Abstract.
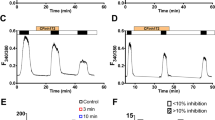
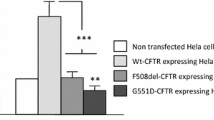
Expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) inhibits Ca2+-activated Cl– channels (CaCC) by an unknown mechanism. This inhibition does not require CFTR activation (activity-independent inhibition), but is potentiated when CFTR is activated (activity-dependent inhibition). In this study, we evaluated, in endothelial cells, possible structural determinants for this interaction. Bovine pulmonary artery endothelium (CPAE) cells, which do not express CFTR, were transfected transiently with three hybrid CFTR constructs. The functional interaction between CaCC and CFTR was assessed using the patch-clamp technique in the whole-cell configuration. CaCC was stimulated by application of adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) to the bath solution. CFTR currents were evoked by application of a forskolin/3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) cocktail. The inhibitory effect of CFTR was conserved when the PDZ (PSD-95/Discs large/ZO-1) binding motif was deleted (CFTR-ΔPDZ). In contrast, both the CFTR activity-independent and -dependent inhibition of CaCC were abolished when the C-terminal part of the regulatory (R)-domain of CFTR was deleted (CFTR-ΔR780–830). The activity-dependent inhibition of CaCC, but not the activity-independent inhibition, could be rescued by introducing the multiple drug resistance (MDR)-1 mini-linker in place of the deletion (CFTR-ΔR-linker). It is concluded that the C-terminal part of the R-domain is an important determinant for CFTR-CaCC interaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received after revision: 5 January 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, L., Vankeerberghen, A., Cuppens, H. et al. The C-terminal part of the R-domain, but not the PDZ binding motif, of CFTR is involved in interaction with Ca2+-activated Cl– channels. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 442, 280–285 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100531
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100531