Summary
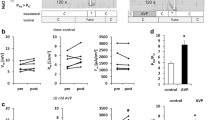
Cellular impalements were used in combination with standard transepithelial electrical measurements to evaluate some of the determinants of the spontaneous lumen-positive voltage,V e , which attends net Cl− absorption,J netCl , and to assess how ADH might augment bothJ metCl andV e in the mouse medullary thick ascending limb of Henle microperfusedin vitro. Substituting luminal 5mm Ba++ for 5mm K+ resulted in a tenfold increase in the apical-to-basal membrane resistance ratio,R c /R bl , and increasing luminal K+ from 5 to 50mm in the presence of luminal 10−4 m furosemide resulted in a 53-mV depolarization of apical membrane voltage,V a . Thus K+ accounted for at least 85% of apical membrane conductance. Either with or without ADH. 10−4 m luminal furosemide reducedV e andJ netCl to near zero values and hyperpolarized bothV a andV bl , the voltage across basolateral membranes; however, the depolarization ofV bl was greater in the presence than in the absence of hormone while the hormone had no significant effect on the depolarization ofV a , Thus ADH-dependent increases inV b were referable to greater depolarizations ofV bl in the presence of ADH than in the absence of ADH 68% of the furosemide-induced hyperpolarization ofV a was referable to a decrease in the K+ current across apical membranes, but, at a minimum, only 19% of the hyperpolarization ofV bl could be accounted for by a furosemide-induced reduction in basolateral membrane Cl− current. Thus an increase in intracellular Cl− activity may have contributed to the depolarization ofV bl during net Cl− absorption, and the intracellular Cl− activity was likely greater with ADH than without hormone. Since ADH increases apical K+ conductance and since the chemical driving force for electroneutral Na+,K+,2Cl− cotransport from lumen to cell may have been less in the presence of ADH than in the absence of hormone, the cardinal effects of ADH may have been to increase the functional number of both Ba++-sensitive conductance K+ channels and electroneutral Na+,K+,2Cl− cotransport units in apical plasma membranes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Zahid, G., Schafer, J.A., Troutman, S.L., Andreoli, T.E. 1977. Effect of antidiuretic hormone on water and solute permeation, and the activation energies for these processes, in mammalian cortical collecting tubules: Evidence for parallel ADH-sensitive pathways for water and solute diffusion in luminal plasma membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 31:103–129
Anagnostopoulos, T., Teulon, J., Edelman, A. 1980. Conductive properties of the proximal tubule inNecturus kidney.J. Gen. Physiol. 75:553–587
Biagi, B., Kubota, T., Sohtell, M., Giebisch, G. 1981. Intracellular potentials in rabbit proximal tubules perfusedin vitro.Am. J. Physiol. 240:F200-F210
Blatt, M.R., Slayman, C.L. 1983. KCl leakage from microelectrodes and its impact on the membrane parameters of a nonexcitable cell.J. Membrane Biol. 72:223–234
Boulpaep, E.L., Sackin, H. 1980. Electrical analysis of intraepithelial barriers.Curr. Top. Membr. Transp. 13:169–197
Bourguet, J., Chevalier, J., Hugon, J.S., 1976. Alterations in membrane-associated particle distribution during antidiuretic challenge in frog urinary bladder epithelium.Biophys. J. 6:627–639
Chevalier, J., Bourguet, J., Hugon, J.S. 1974. Membrane associated particles: Distribution in frog urinary bladder epithelium at rest and after oxytocin treatment.Cell Tiss. Res. 152:129–140
Chevalier, J., Parisi, M., Bourguet, J. 1979. Particle aggregation during antidiuretic action: Some comments on their formation.Biol. Cellulaire 35:207–210
Fromm, M., Schultz, S.G. 1981. Some properties of KCl-filled microelectrodes: Correlation of potassium “leakage” with tip resistance.J. Membrane Biol. 62:239–244
Grantham, J.J., Burg, M.B. 1966. Effect of vasopressin and cyclic AMP on permeability of isolated collecting tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 211:255–259
Greger, R. 1981. Coupled transport of Na+ and Cl− in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit nephron.Scand. Audiology Suppl. 14:1–15
Greger, R., Frömter, E., Schlatter, E. 1981. Intracellular measurements of the electrical potential difference in the isolated perfused cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit nephrons.Pfluegers Arch. 389:R40
Greger, R., Oberleithner, H., Schlatter, E., Cassola, A.C., Weidtke, C. 1983. Chloride activity in cells of isolated perfused cortical thick ascending limbs of rabbit kidney.Pfluegers Arch. 399:29–34
Greger, R., Schlatter, E. 1983. Properties of the lumen membrane of the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney.Pfluegers Arch. (in press).
Guggino, W.B., Stanton, B.A., Giebisch, G. 1982a. Regulation of apical potassium conductance in the isolated early distal tubule of theAmphiuma kidney.Biophys. J. 37:338a
Guggino, W.B., Stanton, B.A., Giebisch, G., 1982b. Electrical properties of isolated early distal tubule of theAmphiuma kidney.Fed. Proc. 41:1597
Guggino, W.B., Windhager, E.E., Boulpaep, E.L., Giebisch, G. 1982c. Cellular and paracellular resistances of theNecturus proximal tubule.J. Membrane Biol. 67:143–154.
