Abstract
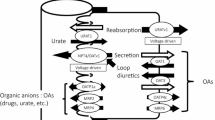
A wide variety of endogenous organic ions and xenobiotics are secreted into the urine via organic anion and cation transport systems, expressed in brush-border and basolateral membranes of renal tubular cells. Using membrane vesicles isolated from the kidney, cultured renal epithelial cells, isolated renal tubules, and slices of renal cortex, extensive studies have been done regarding the mechanisms of renal tubular secretion of organic ions. Basolateral entry of organic anions is mediated by the organic anion/dicarboxylate exchange system, whereas apical extrusion of organic anions from epithelial cells is mediated by an anion exchanger and/or by membrane potential-sensitive transport systems. Studies using membrane vesicles have made clear the fact that the basolateral transport of organic cations is stimulated by inside-negative membrane potential, whereas the transport of organic cations in brush-border membranes is achieved by a proton gradient. Trasport studies using cultured renal epithelial cells have shown other aspects of organic ion transport, such as regulatory mechanisms for transcellular transport of orgnaic anions and cations. The recent development of molecular techniques has greatly advanced our understanding of the molecular aspects of various transport processes. In 1994, a cDNA clone encoding the prototype organic cation transporter was isolated from rat kidney. Within the last 3 years, several organic anion and cation transporters in the kidney have been identified by different cloning techniques. In this review, we describe the mechanisms mediating renal tubular secretion of organic anions and cations, including recent topics in this area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pritchard JB, Miller DS. Mechanisms mediating renal secretion of organic anions and cations. Physiol Rev 1993;73:765–796.
Ullrich KJ. Specificity of transporters for ‘organic anions’ and ‘organic cations’ in the kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta 1994;1197:45–62.
Gründemann D, Gorboulev V, Gambaryan S, Veyhl M, Koepsell H. Drug excretion mediated by a new prototype of polyspecific transporter. Nature 1994;372:549–552.
Shimada H, Moewes B, Burckhardt G. Indirect coupling to Na+ ofp-aminohippuric acid uptake into rat renal basolateral membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol 1987;253:F795-F801.
Pritchard JB. Coupled transport ofp-aminohippurate by rat kidney basolateral membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol 1988;255:F597-F604.
Steffens TG, Holohan PD, Ross CR. Operational modes of the organic anion exchanger in canine renal brush-border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol 1989;256: F596-F609.
Martinez F, Manganel M, Montrose-Rafizadeh C, Werner D, Roch-Ramel F. Transport of urate andp-aminohippurate in rabbit renal brush-border membranes. Am J Physiol 1990;258:F1145-F1153.
Ohoka K, Takano M, Okano T, Maeda S, Inui K, Hori R.p-Aminohippurate transport in rat renal brush-border membranes: a potential-sensitive transport system and an anion exchanger. Biol Pharm Bull 1993;16:395–401.
Handler JS. Studies of kidney cells in culture. Kidney Int 1986;30:208–215.
Kreisberg JI, Wilson PD. Renal cell culture. J Electron Microsc Tech 1988;9: 235–263.
Takano M, Hirozane K, Okamura M, Takayama A, Nagai J, Hori R.p-aminohippurate transport in apical and basolateral membranes of the OK kidney epithelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1994;269:970–975.
Nagai J, Takano M, Hirozane K, Yasuhara M, Inui K. Specificity ofp-aminohippurate transport system in the OK kidney epithelial cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1995;274:1161–1166.
Nagai J, Yano I, Hashimoto Y, Takano M, Inui K. Efflux of intracellular α-ketoglutarate viap-aminohippurated/dicarboxylate exchange in OK kidney epithelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1998;285:422–427.
Quamme G, Pfeilschifter J, Murer H. Parathyroid hormone inhibition of Na+/phosphate cotransport in OK cells: requirement of protein kinase C-dependnet pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta 1989;1013:159–165.
