, Fischer JA (1988) Calcitonin generelated peptide and calcitonin secretion from a human medullary thyroid carcinoma cell line: effects of ionomycin, phorbol ester and forskolin. J Endocr 119:147–152
Haller-Brem S, Muff R, Petermann JB, Born W, Roos BA, Fischer JA (1987) Role of cytosolic free calcium concentration in the secretion of calcitonin gene-related peptide and calcitonin from medullary thyroid carcinoma cells. Endocrinology 121:1272–1277
Hishikawa R, Fukase M, Takenaka M, Fujita T (1985) Effect of calcium channel agonist BAY K 8644 on calcitonin secretion from a rat C-cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Com 130:454–459
Muff R, Nemeth EF, Haller-Brem S, Fischer JA (1988) Regulation of hormone secretion and cytosolic Ca2+ by extracellular Ca2+ in parathyroid cells and C-cells: role of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Arch Biochem Biophys 265:128–135
Nakamura A, Kakuda K, Watanabe K (1987) Estabishment of new human thyroid medullary carcinoma cell line, morphological studies. Virchows Arch B 53:332–335
Rasmussen H (1986) The calcium messenger system. N Engl J Med 314:1164–1170
Raue F, Boller G, Rix E, Schmidt-Gayk H, Ziegler R (1985) Secretion of calcitonin and carcinoembryonic antigen in long term organ culture of human medullary thyroid carcinoma: biochemical and immunocytochemical studies. Klin Wochenschr 63:205–210
Raue F, Minne H, Ziegler R (1987) Calcitonin. In: Pesca AJ, Kaplan LA (eds) Methods in clinical chemistry. CV Mosby, St. Louis, pp 696–701
Raue F, Wieland U, Weiler C, Ziegler R (1988) Enhanced calcitonin secretion in the rat after parathyroidectomy and during chronic calcium deprivation. Europ J Clin Invest 18:284–289
Roos BA, Bundy LL, Miller EA, Deftos LJ (1975) Calcitonin secretion by monolayer cultures of human C-cells derived from medullary thyroid carcinoma. Endocrinology 97:39–45
Scherübl H, Raue F, Zopf G, Schneider HG, Ziegler R (1988) Calcitonin secretion from a rat C-cell line, synergistic stimulatory effects of glucagon and calcium, BAY K 8644 or A 23187, respectively. Acta Endocr 117, Suppl 287: Abstr 77
Schurr W, Rix E, Schmidt-Gayk H, Raue F, Ziegler R (1986) Metastatic C-cell carcinoma: calcitonin and CEA production in monolayer culture. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 111:284–288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, grant Raue 327/1–2 and Tumorzentrum Heidelberg/Mannheim
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raue, F., Serve, H., Grauer, A. et al. Role of voltage-dependent calcium channels in secretion of calcitonin from human medullary thyroid carcinoma cells. Klin Wochenschr 67, 635–639 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01718147
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01718147