Abstract
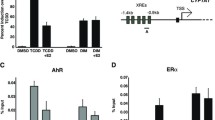
The aim of this study was to examine whether changes in growth factor or cytokine expression could be responsible for the growth inhibitory effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on the human breast cancer MCF-7 cell line. Treatment of MCF-7 cells with 10 nM TCDD for 7 days reduced the cell growth to 60% of control; this effect was partly abolished by cotreatment of the cells with 100 nM 17β-estradiol (E2). The inhibition of cell growth by TCDD was accompanied by an enhanced secretion of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and the TGF-β content in cell culture supernatants was 2-fold higher than in controls. Using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), the effect of TCDD on the expression of TGF-β isoforms, transforming growht factor-α (TGF-α), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) was investigated. It was demonstrated that incubation with 1, 10 and 100 nM TCDD for 24 h increased mRNA levels of TGF-α, TNF-α and IL-1β. The strongest effect was found on IL-1β, the mRNA level of which was dose-dependently increased. TCDD had a minor effect on TGF-α and TNF-α mRNA. The mRNA levels were significantly increased after treatment with 10 and 100 nM TCDD. The mRNA expression of \(TGF - \beta _1 \) and \(TGF - \beta _2 \) was unchanged, whereas the \(TGF - \beta _3 \) mRNA level was enhanced 2 to 3-fold after TCDD treatment. From the results, we suggest that TCDD-induced growth inhibition in MCF-7 cells is related to the growth inhibitory action of a set of growth factors and cytokines which have a contextual action on MCF-7 cell proliferation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aakvaag A, Utaaker E, Thorsen T, Lea OA, Lahooti H (1990) Growth control of human mammary cancer cells (MCF-7 cells) in culture: effect of estradiol and growth factors in serum-containing medium. Cancer Res 50: 7806–7810
Abbott BD, Birnbaum LS (1990) TCDD-induced altered expression of growth factors may have a role in producing cleft palate and enhancing the incidence of clefts after coadministration of retionic acid and TCDD. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 106: 418–432
Albino AP, Davis BM, Nanus DM (1991) Induction of growth factor RNA expression in human malignant melanoma: markers of transformation. Cancer Res 51: 4815–4820
Biegel L, Safe S (1990) Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on cell growth and the secretion of the estrogen-induced 34-, 52-, and 160-kDa proteins in human breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 37: 725–732
Bombick DW, Madhukar BV, Brewster DW, Matsumura F (1985) TCDD (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin), causes increases in protein kinases particularly protein kinase C in the hepatic plasma membrane of the rat and the guinea pig. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 127: 296–302
Butta A, MacLennan K, Flanders KC, Sacks NPM, Smith I, McKinna A, Dowsett M, Wakefield LM, Sporn MB, Baum M, Colletta AA (1992) Induction of transforming growth factor β1 in human breast cancer in vivo following tamoxifen treatment. Cancer Res 52: 4261–4264.
Carpenter G, Wahl MI (1990) The epidermal growth factor family. In: Sporn MB, Roberts AB (eds) Peptide growth factors and their receptors, vol. 1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 69–171
Chantry D, Turner M, Abney E, Feldmann M (1989) Modulation of cytokine production by transforming growth factor-β. J Immunol 142: 4295–4300
Chirgwin JM, Przbyla RJ, MacDonald RJ, Rutter WJ (1979) Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry 18: 5294–5299
Choi EJ, Toscano DG, Ryan JA, Riedel N, Toscano WA (1991) Dioxin induces transforming growth factor-α in human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem 266: 9591–9597
Clark GC, Taylor MJ, Tritscher AM, Lucier GW (1991) Tumor necrosis factor involvement in 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-mediated endotoxin hypersensitivity in C57BL/6J mice congenic at the Ah locus. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 111: 422–431
Darbre P, Yates J, Curtis J, King RJB (1983) Effects of estradiol on human breast cancer cells in culture. Cancer Res 43: 349–354
Döhr O, Vogel C, Abel J (1994) Modulation of growth factor expression by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Exp Clin Immunogen 11: 142–148
Ercolani L, Florence B, Denaro M, Alexander M (1988) Isolation and complete sequence of a functional human glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. J Biol Chem 263: 15335–15341