Helmle-Korb C, Montrose MH, Stange G, Murer H. Regulation of Na+/H+ exchange in opossum kidney cells by parathyroid hormone, cyclic AMP and phorbol esters. Pflügers Arch 1990;415:461–470.
Takano M, Nagai J, Yasuhara M, Inui K. Regulation ofp-aminohippurate transport by protein kinase C in OK kidney epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 1996;271:F469-F475.
Nagai J, Yano I, Hashimoto Y, Takano M, Inui K. Inhibition of PAH transport by parathyroid hormone in OK cells: involvement of protein kinase C pathway. Am J Physiol 1997;273:F674-F679.
Jacquemin E, Hagenbuch B, Stieger B, Wolkoff AW, Meier PJ. Expression cloning of a rat liver Na+-independent organic anion transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994;91:133–137.
Kullak-Ublick GA, Hagenbuch B, Stieger B, Schteingart CD, Hofmann AF, Wolkoff AW, Meier PJ. Molecular and functional characterization of an organic anion transporting polypeptide cloned from human liver. Gastroenterology 1995;109:1274–1282.
Saito H, Masuda S, Inui K. Cloning and functional characterization of a novel rat organic anion transporter mediating basolateral uptake of methotrexate in the kidney. J Biol Chem 1996;271:20719–20725.
Masuda S, Saito H, Nonoguchi H, Tomita K, Inui K. mRNA distribution and membrane localization of the OAT-K1 organic anion transporter in rat renal tubules. FEBS Lett 1997;407:127–131.
Sekine T, Watanabe N, Hosoyamada M, Kanai Y, Endou H. Expression cloning and characterization of a novel multispecific organic anion transporter. J Biol Chem 1997;272:18526–18529.
Sweet DH, Wolff NA, Pritchard JB. Expression cloning and characterization of ROAT1: the basolateral organic anion transporter in rat kidney. J Biol Chem 1997;272:30088–30095.
Wolff NA, Werner A, Burckhardt S, Burckhardt G. Expression clonoing and characterization of a renal organic anion transporter from winter flounder. FEBS Lett 1997;417:287–291.
Zhang L, Dresser MJ, Gray AT, Yost SC, Terashita S, Giacomini KM. Cloning and functional expression of a human liver organic cation transporter. Mol Pharmacol 1997;51:913–921.
Zhang L, Dresser MJ, Chun JK, Babbitt PC, Giacomini KM. Cloning and functional characterization of a rat renal organic cation transporter isoform (rOCT1A). J Biol Chem 1997;272:16548–16554.
Okuda M, Saito H, Urakami Y, Takano M, Inui K. cDNA cloning and functional expression of a novel rat kidney organic cation transporter, OCT2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996;224:550–507.
Gorboulev V, Ulzheimer JC, Akhoundova A, Ulzheimer-Teuber I, Karbach U, Quester S, Baumann C, Lang F, Busch AE, Koepsell H. Cloning and characterization of two human polyspecific organic cation transporters. DNA Cell Biol 1997;16:871–881.
Gründemann D, Babin-Ebell J, Martel F, Örding N, Schmidt A, Schömig E. Primary structure and functional expression of the apical organic cation transporter from kidney epithelial LLC-PK1 cells. J Biol Chem 1997;272:10408–10413.
Takano M, Inui K, Okano T, Saito H, Hori R. Carrier-mediated transport system of tetraethylammonium in rat renal brush-border and basolateral membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1984;773:113–124.
Inui K, Takano M, Hori R. Organic cation transport in the renal brush-border and basolateral membranes. In: Hatano M (ed) Nephrology. Tokyo: Springer-Verlag, 1991:1391–1398.
Hori R, Maegawa H, Okano T, Takano M, Inui K. Effect of sulfhydryl reagents on tetraethylammonium transport in rat renal brush border membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1987;241:1010–1016.
Takano M, Inui K, Okano T, Hori R. Cimetidine transport in rat renal brush border and basolateral membrane vesicles. Life Sci 1985;37:1579–1585.
