Summary
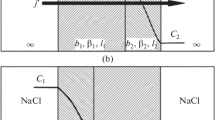
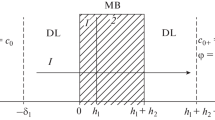
Evidence is presented that the transport of lipid-soluble ions through bilayer membranes occurs in three distinct steps: (1) adsorption to the membranesolution interface; (2) passage over an activation barrier to the opposite interface; and (3) desorption into the aqueous solution. Support for this mechanism comes from a consideration of the potential energy of the ion, which has a minimum in the interface. The formal analysis of the model shows that the rate constants of the individual transport steps can be determined from the relaxation of the electric current after a sudden change in the voltage. Such relaxation experiments have been carried out with dipicrylamine and tetraphenylborate as permeable ions. In both cases the rate-determining step is the jump from the adsorption site into the aqueous phase. Furthermore, it has been found that with increasing ion concentration the membrane conductance goes through a maximum. In accordance with the model recently developed by L. J. Bruner, this behavior is explained by a saturation of the interface, which leads to a blocking of the conductance at high concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruner L. J. 1970. Blocking phenomena and charge transport through membranes.Biophysik 6:241.
Ciani, S., Eisenman, G., Szabo, G. 1969. A theory for the effects of neutral carriers such as the macrotetralide actin antibiotics on the electric properties of bilayer membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 1:1.
Gaboriaud, R. 1966. Sur le comportement des acides non chargés dans les milieux eau-méthanol.Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. (Paris) C 263:911.
Grunwald, E., Baughman, G., Kohnstam, G. 1960. The solvation of electrolytes in dioxane-water mixtures, as deduced from the effect of solvent change on the standard partial molar free energy.J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 82:5801.
Läuger, P., Lesslauer, W., Marti, E., Richter, J. 1967. Electrical properties of bimolecular phospholipid membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 135:20.
Le Blanc, Jr., O. H. 1969. Tetraphenylborate conductance through lipid bilayer membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 193:350.
Liberman, E. A., Topaly, V. P. 1968. Selective transport of ions through bimolecular phospholipid membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 163:125.
—— 1969. Permeability of bimolecular phospholipid membranes for lipid-soluble ions.Biophysics 14:477.
Mueller, P., Rudin, D. O. 1967. Development of K+−Na+ discrimination in experimental bimolecular lipid membranes by macrocyclic antibiotics.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 26:398.
Neumcke, B. 1970. Ion flux across lipid bilayer membranes with charged surfaces.Biophysik 6:231.
— 1971. Diffusion polarization at lipid bilayer membranes.Biophysik 7:95.
—, Läuger, P. 1969. Nonlinear electrical effects in lipid bilayer membranes. II. Integration of the generalized Nernst-Planck equations.Biophys. J. 9:1160.
—— 1970. Space charge-limited conductance in lipid bilayer membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 3:54.
Robles, E. C., Van den Berg, D. 1969. Synthesis of lecithins by acylation of O-(sn-glycero-3-phosphoryl) choline with fatty acid anhydrides.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 187:520.
Skinner, J. F., Fuoss, R. M. 1964. Conductance of triisoamylbutylammonium and tetraphenylboride.J. Phys. Chem. 68:1882.
Walz, D., Bamberg, E., Läuger, P. 1969. Nonlinear electrical effects in lipid bilayer membranes. I. Ion injection.Biophys. J. 9:1150.
Zwolinsky, B. J., Eyring, H., Reese, C. 1949. Diffusion and membrane permeability.J. Phys. Colloid Chem. 53:1426.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ketterer, B., Neumcke, B. & Läuger, P. Transport mechanism of hydrophobic ions through lipid bilayer membranes. J. Membrain Biol. 5, 225–245 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870551
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870551