Frazer A, Seid JM, Hart KA, Bentley H, Bunning AD, Russell RGG (1991) Detection of mRNA for the transforming growth factor β family in human articular chondrocytes by the polymerase chain reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 180: 602–608
Frolik CA, Wakefield LM, Smith DM, Sporn MB (1984) Characterization of a membrane receptor for transforming growth factor β in normal rat kidney fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 259: 10995–11000
Gaffney EV, Tsai SC (1986) Lymphocyte-activating and growth-inhibitory activities for several sources of native and recombinant interleukin 1. Cancer Res 46: 3834–3837
Gaido KW, Maness SC, Leonard LS, Greenlee WF (1992) 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-dependent regulation of transforming growth factors-α and -β2 expression in a human kerationocyte cell line involves both transcriptional and post transcriptional control. J Biol Chem 267: 24591–24595
Gierthy JF, Lincoln II DW (1988) Inhibition of postconfluent focus production in cultures of MCF-7 breast cancer cells by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Breast Cancer Res Treat 12: 227–233
Gierthy JF, Lincoln II DW, Kampcik SJ, Dickerman HW, Bradlow HL, Niwa T, Swaneck GE (1988) Enhancement of 2- and 16α-estradiol hydroxylation in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 157: 515–520
Glisin V, Crkvenjakov R, Byus C (1974) Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry 13: 2633–2637
Knabbe CK, Lippman ME, Wakefield LM, Flanders KC, Kasid A, Derynck R, Dickson RB (1987) Evidence that transforming growth factor-β is a hormonally regulated negative growth factor in human breast cancer cells. Cell 48: 417–428
Kociba RJ, Keyes DG, Beyer JE, Carreon RM, Wade CE, Dittenber DA, Kalnins RP, Frauson LE, Park CN, Barnard SD Hummel RA, Humiston CG (1978) Results of two year chronic toxicity and oncogenicity study of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 46: 279–303
Labarca C, Paigen K (1980) A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem 102: 344–352
Lawrence DA, Pircher R, Kryceve-Martinerie A, Lullien P (1984) Normal embryo fibroblast release transforming growth factors in a latent form. J Cell Physiol 121: 184–188
Liu H, Biegel L, Narasimhan TR, Rowlands C, Safe S (1992) Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-I responses in MCF-7 cells by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related compounds. Mol Cell Endocrinol 87: 19–28
Lohi J, Pertovaara L, Sistonen L, Alitalo K, Keski-Oja J (1990) Regulation by TGF-β of genes involved in growth control: interleukin-6 Ann NY Acad Sci 593: 318–320
Lu YF, Safe S (1992) Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on the secretion of \(TGF - \beta _1 \) in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Organohalogen Compounds 10: 149–152
Lucier G, Tritscher A, Goldsworthy T, Foley J, Clark G, Goldstein J, Maronpot R (1991) Ovarian hormones enhance TCDD-mediated increases in cell proliferation and preneoplastic foci in a two stage model for hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res 51: 1391–1397
Ma XF, Babish JG (1993) Acute 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin results in enhanced tyrosylphosphorylation and expression of murine hepatic cyclin dependent kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197: 1070–1077
MacKenzie SA, Thomas T, Umbreit TH, Gallo MA (1992) The potentiation of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin toxicity by tamoxifen in female CD1 mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 116: 101–109
Madhukar BV, Brewster DW, Matsumura F (1984) Effects of in vitro-administered 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on receptor binding of epidermal growth factor in the hepatic plasma membrane of rat, guinea pig, mouse, and hamster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 7407–7411
Massague J (1990) The transforming growth factor-β family. Annu Rev Cell Biol 6: 597–641
Matsumura F, Madhukar BV, Bombick DW Brewster DW (1984) Toxicological significance of pleiotropic changes of plasma membrane functions particularly that of EGF receptor caused by 2,3,7,8-TCDD. In: Poland A, Kimbrough RD (eds) Biological mechanisms of dioxin action Banburry Report., vol. 18, Cold Spring Habor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, p 267
Rappolee DA, Mark D, Banda MJ, Werb Z (1988) Wound macrophages express TGF-α and other growth factors “in vivo”: analysis by mRNA phenotyping. Science 241: 708–712
Rosenthal G, Lebetkin E, Thigpen J, Wilson R, Tucker A, Luster M (1989) Characteristics of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induced endotoxin hypersensitivity: association with heptatotoxicity. Toxicology 56: 239–251