Inui K, Takano M, Okano T, Hori R. H+ gradient-dependent transport of aminocephalosporins in rat renal brush border membrane vesicles: role of H+/organic cation antiport system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1985; 233:181–185.
Hull RN, Cherry WR, Weaver GW. The origin and characteristics of a pig kidney cell strain, LLC-PK1. In Vitro 1976;12:670–677.
Amsler K, Cook JS. Development of Na+-dependent hexose transport in a cultured line of porcine kidney cells. Am J Physiol 1982;242:C94-C101.
Hori R, Yamamoto K, Saito H, Kohno M, Inui K. Effect of aminoglycoside antibiotics on cellular functions of kidney epithelial cell line (LLC-PK1): a model system for aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1984;230:742–748.
Inui K, Saito H, Hori R. H+-gradient-dependent active transport of tetraethylammonium cation in apical-membrane vesicles isolated from kidney epithelial cell line LLC-PK1. Biochem J 1985;227:199–203.
Fauth C, Rossier B, Roch-Ramel F. Transport of tetraethylammoinum by a kidney epithelial cell line (LLC-PK1). Am J Physiol 1988;254:F351-F357.
Saito H, Yamamoto M, Inui K, Hori R. Transcellular transport of organic cation across monolayers of kidney epithelial cell line LLC-PK1. Am J Physiol 1992; 262:C59-C66.
Okano T, Maegawa H, Inui K, Hori R. Interaction of ofloxacin with organic cation transport system in rat renal brush-border membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1990;255:1033–1037.
Ohtomo T, Saito H, Inotsume N, Yasuhara M, Inui K. Transport of levofloxacin in a kidney epithelial cell line, LLC-PK1: interaction with organic cation transporters in apical and basolateral membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1996;276:1143–1148.
Tomita Y, Otsuki Y, Hashimoto Y, Inui K. Kinetic analysis of tetraethylammonium transport in the kidney epithelial cell line, LLC-PK1. Pharm Res 1997;14:1236–1240.
Holohan PD, White KE, Sokol PP, Rebbeor J, Photoaffinity labeling of the organic cation/H+ exchanger in renal brush border membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem 1992;267:13513–13519.
Gilsdorf JS, Rebbeor JF, Holohan PD. Evidence that the organic cation/H+ exchanger in the brush border membrane of dog kidney is a 41-kDa protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997;280:1043–1050.
Kimura M, Nabekura T, Katsura T. Takano M, Hori R. Identification of organic cation transporter in rat renal brush-border membrane by photoaffinity labeling. Biol Pharm Bull 1995;18:388–395.
Martel F, Vetter T, Russ H, Gründemann D, Azevedo I, Koepsell H, Schömig E. Transport of small organic cations in the rat liver: the role of the small organic cation transporter OCT1. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 1996;354:320–326.
Busch AE, Quester S, Ulzheimer JC, Waldegger S, Gorboulev V, Arndt P, Lang F, Koepsell H. Electrogenic properties and substrate specificity of the polyspecific rat cation transporter rOCT1. J Biol Chem 1996;271: 32599–32604.
Busch AE, Quester S, Ulzheimer JC, Gorboulev V, Akhoundova A, Waldegger S, Lang F, Koepsell H. Monoamine neurotransmitter transport mediated by the polyspecific cation transporter rOCT1. FEBS Lett 1996;395:153–156.
Okuda M, Urakami Y, Saito H, Inui K. Functional characterization of rat renal organic cation transporter, OCT2, mediating tubular secretion of cationic drugs. Nephrology 1997;3:suppl 1 (Abstracts of XIVth International Congress of Nephrology):S15.
Urakami Y, Okuda M, Masuda S, Saito H, Inui K. Functional characteristics and membrane localization of rat multispecific organic cation transporters, OCT1 and OCT2, mediating tubular secretion of cationic drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Inui, Ki., Okuda, M. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal tubular secretion of organic anions and cations. Clin Exper Neph 2, 100–108 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02479930
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02479930