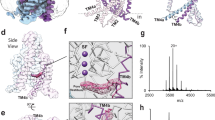
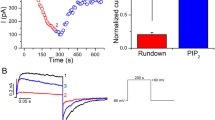
Abstract
TREK-1 is an unconventional K+ channel that is activated by both physical and chemical stimuli. In this study, we show that the inner leaflet membrane phospholipids, including PIP2, exert a mixed stimulatory and inhibitory effect on TREK-1. Intra-cellular phospholipids inhibit basal channel activity and activation by membrane stretch, intra-cellular acidosis and arachidonic acid. However, binding of endogenous negative inner leaflet phospholipids with poly-lysine reduces inhibition and reveals channel stimulation by exogenous intra-cellular phospholipids. A similar effect is observed with PI, PE, PS and PA, unlike DG, demonstrating that the phosphate at position 3 is required although the global charge of the molecule is not critical. Inhibition depends on the distal C-terminal domain that conditions channel mechano-sensitivity, but is independent of the positively charged PIP2 stimulatory site in the proximal C-terminal domain. This is, to our knowledge, the first report of an ion channel dually regulated by membrane phospholipids.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bockenhauer D, Zilberberg N, Goldstein SA (2001) KCNK2: reversible conversion of a hippocampal potassium leak into a voltage-dependent channel. Nat Neurosci 4:486–491
Chemin J, Girard C, Duprat F, Lesage F, Romey G, Lazdunski M (2003) Mechanisms underlying excitatory effects of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors via inhibition of 2P domain K+ channels. EMBO J 22:5403–5411
Chemin J, Patel AJ, Duprat F, Lauritzen I, Lazdunski M, Honoré E (2005) A phospholipid sensor controls mechanogating of the K+ channel TREK-1. EMBO J 24:44–53
Fink M, Duprat F, Lesage F, Reyes R, Romey G, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M (1996) Cloning, functional expression and brain localization of a novel unconventional outward rectifier K+ channel. EMBO J 15:6854–6862
Honoré E, Maingret F, Lazdunski M, Patel AJ (2002) An intracellular proton sensor commands lipid- and mechano-gating of the K+ channel TREK-1. EMBO J 21:2968–2976
Honoré E, Patel AJ, Chemin J, Suchyna T, Sachs F (2006) Desensitization of mechano-gated K2P channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6859–6864
Huang CL, Feng S, Hilgemann DW (1998) Direct activation of inward rectifier potassium channels by PIP2 and its stabilization by Gbetagamma. Nature 391:803–806
Kim Y, Gnatenco C, Bang H, Kim D (2001) Localization of TREK-2 K+ channel domains that regulate channel kinetics and sensitivity to pressure, fatty acids and pHi. Pflugers Arch 2001:952–960
Lauritzen I, Chemin J, Honoré E, Jodar M, Guy N, Lazdunski M, Patel AJ (2005) Cross-talk between the mechano-gated K2P channel TREK-1 and the actin cytoskeleton. EMBO Rep 6:642–648
Lauritzen I, Zanzouri M, Honoré E, Duprat F, Ehrengruber MU, Lazdunski M, Patel AJ (2003) K+-dependent cerebellar granule neuron apoptosis: role of TASK leak K+ channels. J Biol Chem 278:32068–32076
Lesage F (2003) Pharmacology of neuronal background potassium channels. Neuropharmacology 44:1–7
Lesage F, Lazdunski M (2000) Molecular and functional properties of two-pore-domain potassium channels. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F793–F801
Lopes CM, Rohacs T, Czirjak G, Balla T, Enyedi P, Logothetis DE (2005) PIP2 hydrolysis underlies agonist-induced inhibition and regulates voltage gating of two-pore domain K+ channels. J Physiol 564:117–129
Maingret F, Fosset M, Lesage F, Lazdunski M, Honoré E (1999) TRAAK is a mammalian neuronal mechano-gated K+ channel. J Biol Chem 274:1381–1387
Maingret F, Honoré E, Lazdunski M, Patel AJ (2002) Molecular basis of the voltage-dependent gating of TREK-1, a mechano-sensitive K+ channel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 292:339–346
Maingret F, Patel AJ, Lesage F, Lazdunski M, Honoré E (1999) Mechano- or acid stimulation, two interactive modes of activation of the TREK-1 potassium channel. J Biol Chem 274:26691–26696
Moore AL, Roe MW, Melnick RF, Lidofsky SD (2002) Calcium mobilization evoked by hepatocellular swelling is linked to activation of phospholipase Cgamma. J Biol Chem 277:34030–34035
Murbartian J, Lei Q, Sando JJ, Bayliss DA (2005) Sequential phosphorylation mediates receptor- and kinase-induced inhibition of TREK-1 background potassium channels. J Biol Chem 280:30175–30184
Patel AJ, Honoré E (2001) Anesthetic-sensitive 2P domain K+ channels. Anesthesiology 95:1013–1025
Patel AJ, Honoré E (2001) Properties and modulation of mammalian 2P domain K+ channels. Trends Neurosci 24:339–346
Patel AJ, Honoré E, Maingret F, Lesage F, Fink M, Duprat F, Lazdunski M (1998) A mammalian two pore domain mechano-gated S-like K+ channel. EMBO J 17:4283–4290
Patel AJ, Lazdunski M, Honoré E (2001) Lipid and mechano-gated 2P domain K+ channels. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:422–428
Ruwhof C, van Wamel JT, Noordzij LA, Aydin S, Harper JC, van der Laarse A (2001) Mechanical stress stimulates phospholipase C activity and intracellular calcium ion levels in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Cell Calcium 29:73–83
Sachs F, Morris CE (1998) Mechanosensitive ion channels in nonspecialized cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 132:1–77
Sandoz G, Thummler S, Duprat F, Feliciangeli S, Vinh J, Escoubas P, Guy N, Lazdunski M, Lesage F (2006) AKAP150, a switch to convert mechano-, pH- and arachidonic acid-sensitive TREK K+ channels into open leak channels. EMBO J 25:5864–5872
Sheetz MP, Singer SJ (1974) Biological membranes as bilayer couples. A molecular mechanism of drug–erythocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:4457–4461
Suchyna TM, Sachs F (2007) Mechanosensitive channel properties and membrane mechanics in mouse dystrophic myotubes. J Physiol (in press)
Suchyna TM, Tape SE, Koeppe RE 2nd, Andersen OS, Sachs F, Gottlieb PA (2004) Bilayer-dependent inhibition of mechanosensitive channels by neuroactive peptide enantiomers. Nature 430:235–240
Voets T, Nilius B (2003) TRPs make sense. J Membr Biol 192:1–8
Zhang H, He C, Yan X, Mirshahi T, Logothetis DE (1999) Activation of inwardly rectifying K+ channels by distinct PtdIns(4,5)P2 interactions. Nat Cell Biol 1:183–188
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the CNRS, the FRM, l’ARC, la Ligue contre le cancer, the Fondation Paul Hamel and the ANR COD 2005. Martine Jodar is acknowledged for the expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chemin, J., Patel, A.J., Duprat, F. et al. Up- and down-regulation of the mechano-gated K2P channel TREK-1 by PIP2 and other membrane phospholipids. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 455, 97–103 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0250-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0250-2