Abstract.
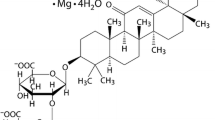
Chromanol HMR 1556 [(3R,4S)-(+)-N-[3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-6-(4,4,4-trifluorobutoxy)chroman-4-yl]-N-methylmethanesulfonamide], a novel inhibitor of the slow component of the delayed outward current in heart muscle cells (I Ks), has been characterized in several in-vitro systems. mRNA encoding for the human protein minK was injected into Xenopus oocytes, leading to the expression of I Ks channels. HMR 1556 inhibited this current half-maximally at a concentration of 120 nmol/l (IC50). Expression of the K+ channels Herg, Kv1.5, Kv1.3 and Kir2.1, and also the cationic current HCN2, were blocked little or not at all by 10 µmol/l HMR 1556. In isolated ventricular myocytes from the guinea pig the whole-cell patch-clamp method revealed inhibition of the I Ks current with an IC50 of 34 nmol/l. Other current components, like I Kr and I K1, were only slightly blocked at an HMR 1556 concentration of 10 µmol/l, whereas 10 µmol/l HMR 1556 inhibited the transient outward current I to and the sustained outward current I sus in rat ventricular myocytes by 25% and 36%, respectively. The L-type Ca2+ channel in guinea pig cardiomyocytes was blocked by 10 µmol/l HMR 1556 by 31%. Guinea pig right papillary muscles were investigated by the micropuncture technique at various pacing rates. In the frequency range of 0.5–7 Hz HMR 1556 (1 µmol/l) caused a prolongation of the action potential duration at 90% repolarization (APD90) by 19%–27%. In the presence of isoproterenol (10 µmol/l) the prolongation of the APD90 was more pronounced at low pacing rates (47% at 0.5 Hz and 35% at 1 Hz, compared with 25% at 7 Hz). The monophasic action potential was recorded in Langendorff-perfused guinea pig hearts. In spontaneously beating preparations, HMR 1556, at 0.1 µmol/l and 1 µmol/l, prolonged the MAPD90 by 3% and 10%, respectively, with no further prolongation at 10 µmol/l. The prolongation was much greater at low pacing rates [25% at 100 beats per min (bpm) and 13% at 150 bpm] than at fast pacing rates (9% at 350 bpm). The left ventricular pressure LVPmax was not affected at 1 µmol/l HMR 1556, but it decreased by 15% at 10 µmol/l. Other parameters, like the heart rate and coronary flow, were only slightly decreased at 1 µmol/l HMR 1556. In conclusion, HMR 1556 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the I Ks current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. The prolongation of the action potential duration is maintained at fast pacing rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gögelein, H., Brüggemann, A., Gerlach, U. et al. Inhibition of IKs channels by HMR 1556. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 362, 480–488 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002100000284
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002100000284