Summary
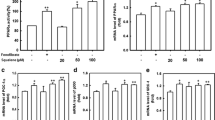
Carotenoids are important micronutrients in the human diet and are present in human serum at micromolar concentrations. In addition to their antioxidant potential, carotenoids obtain physiologically relevant properties such as influencing cellular signal pathways, gene expression or induction of detoxifying enzymes. In this study, we determined the transactivation of PXR by cotransfection with the full-length receptor and a PXR-responsive reporter gene. Carotenoids and retinol revealed a 5–6-fold reporter gene activity in HepG2 cells in comparison to a 7-fold induction by the well known PXR agonist rifampicin whereas apo-carotenals and lycopene exerted less or no activation potential. The inductive efficacy was hereby concentration-dependent. In addition, carotenoid or retinol mediated gene expression of PXR responsive genes like CYP3A4/CYP3A7, CYP3A5,MDR-1 and MRP-2 has been determined in HepG2 cells by RT-PCR with upregulative properties of β-carotene or retinol being comparable or even higher than that of rifampicin. In conclusion, PXR-mediated upregulation of CYP3A4/CYP3A7 and CYP3A5 as well as MDR1 and MRP2 by carotenoids points to a potential interference on the metabolism of xenobiotic and endogenous relevant compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Redmond TM, Gentleman S, Duncan T, Yu S, Wiggert B, Gantt E, Cunningham FX Jr (2001) Identification, expression, and substrate specificity of a mammalian beta-carotene 15.15’-dioxygenase. J Biol Chem 276:6560–6565
Wolf G (2001) The enzymatic cleavage of beta-carotene: end of a controversy. Nutr Rev 59:116–118
Silveira ER, Moreno FS (1998) Natural retinoids and β-carotene: end of a controversy. J Nutr Biochem 9:446–456
Stahl W (2000) Lipid oxidation and antioxidants. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 3:121–126
Chew BP (1995) Antioxidant vitamins affect food animal immunity and health. J Nutr 125:1804S-1808S
Astorg P, Gradelet S, Leclerc J, Siess MH (1997) Effects of provitamin A or nonprovitamin A carotenoids on liver xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes in mice. Nutr Cancer 27:245–249
Paolini M, Antelli A, Pozzetti L, Spetlova D, Perocco P, Valgimigli L, Pedulli GF, Cantelli-Forti G (2001) Induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes and overgeneration of oxygen radicals in betacarotene supplemented rats. Carcinogenesis 22:1483–1495
Kliewer SA, Lehmann JM, Willson TM (1999) Orphan nuclear receptors: shifting endocrinology into reverse. Science 284:757–760
Kitareewan S, Burka LT, Tomer KB, Parker CE, Deterding LJ, Stevens RD, Forman BM, Mais DE, Heyman RA, Mc-Morris T, Weinberger C (1996) Phytol metabolites are circulating dietary factors that activate the nuclear receptor RXR. Mol Biol Cell 7:1153–1166
Aranda A, Pascual A (2001) Nuclear hormone receptors and gene expression. Physiol Rev 81:1269–1304
Mangelsdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G, Umesono K, Blumberg B, Kastner P, Mark M, Chambon P et al. (1995) The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell 83:835–839
Bertilsson G, Heidrich J, Svensson K, Asman M, Jendeberg L, Sydow-Backman M, Ohlsson R, Postlind H, Blomquist P, Berkenstam A (1998) Identification of a human nuclear receptor defines a new signaling pathway for CYP3A induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12208–12213
Waxman DJ (1999) P450 gene induction by structurally diverse xenochemicals: central role of nuclear receptors CAR, PXR, and PPAR. Arch Biochem Biophys 369:11–23
Goodwin B, Redinbo MR, Kliewer SA (2002) Regulation of cyp3a gene transcription by the pregnane x receptor. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 42:1–23
Kliewer SA, Willson TM (2002) Regulation of xenobiotic and bile acid metabolism by the nuclear pregnane X receptor. J Lipid Res 43:359–364
Geick A, Eichelbaum M, Burk O (2001) Nuclear receptor response elements mediate induction of intestinal MDR1 by rifampin. J Biol Chem 276:14581–14587
Payen L, Sparfel L, Courtois A, Vernhet L, Guillouzo A, Fardel O (2002) The drug efflux pump MRP2: regulation of expression in physiopathological situations and by endogenous and exogenous compounds. Cell Biol Toxicol 18:221–233
