Abstract
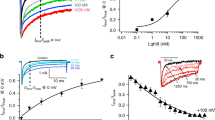
We have examined the effects of a β-scorpion toxin purified from the venom of the Venezuelan scorpion Tityus discrepans, TdVIII, on heterologously expressed rat skeletal muscle Na+ channels (rSkM1). TdVIII (100 nM) produced a leftward shift in the voltage dependence of activation and reduced the peak Na+ conductance of rSkM1 channels coexpressed with the rat brain β1 subunit in Xenopus laevis oocytes, suggesting that TdVIII is a β-scorpion toxin. These effects did not depend on the presence of the β1 subunit. Modification of rSkM1 activation by TdVIII could be augmented by increasing the rate of stimulation (enhanced use-dependence). Shifts in channel activation were also enhanced by introducing conditioning pulses to –10 mV, and this enhancement increased with conditioning pulse duration. On the other hand, TdVIII did not affect the activation of fast-inactivation deficient mutant Na+ channels, I1303Q/ F1304Q/M1305Q. These results suggest that modulation of rSkM1 Na+ channel gating by TdVIII depends on the toxin interacting with the inactivated state of the α subunit.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 September 1998 / Received after revision: 9 November 1998 / Accepted: 2 December 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsushima, R., Borges, A. & Backx, P. Inactivated state dependence of sodium channel modulation by β-scorpion toxin. Pflügers Arch 437, 661–668 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050830
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050830