Schmidt JA, Tocci MJ (1990) Interleukin-1. In: Sporn MB, Roberts MA, (eds) Peptide growth factors and their receptors. vol. 1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 473–521
Snyder NK, Kramer CM, Dooley RK, Holsapple MP (1993) Characterization of protein phosphorylation by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in murine lymphocytes: indirect evidence for a role in the suppression of humoral immunity. Drug Chem Toxicol 16 [2]: 135–163
Spink DC, Lincoln II DW, Dickerman HW, Gierthy JF (1990) 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin causes an extensive alteration of 17β-estradiol metabolism in MCF-7 breast tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 6917–6921
Spink DC, Eugster HP, Lincoln II DW, Schuet JD, Schuetz EG, Johnson JA, Kaminsky LS, Gierthy JF (1992) 17β-Estradiol hydroxylation catalyzed by human cytochrome P450 1A1: a comparison of the activities induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in MCF-7 cells with those from heterologous expression of the cDNA. Arch Biochem Biophys 293: 342–348
Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Wakefield LM, Assoin RK (1986) Transforming growth factor-β: biological function and chemical structure. Science 233: 532–534
Sugarman BJ, Aggarwal BB, Hass PE, Figari IS, Palladino MA, Jr, Shepard HM (1985) Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-α: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science 230: 943–945
Sutter TR, Guzman K, Dold KM, Greenlee WF (1991) Targets for dioxin: genes for plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 and interleukin-1β. Science 254: 415–418
Taylor MJ, Lucier GW, Mahler JF, Thompson M, Lockhart AC, Clark GC (1992) Inhibition of acute TCDD toxicity by treatment with anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody or dexamethasone. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 117: 126–132
Thomson JS, Nissen L, Stacey SN, Hines RN, Autrup H (1991) Differences in 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-inducible CYP1A1 expression in human breast carcinoma cell lines involve transacting factors. Eur J Biochem 197: 577–582
Thomsen JS, Wang X, Hines RN, Safe S (1994) Restoration of aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) responsiveness in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells by transient expression of the estrogen receptor. Carcinogenesis 15: 933–937
Thompson EW, Reich R, Shima TB, Albini A, Graf J, Martin GR, Dickson RB, Lippman ME (1988) Differential regulation of growth and invasiveness of MCF-7 breast cancer cells by antiestrogens. Cancer Res 48: 6764–6768
Valverius EM, Bates SE, Stampfer MR, Clark R, McCormick F, Salomon DS, Lippmann ME, Dickson RB (1989) Transforming growth factor-α production and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in normal and oncogene transformed human mammary epithelial cells. Mol Endocrinol 3: 203–214
Vignon F, Bouton MM, Rochefort H (1987) Antiestrogens inhibit the mitogenic effect of growth factors on breast cancer cells in the total absence of estrogens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 146: 1502–1508
Vilcek J, Lee TH (1991) Tumor necrosis factor. New insights into the molecular mechanism of its multiple actions. J Biol Chem 266: 7313–7316
Vos J, Kreeftenberg J, Engel H, Minderhoud A, Vannoorlejansen L (1978) Studies on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induced immune suppression and decreased resistence to infection: endotoxin hypersensitivity, serum zinc concentrations and effect of thymosin treatment. Toxicology 9: 75–86
Wang AM, Doyle MV, Mark DF (1989) Quantitation of mRNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Biochemistry 86: 9717–9721
White TEK, Gasiewicz TA (1993) The human estrogen receptor structural gene contains a DNA sequence that binds activated mouse and human Ah receptors: a possible mechanism of estrogen receptor regulation by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 193: 956–962
Zeise L, Huff J, Salmon A, Hooper N (1990) Human risks from 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and hexachlorodibenzo-p-dioxins. Adv Mod Environ Toxicol 17: 293–342
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vogel, C., Abel, J. Effect of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on growth factor expression in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Arch Toxicol 69, 259–265 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050168
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050168