Kast HR, Goodwin B, Tarr PT, Jones SA, Anisfeld AM, Stoltz CM, Tontonoz P, Kliewer S, Willson TM, Edwards PA (2002) Regulation of multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (ABCC2) by the nuclear receptors pregnane X receptor, farnesoid X-activated receptor, and constitutive androstane receptor. J Biol Chem 277:2908–2915
Falkner KC, Pinaire JA, Xiao GH, Geoghegan TE, Prough RA (2001) Regulation of the rat glutathione S-transferase A2 gene by glucocorticoids: involvement of both the glucocorticoid and pregnane X receptors. Mol Pharmacol 60:611–619
Sonoda J,Xie W, Rosenfeld JM, Barwick JL, Guzelian PS, Evans RM (2002) Regulation of a xenobiotic sulfonation cascade by nuclear pregnane X receptor (PXR). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13801–13806
Landes N, Pfluger P, Kluth D, Birringer M, Ruhl R, Bol GF, Glatt H, Brigelius-Flohe R (2003) Vitamin E activates gene expression via the pregnane X receptor. Biochem Pharmacol 65:269–273
Staudinger JL, Goodwin B, Jones SA, Hawkins-Brown D, MacKenzie KI, La-Tour A, Liu Y, Klaassen CD, Brown KK, Reinhard J, Willson TM, Koller BH, Kliewer SA (2001) The nuclear receptor PXR is a lithocholic acid sensor that protects against liver toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:3369–3374
Xie W, Barwick JL, Downes M, Blumberg B, Simon CM, Nelson MC, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Brunt EM, Guzelian PS, Evans RM (2000) Humanized xenobiotic response in mice expressing nuclear receptor SXR. Nature 406:435–439
Cai Y, Konishi T, Han G, Campwala KH, French SW, Wan YJ (2002) The role of hepatocyte RXR alpha in xenobiotic-sensing nuclear receptor-mediated pathways. Eur J Pharm Sci 15:89–96
Brown ED, Micozzi MS, Craft NE, Bieri JG, Beecher G, Edwards BK, Rose A, Taylor PR, Smith JC Jr (1989) Plasma carotenoids in normal men after a single ingestion of vegetables or purified beta-carotene. Am J Clin Nutr 49:1258–1265
Gueguen S, Herbeth B, Siest G, Leroy P (2002) An isocratic liquid chromatographic method with diode-array detection for the simultaneous determination of alpha-tocopherol, retinol, and five carotenoids in human serum. J Chromatogr Sci 40:69–76
Schmitz HH, Poor CL, Gugger ET, Erdman JW Jr (1993) Analysis of carotenoids in human and animal tissues. Methods Enzymol 214:102–116
Schmidt CK, Brouwer A, Nau H (2003) Chromatographic analysis of endogenous retinoids in tissues and serum. Anal Biochem 315:36–48
von Lintig J, Wyss A (2001) Molecular analysis of vitamin A formation: cloning and characterization of betacarotene 15,15’-dioxygenases. Arch Biochem Biophys 385:47–52
Wyss A, Wirtz GM, Woggon WD, Brugger R, Wyss M, Friedlein A, Riss G, Bachmann H, Hunziker W (2001) Expression pattern and localization of beta, betacarotene 15,15’-dioxygenase in different tissues. Biochem J 354:521–529
Kiefer C, Hessel S, Lampert JM, Vogt K, Lederer MO, Breithaupt DE, von Lintig J (2001) Identification and characterization of a mammalian enzyme catalyzing the asymmetric oxidative cleavage of provitamin A. J Biol Chem 276:14110–14116
Yeum KJ, Lee-Kim YC, Yoon S, Lee KY, Park IS, Lee KS, Kim BS, Tang G, Russell RM, Krinsky NI (1995) Similar metabolites formed from beta-carotene by human gastric mucosal homogenates, lipoxygenase, or linoleic acid hydroperoxide. Arch Biochem Biophys 321:167–174
Moore JT, Kliewer SA (2000) Use of the nuclear receptor PXR to predict drug interactions. Toxicology 153:1–10
Loo TW, Clarke DM (1999) Merck Frosst Award Lecture 1998. Molecular dissection of the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Biochem Cell Biol 77:11–23
Paulusma CC, Kothe MJ, Bakker CT, Bosma PJ, van Bokhoven I, van Marle J, Bolder U, Tytgat GN, Oude Elferink RP (2000) Zonal down-regulation and redistribution of the multidrug resistance protein 2 during bile duct ligation in rat liver. Hepatology 31:684–693
Buchler M, Konig J, Brom M, Kartenbeck J, Spring H, Horie T, Keppler D (1996) cDNA cloning of the hepatocyte canalicular isoform of the multidrug resistance protein, cMrp, reveals a novel conjugate export pump deficient in hyperbilirubinemic mutant rats. J Biol Chem 271:15091–15098
Schrenk D, Baus PR, Ermel N, Klein C, Vorderstemann B, Kauffmann HM (2001) Up-regulation of transporters of the MRP family by drugs and toxins. Toxicol Lett 120:51–57
