Abstract
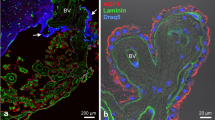
The normal brain develops within a well-controlled stable internal “milieu” protected by specialised mechanisms referred to collectively as blood–brain barriers. A fundamental feature of this environment is the control of water flow in and out of the developing brain. Because of limited vascularisation of the immature brain, choroid plexuses, via the cerebrospinal fluid, have been proposed as the main route of fluid exchange between the blood and brain interfaces. We describe the temporal expression and appearance of aquaporin-1 (AQP1) which is important for water transfer across adult choroid plexuses. AQP1 expression was studied in rat embryos using real time reverse transcription/polymerase chain reaction. mRNA for AQP1 was present in rat brain at embryonic day 12 (E12) one day before the protein was detectable in the fourth ventricular choroid plexus (the first plexus to appear); its relative levels increased at E13-E14 when more AQP1-immunoreactive cells appeared in all plexuses. The presence of AQP1 was determined immunocytochemically in five different mammalian species (rat, mouse, human, sheep and opossum) in all four choroid plexuses from their earliest appearance. In all five species studied, the appearance of AQP1 immunoreactivity followed the same developmental sequence: the fourth, lateral and, finally, third ventricular choroid plexus. The stage of choroid plexus development when AQP1 was first detected in all five species and in all four choroid plexuses corresponded to the transition between Stages I and II. The cellular localisation of AQP1 in all choroid plexuses, as soon as it was detectable, had the characteristic apical membrane distribution previously described in the adult; a basolateral membrane localisation was also observed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agre P, King LS, Yasui M, Guggino WB, Ottersen OP, Fujiyoshi Y, Engel A, Nielsen S (2002) Aquaporin water channels—from atomic structure to clinical medicine. J Physiol (Lond) 542:3–16
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Xue R, Haug FM, Neely JD, Bhardwaj A, Agre P, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Mori S, Ottersen OP (2004) Alpha-syntrophin deletion removes the perivascular but not endothelial pool of aquaporin-4 at the blood–brain barrier and delays the development of brain edema in an experimental model of acute hyponatremia. FASEB J 18:542–544
Aoki K, Uchihara T, Tsuchiya K, Nakamura A, Ikeda K, Wakayama Y (2003) Enhanced expression of aquaporin 4 in human brain with infarction. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 106:121–124
Badaut J, Petit JM, Brunet JF, Magistretti PJ, Charriaut-Marlangue C, Regli L (2004) Distribution of aquaporin 9 in the adult rat brain: preferential expression in catecholaminergic neurons and in glial cells. Neuroscience 128:27–38
Bondy C, Chin E, Smith BL, Preston GM, Agre P (1993) Developmental gene expression and tissue distribution of the CHIP28 water-channel protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:4500–4504
Brightman MW, Reese TS (1969) Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J Cell Biol 40:648–677
Caley DW, Maxwell DS (1970) Development of the blood vessels and extracellular spaces during postnatal maturation of rat cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol 138:31–47
Davson H, Segal MB (1996) Physiology of the CSF and blood–brain barriers. CRC, Boca Raton USA
Desmond ME, Jacobson AG (1977) Embryonic brain enlargement requires cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Dev Biol 57:188–198
Dziegielewska KM, Williams RT, Knott GW, Kitchener PD, Monk SE, Potter A, Saunders NR (1997) TGF-beta receptor type II and fetuin in the developing sheep neocortex. Cell Tissue Res 290:515–524
Dziegielewska KM, Ek J, Habgood MD, Saunders NR (2001) Development of the choroid plexus. Microsc Res Tech 52:5–20
Ek CJ, Habgood MD, Dziegielewska KM, Saunders NR (2003) Structural characteristics and barrier properties of the choroid plexuses in developing brain of the opossum (Monodelphis domestica). J Comp Neurol 460:451–464
Endo M, Jain RK, Witwer B, Brown D (1999) Water channel (aquaporin 1) expression and distribution in mammary carcinomas and glioblastomas. Microvasc Res 58:89–98
Jacobsen M, Clausen PP, Jacobsen GK, Saunders NR, Møllgård K (1982) Intracellular plasma proteins in human fetal choroid plexus during development. I. Developmental stages in relation to the number of epithelial cells which contain albumin in telencephalic, diencephalic and myelencephalic choroid plexus. Brain Res 255:239–250
Jacobsen M, Møllgård K, Reynolds M, Saunders NR (1983) The choroid plexus in fetal sheep during development with special reference to intracellular plasma protein. Dev Brain Res 8:77–88
Jung JS, Bhat RV, Preston GM, Guggino WB, Baraban JM, Agre P (1994) Molecular characterization of an aquaporin cDNA from brain: candidate osmoreceptor and regulator of water balance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:13052–13056
