Abstract
The constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) belongs to the superfamily of nuclear-hormone receptors that function as ligand-activated transcription factors. CAR plays an essential role in the metabolism of xenobiotics and shows—in contrast to related receptors—constitutive activity. However, the molecular basis for the constitutive activity remains unclear. In the present study, homology models of the ligand binding domain (LBD) were generated based on the crystal structures of the related pregnane X (PXR) and the vitamin D receptor (VDR). The models were used to investigate the basal activity of CAR and the effect of coactivator binding. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of complexed and uncomplexed receptor revealed a hypothesis for the activation mechanism. The suggested mechanism is supported by experimental results from site-directed mutagenesis. The basal activity of CAR can be explained by specific van-der-Waals interactions between amino acids on the LBD and its C-terminal activation domain (AF-2). Docking studies with the GOLD program yielded the interaction modes of structurally diverse agonists, giving insight into mechanisms by which ligands enhance CAR activity.
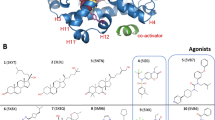
Figure The constitutive activity. Favorable regions of interactions between the GRID methyl probe and the AF-2 truncated LBD (colored magenta, contour level -2.5 kcal mol 1). Only the MOLCAD surface of the LBD is shown, colored according to the lipophilic potential (blue polar, brown lipophilic). The position of the two hydrophobic residues Leu343 and Ile346 from the AF-2 helix (colored cyan) is in close agreement with the GRID results.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAR:
-
Constitutive androstane receptor
- CITCO:
-
(6-(4-chlorophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]thiazole-5-carbaldehyde O-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)oxime
- DBD:
-
DNA binding domain
- LBD:
-
Ligand binding domain
- PXR:
-
Pregnane X receptor
- RXR:
-
Retinoid X receptor
- SRC-1:
-
Steroid receptor coactivator 1
- TMPP:
-
Tri-p-methylphenylphosphate
- VDR:
-
Vitamin D receptor
References
Guengerich FP (1989) Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 29:241–263
Turkey RH, Strassburg CP (2000) Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 40:581–616
Borst P, Oude Elferink R (2002) Annu Rev Biochem 71:537–592
Okey AB (1990) Pharmacol Ther 45:241–298
Willson TM, Kliewer SA (2002) Nat Rev 1:259–266
Baes M, Gulick T, Choi HS, Martinoli MG, Simha G, Moore DD (1994) Mol Cell Biol 14:1544–1551
Kliewer SA, Moore JT, Wade L, Staudinger JL, Watson MA, Jones SA, McKee DD, Oliver BB, Willson TM, Zetterstrom RH, Perlmann T, Lehmann JM (1998) Cell 92:73–82
Laudet V, Gronemeyer H (2002) The nuclear receptor factsbook. Academic Press, London
Moras D, Gronemeyer H (1998) Curr Opin Cell Biol 10:384–391
McKenna NJ, Lanz RB, O’Malley BW (1999) Endocr Rev 20:321–344
Honkakoski P, Zelko I, Sueyoshi T, Negishi M (1998) Mol Cell Biol 1:5652–5658
Ueda A, Hamadeh HK, Webb HK, Yamamoto Y, Sueyoshi T, Afshari CA, Lehmann JM, Negishi M (2002) Mol Pharmacol 61:1–6
Nolte RT, Wisely GB, Westin S, Cobb JE, Lambert MH, Kurokawa R, Rosenfeld MG, Willson TM, Glass CK, Milburn MV (1998) Nature 395:137–143
Maglich JM, Parks DJ, Moore LB, Collins JL, Goodwin B, Billin AN, Stoltz CA, Kliewer SA, Lambert MH, Willson TM, Moore JT (2003) J Biol Chem 278:17277–17283
Honkakoski P, Palvimo JJ, Penttila L, Vepsäläinen J, Auriola S (2004) Biochem Pharmacol 67:97–106