Hays, R.M., Bourguet, J., Chevalier, J. 1981. Membrane fusion in the action of ADH, determined with a ultrarapid freezing technique.Am. Soc. Nephrol. 14th Annual Meeting, Nov. 22–24, 149a
Hays, R.M., Franki, N. 1970. The role of water diffusion in the action of vasopressin.J. Membrane Biol. 2:263–276
Hebert, S.C., Andreoli, T.E. 1980. Interactions of temperature and ADH on transport processes in cortical collecting tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 238:F470-F480
Hebert, S.C., Culpepper, R.M., Andreoli, T.E. 1981a. NaCl transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs: I. Functional nephron heterogeneity and ADH-stimulated NaCl cotransport.Am. J. Physiol. 241:F412-F431
Hebert, S.C., Culpepper, R.M., Andreoli, T.E., 1981b. NaCl transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs, II. ADH enhancement of transcellular NaCl cotransport: origin of transepithelial voltage.Am. J. Physiol. 241:F432-F442
Hebert, S.C., Friedman, P.A., Andreoli, T.E. 1984. Effects of antidiuretic hormone on cellular conductive pathways in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs of Henle. I. ADH increases transcellular conductance pathways.J. Membrane Biol. 80:201–219
Kachadorian, W.A., Wade, J.B., Uiterwyk, C.C., DiScala, V.A., 1977. Membrane structural and functional responses to vasopressin in toad bladder.J. Membrane Biol. 30:381–401
Koeppen, B.M., Biagi, B.A., Giebisch, G.H. 1983. Intracellular microelectrode characterization of the rabbit cortical collecting duct.Am. J. Physiol. 244:F35-F47
Leaf, A. 1965. Transepithelial transport and its hormonal control in toad bladder.Ergeb. Physiol. 56:216–263
Levine, S.D., Jacoby, M., Finkelstein, A. 1983. The length of the single-file channel in toad urinary bladder.Kidney Int. 23:262
Li, H.-Y.S., Palmer, L.G., Edelman, I.S., Lindemann, B. 1982. The role of sodium-channel density in the natriferic response of the toad urinary bladder to an antidiuretic hormone.J. Membrane Biol. 64:77–89
Murer, H., Greger, R. 1982. Membrane transport in the proximal tubule and thick ascending limb of Henle's loop: Mechanisms and their alterations.Klin. Wochenschr. 60:1103–1113
Oberleithner, H., Giebisch, G. Lang, F., Wang, W. 1982a. Cellular mechanism of the furosemide sensitive transport system in the kidney.Klin. Wochenschr. 60:1173–1179
Oberleithner, H., Guggino, W., Giebisch, G. 1982b. Mechanism of distal tubular chloride transport inAmphiuma kidney.Am. J. Physiol. 242:F331-F339
Oberleithner, H., Guggino, W., Giebisch, G. 1983a. The effect of furosemide on luminal sodium, chloride and potassium transport in the early distal tubule ofAmphiuma kidney: Effects of potassium adaptation.Pfluegers Arch. 396:27–33
Oberleithner, H., Lang, F., Greger, R., Wang, W., Giebisch, G., 1983b. Effect of luminal potassium on cellular sodium activity in the early distal tubule ofAmphiuma kidney.Pfluegers Arch. 396:34–40
Oberleithner, H., Lang, F., Wang, W., Giebisch, G. 1982c. Effects of inhibition of chloride transport on intracellular sodium activity in distal amphibian nephron.Pfluegers Arch. 394:55–60
Sackin, H., Boulpaep, E.L., 1981. Isolated perfused salamander proximal tubule: Methods, electrophysiology, and transport.Am. J. Physiol. 241:F39-F52
Sackin, H., Morgunov, N., Boulplaep, E.L. 1982. Electrical potentials and luminal membrane ion transport in the amphibian renal diluting segment.Fed. Proc. 41:1495
Schafer, J.A., Andreoli, T.E., 1972. Cellular constraints to diffusion. The effect of antidiuretic hormone on water flows in isolated mammalian collecting tubules.J. Clin. Invest. 51:1264–1268
Schultz, S.G., Frizzell, R.A., Nellans, H.N. 1977. An equivalent electrical circuit model for “sodium-transporting” epithelia in the steady-state.J. Theor. Biol. 65:215–229
Wade, J.B., Stetson, D.L., Lewis, S.A. 1981. ADH action: Evidence for a membrane shuttle mechanism.Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 372:106–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hebert, S.C., Andreoli, T.E. Effects of antidiuretic hormone on cellular conductive pathways in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs of Henle: II. Determinants of the ADH-mediated increases in transepithelial voltage and in net Cl− absorption. J. Membrain Biol. 80, 221–233 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868440
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868440