Ke C, Poon WS, Ng HK, Pang JC, Chan Y (2001) Heterogeneous responses of aquaporin-4 in oedema formation in a replicated severe traumatic brain injury model in rats. Neurosci Lett 301:21–24
Klosovskii B (ed) (1963) The development of the brain and its disturbance by harmful factors. Pergamon, London
Knott GW, Dziegielewska KM, Habgood MD, Li ZS, Saunders NR (1997) Albumin transfer across the choroid plexus of South American opossum (Monodelphis domestica). J Physiol (Lond) 499:179–194
Masseguin C, Corcoran M, Carcenac C, Daunton NG, Guell A, Verkman AS, Gabrion J (2000) Altered gravity downregulates aquaporin-1 protein expression in choroid plexus. J Appl Physiol 88:843–850
Milhorat TH (1976) Structure and function of the choroid plexus and other sites of cerebrospinal fluid formation. Int Rev Cytol 47:225–288
Milhorat TH, Davis DA, Lloyd BJJ (1973) Two morphologically distinct blood–brain barriers preventing entry of cytochrome c into cerebrospinal fluid. Science 180:76–78
Mizuno R, Cavallaro T, Herbert J (1992) Temporal expression of the transthyretin gene in the developing rat eye. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 33:341–349
Mobasheri A, Marples D (2004) Expression of the AQP-1 water channel in normal human tissues: a semiquantitative study using tissue microarray technology. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C529–C537
Moos T, Møllgård K (1993) Cerebrovascular permeability to azo dyes and plasma proteins in rodents of different ages. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 19:120–127
Møllgård K, Schumacher U (1993) Immunohistochemical assessment of cellular proliferation in the developing human CNS using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded material. J Neurosci Methods 46:191–196
Netsky M, Shuangshoti S (1975) The choroid plexus in health and disease. Wright, Bristol
Nico B, Paola Nicchia G, Frigeri A, Corsi P, Mangieri D, Ribatti D, Svelto M, Roncali L (2004) Altered blood–brain barrier development in dystrophic MDX mice. Neuroscience 125:921–935
Nielsen S, Smith BL, Christensen EI, Agre P (1993) Distribution of the aquaporin CHIP in secretory and resorptive epithelia and capillary endothelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7275–7279
Nielsen S, Nagelhus EA, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Bourque C, Agre P, Ottersen OP (1997) Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells: high-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J Neurosci 17:171–180
Oshio K, Song Y, Verkman AS, Manley GT (2003) Aquaporin-1 deletion reduces osmotic water permeability and cerebrospinal fluid production. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 86:525–528
Praetorius J, Nejsum LN, Nielsen S (2004) A SCL4A10 gene product maps selectively to the basolateral plasma membrane of choroid plexus epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C601–C610
Robertson PL, Du Bois M, Bowman PD, Goldstein GW (1985) Angiogenesis in developing rat brain: an in vivo and in vitro study. Brain Res 355:219–223
Saunders NR (1992) Ontogenic development of brain barrier mechanisms. In: Bradbury M (ed) Pharmacology and physiology of the blood brain–barrier, vol 103. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 327–369
Saunders NR, Adam E, Reader M, Møllgård K (1989) Monodelphis domestica (grey short-tailed opossum): an accessible model for studies of early neocortical development. Anat Embryol (Berl) 180:227–236
Saunders NR, Habgood MD, Dziegielewska KM (1999) Barrier mechanisms in the brain. I. Adult brain. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 26:11–19
Speake T, Freeman LJ, Brown PD (2003) Expression of aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 water channels in rat choroid plexus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1609:80–86
Sun MC, Honey CR, Berk C, Wong NL, Tsui JK (2003) Regulation of aquaporin-4 in a traumatic brain injury model in rats. J Neurosurg 98:565–569
Thomas T, Power B, Hudson P, Schreiber G, Dziadek M (1988) The expression of transthyretin mRNA in the developing rat brain. Dev Biol 128:415–427
Verkman AS (2002) Aquaporin water channels and endothelial cell function. J Anat 200:617–627
Wen H, Nagelhus EA, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Agre P, Ottersen OP, Nielsen S (1999) Ontogeny of water transport in rat brain: postnatal expression of the aquaporin-4 water channel. Eur J Neurosci 11:935–945
Wu Q, Delpire E, Hebert SC, Strange K (1998) Functional demonstration of Na+–K+–2Cl-cotransporter activity in isolated, polarized choroid plexus cells. Am J Physiol 275:C1565–C1572
Acknowledgements
The excellent technical assistance by S. Forchhammer and K. Ottosen is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by NIH grant R01NS043949-01A1, NIH grant 5R01NS043949 and the Vera and Carl Michaelsen Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johansson, P.A., Dziegielewska, K.M., Ek, C.J. et al. Aquaporin-1 in the choroid plexuses of developing mammalian brain. Cell Tissue Res 322, 353–364 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-005-1120-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-005-1120-x