Toell A, Kröncke KD, Kleinert H, Carlberg C (2002) J Cell Biochem 85:72–82
Mäkinen J, Frank C, Jyrkkärinne J, Gynther J, Carlberg C, Honkakoski P (2002) Mol Pharmacol 62:366–378
Jyrkkärinne J, Makinen J, Gynther J, Savolainen H, Poso A, Honkakoski P (2003) J Med Chem 46:4687–4695
Watkins RE, Wisely GB, Moore LB, Collins JL, Lambert MH, Williams SP, Willson TM, Kliewer SA, Redinbo MR (2001) Science 292:2329–2333
Rochel N, Wurtz JM, Mitschler A, Klaholz B, Moras D (2000) Mol Cell 5:173–179
Watkins RE, Davis-Searles PR, Lambert MH, Redinbo MR (2003) J Mol Biol 331:815–828
Andersin T, Väisänen S, Carlberg C (2003) Mol Endocrinol 17:234–246
Frank C, Molnar F, Matilainen M, Lempiainen H, Carlberg C (2004) J Biol Chem 279:33558–33566
Darimont BD, Wagner RL, Apriletti JW, Stallcup MR, Kushner PJ, Baxter JD, Fletterick RJ, Yamamoto KR (1998) Genes Dev 12:3343–3356
Feng W, Ribeiro RC, Wagner RL, Nguyen H, Apriletti JW, Fletterick RJ, Baxter JD, Kushner PJ, West BL (1998) Science 280:1747–1749
Xu HE, Lambert MH, Montana VG, Plunket KD, Moore LB, Collins JL, Oplinger JA, Kliewer SA, Gampe Jr RT, McKee DD, Moore JT, Willson TM (2001) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13919–13924
Gampe Jr RT, Montana VG, Lambert MH, Miller AB, Bledsoe RK, Milburn MV, Kliewer SA, Willson TM, Xu HE (2001) Mol Cell 5:545–555
GOLD Version 2.1 (2003) CCDC, Cambridge, UK
Sablin EP, Krylova IN, Fletterick RJ, Ingraham HA (2003) Mol Cell 11:1575–1585
Greschik H, Wurtz JM, Sanglier S, Bourguet W, van Dorsselaer A, Moras D, Renaud JP (2002) Mol Cell 9:303–313
Xiao L, Cui X, Madison V, White RE, Cheng KC (2003) Drug Metab Dispos 30:951–956
Watkins RE, Maglich JM, Moore LB, Wisely GB, Noble SM, Davis-Searles PR, Lambert MH, Kliewer SA, Redinbo MR (2003) Biochemistry 42:1430–1438
Dussault I, Lin M, Hollister K, Fan M, Termini J, Sherman MA, Forman BM (2002) Mol Cell Biol 22:5270–5280
Moore JT, Moore LB, Maglich JM, Kliewer SA (2003) Biochim Biophys Acta 1691:235–238
Jacobs MN, Dickins M, Lewis DFV (2003) J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 84:117–132
INSIGHT II (2000) MSI, San Diego, USA
Higgins D, Thompson J, Gibson T, Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Bower MJ, Cohen FE, Dunbrack Jr LR (1997) J Mol Biol 267:1268–1280
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, Hermans J (1981) Interaction models for water in relation to protein hydration. In: Pullman B (ed) Intermolecular forces. Reidel, Dordrecht, pp 331–342
GROMACS Version 3.1.4 (2002) BIOSON Research institute and laboratory of biophysical chemistry, University of Groningen, The Netherlands
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, DiNola A, Haak JR (1984) J Chem Phys 81:3684–3690
Kelley LA, Gardner SP, Sutcliffe MJ (1996) Prot Eng 9:1063–1065
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) J Appl Cryst 26:283–291
Fischer D, Eisenberg D (1999) Curr Opin Struct Biol 9:208–211
Laskowski RA (1995) J Mol Graph 13:323–330
Sybyl 6.9 (2003) Tripos Inc., St. Louis, USA
GRID21 (2003) Moldiscovery Ltd. Pinner, Middlesex, UK
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) J Mol Graph 14:33–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. H-D. Höltje on the occasion of his 65th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Windshügel, B., Jyrkkärinne, J., Poso, A. et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of the human CAR ligand-binding domain: deciphering the molecular basis for constitutive activity. J Mol Model 11, 69–79 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-004-0227-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-004-0227-4