Evers R, Kool M, van Deemter L, Janssen H, Calafat J, Oomen LC, Paulusma CC, Oude Elferink RP, Baas F, Schinkel AH, Borst P (1998) Drug export activity of the human canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter in polarized kidney MDCK cells expressing cMOAT (MRP2) cDNA. J Clin Invest 101:1310–1319
Lampen A, Meyer S, Arnhold T, Nau H (2000) Metabolism of vitamin A and its active metabolite all-trans-retinoic acid in small intestinal enterocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:979–985
Howell SR, Shirley MA, Ulm EH (1998) Effects of retinoid treatment of rats on hepatic microsomal metabolism and cytochromes P450. Correlation between retinoic acid receptor/retinoid x receptor selectivity and effects on metabolic enzymes. Drug Metab Dispos 26:234–239
Marill J, Cresteil T, Lanotte M, Chabot GG (2000) Identification of human cytochrome P450s involved in the formation of all-trans-retinoic acid principal metabolites. Mol Pharmacol 58:1341–1348
Liu C, Russell RM, Wang XD (2003) Exposing ferrets to cigarette smoke and a pharmacological dose of beta-carotene supplementation enhance in vitro retinoic acid catabolism in lungs via induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes. J Nutr 133:173–179
Chen H, Howald WN, Juchau MR (2000) Biosynthesis of all-trans-retinoic acid from all-trans-retinol: catalysis of alltrans-retinol oxidation by human P-450 cytochromes. Drug Metab Dispos 28:315–322
(1994) The effect of vitamin E and beta carotene on the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers in male smokers. The Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta Carotene Cancer Prevention Study Group. N Engl J Med 330:1029–1035
Omenn GS, Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, Balmes J, Cullen MR, Glass A, Keogh JP, Meyskens FL Jr, Valanis B, Williams JH Jr, Barnhart S, Cherniack MG, Brodkin CA, Hammar S (1996) Risk factors for lung cancer and for intervention effects in CARET, the Beta-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy Trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:1550–1559
Liu C, Lian F, Smith DE, Russell RM, Wang XD (2003) Lycopene supplementation inhibits lung squamous metaplasia and induces apoptosis via up-regulating insulin-like growth factorbinding protein 3 in cigarette smoke-exposed ferrets. Cancer Res 63:3138–3144
Zhang H, LeCulyse E, Liu L, Hu M, Matoney L, Zhu W, Yan B (1999) Rat pregnane X receptor:molecular cloning, tissue distribution, and xenobiotic regulation. Arch Biochem Biophys 368:14–22
Liu C, Wang XD, Bronson RT, Smith DE, Krinsky NI, Russell RM (2000) Effects of physiological versus pharmacological beta-carotene supplementation on cell proliferation and histopathological changes in the lungs of cigarette smoke-exposed ferrets. Carcinogenesis 21:2245–2253
Wolf G (2002) The effect of betacarotene on lung and skin carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 23:1263–1265
Sumida A, Fukuen S, Yamamoto I, Matsuda H, Naohara M, Azuma J (2000) Quantitative analysis of constitutive and inducible CYPs mRNA expression in the HepG2 cell line using reverse transcription-competitive PCR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 267:756–760
Renes, JW (2000) (Patho)physiological function of the multidrug resistance protein MRP1. Reiksuniversiteit Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands
Nies AT, Konig J, Pfannschmidt M, Klar E, Hofmann WJ, Keppler D (2001) Expression of the multidrug resistance proteins MRP2 and MRP3 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 94:492–499
Bowen WP, Carey JE, Miah A, McMurray HF, Munday PW, James RS, Coleman RA, Brown AM (2000) Measurement of cytochrome P450 gene induction in human hepatocytes using quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Drug Metab Dispos 28:781–788
Jover R, Bort R, Gomez-Lechon MJ, Castell JV (2001) Cytochrome P450 regulation by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 in human hepatocytes: a study using adenovirus-mediated antisense targeting. Hepatology 33:668–675
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rühl, R., Sczech, R., Landes, N. et al. Carotenoids and their metabolites are naturally occurring activators of gene expression via the pregnane X receptor. Eur J Nutr 43, 336–343 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-004-0475-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-004-0475-1