Abstract.
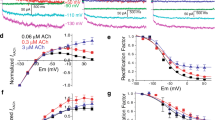
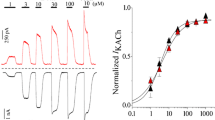
In this study we examined the effects of chloroquine on the muscarinic potassium current, I K-ACh, and the inward rectifying potassium current, I K1. We utilized three ways to induce I K-ACh: activating the M2-muscarinic receptors with carbachol, activating the purinergic A1-receptors with adenosine and directly activating the GK-protein coupled with these receptors in an irreversible way with GTPγS. In experiments using the whole-cell configuration of the patch-clamp technique, we found that chloroquine, independently from the manner of activation of I K-ACh, was able to block this current with similar potency. These results strongly suggest that chloroquine may be acting directly on the muscarinic potassium channel. Chloroquine also blocked I K1 with similar potency, in both guinea pig atrial and ventricular myocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benavides-Haro, D., Sánchez-Chapula, J. Chloroquine blocks the background potassium current in guinea pig atrial myocytes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 361, 311–318 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002109900185
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002109900185