Abstract
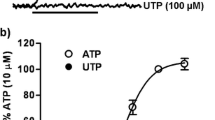
Desensitization is a major mechanism to regulate the functional response of G protein-coupled receptors. In this work we studied whether the human histamine H3 receptor of 445 amino acids (hH3R445) experiences heterologous desensitization mediated by PKC activation. Bioinformatic analysis indicated the presence of Serine and Threonine residues susceptible of PKC-mediated phosphorylation on the third intracellular loop and the carboxyl terminus of the hH3R445. In CHO-K1 cells stably transfected with the hH3R445 direct PKC activation by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (TPA, 200 nM) abolished H3R-mediated inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation. Activation of endogenous purinergic receptors by ATP (adenosine 5′-triphosphate, 10 μM) increased the free calcium intracellular concentration ([Ca2+]i) confirming their coupling to phospholipase C stimulation. Incubation with ATP also abolished H3R-mediated inhibition of forskolin-induced cAMP accumulation, and this effect was prevented by the PKC inhibitors Ro-31-8220 and Gö-6976. Pre-incubation with TPA or ATP reduced H3R-mediated stimulation of [35S]-GTPγS binding to membranes from CHO-K1-hH3R445 cells by 39.7 and 54.2 %, respectively, with no change in the agonist potency, and the effect was prevented by either Ro-31-8220 or Gö-6976. Exposure to ATP or TPA also resulted in the loss of cell surface H3Rs (−30.4 and −45.1 %) as evaluated by [3H]-NMHA binding to intact cells. These results indicate that the hH3R445 undergoes heterologous desensitization upon activation of receptors coupled to PKC stimulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Adenylyl cyclase
- DAG:
-
Diacylglycerol
- H3R:
-
Histamine H3 receptor
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptor
- GRK:
-
GPCR kinase
- PLC:
-
Phospholipase C
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- RAMH:
-
R-α-methylhistamine
- TPA:
-
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
References
Panula P, Nuutinen S (2013) The histaminergic network in the brain: basic organization and role in disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:472–487
Schneider EH, Seifert R (2015) The histamine H4-receptor and the central and peripheral nervous system: a critical analysis of the literature. Neuropharmacology. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.05.004
Feuerstein TJ (2008) Presynaptic receptors for dopamine, histamine, and serotonin. Handb Exp Pharmacol 184:289–338
Panula P, Chazot PL, Cowart M, Gutzmer R, Leurs R, Liu WL, Stark H, Thurmond RL, Haas HL (2015) International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. XCVIII. Histamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 67:601–655
Pillot C, Heron A, Cochois V, Tardivel-Lacombe J, Ligneau X, Schwartz JC, Arrang JM (2002) A detailed mapping of the histamine H3 receptor and its gene transcripts in rat brain. Neuroscience 114:173–193
Gainetdinov RR, Premont RT, Bohn LM, Lefkowitz RJ, Caron MG (2004) Desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors and neuronal functions. Annu Rev Neurosci 27:107–144
Hill SJ (2006) G-protein-coupled receptors: past, present and future. Br J Pharmacol 147(Suppl 1):S27–S37
Kelly E, Bailey CP, Henderson G (2008) Agonist-selective mechanisms of GPCR desensitization. Br J Pharmacol 153(Suppl 1):S379–S388
Mundell S, Kelly E (2011) Adenosine receptor desensitization and trafficking. Biochim Biophys Acta 1808:1319–1328
Ferguson SS (2001) Evolving concepts in G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis: the role in receptor desensitization and signaling. Pharmacol Rev 53:1–24
Gurevich EV, Tesmer JJ, Mushegian A, Gurevich VV (2012) G protein-coupled receptor kinases: more than just kinases and not only for GPCRs. Pharmacol Ther 133:40–69
Osorio-Espinoza A, Escamilla-Sánchez J, Aquino-Jarquin G, Arias-Montaño JA (2014) Homologous desensitization of human histamine H3 receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Neuropharmacology 77:387–397
Ashida N, Ueyama T, Rikitake K, Shirai Y, Eto M, Kondoh T, Kohmura E, Saito N (2008) Ca2+ oscillation induced by P2Y2 receptor activation and its regulation by a neuron-specific subtype of PKC (γPKC). Neurosci Lett 446:123–128
von Kügelgen I, Hoffmann K (2015) Pharmacology and structure of P2Y receptors. Neuropharmacology. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.10.030
Montejo-López W, Rivera-Ramírez N, Escamilla-Sánchez J, García-Hernández U, Arias-Montaño J-A (2015) Activation of endogenous purinergic receptors induces PKC-mediated desensitization of human histamine H3 receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Inflamm Res 64(Suppl 1):S36–S37
Xue Y, Ren J, Gao X, Jin C, Wen L, Yao X (2008) GPS 2.0, a tool to predict kinase-specific phosphorylation sites in hierarchy. Mol Cell Proteomics 7:1598–1608
Flores-Clemente C, Osorio-Espinoza A, Escamilla-Sanchez J, Leurs R, Arias JM, Arias-Montano JA (2013) A single-point mutation (Ala280Val) in the third intracellular loop alters the signalling properties of the human histamine H3 receptor stably expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Br J Pharmacol 170:127–135
Gómez-Viquez L, Rueda A, García U, Guerrero-Hernández A (2005) Complex effects of ryanodine on the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ levels in smooth muscle cells. Cell Calcium 38:121–130
Heding A, Vrecl M, Bogerd J, McGregor A, Sellar R, Taylor PL, Eidne KA (1998) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors with intracellular carboxyl-terminal tails undergo acute desensitization of total inositol phosphate production and exhibit accelerated internalization kinetics. J Biol Chem 273:11472–11477
Zeng L, Webster SV, Newton PM (2012) The biology of protein kinase C. Adv Exp Med Biol 740:639–661
Beazely MA, Alan JK, Watts VJ (2005) Protein kinase C and epidermal growth factor stimulation of Raf1 potentiates adenylyl cyclase type 6 activation in intact cells. Mol Pharmacol 67:250–259
Willoughby D, Cooper DM (2007) Organization and Ca2+ regulation of adenylyl cyclases in cAMP microdomains. Physiol Rev 87:965–1010
Varga EV, Stropova D, Rubenzik M, Wang M, Landsmana RS, Roeske WR, Yamamura HI (1998) Identification of adenylyl cyclase isoenzymes in CHO and B82 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 348:R1–R2
Alexander SPH, Mathie A, Peters JA (2011) Guide to receptors and channels (GRAC). Br J Pharmacol 164(Suppl 1):S91–S92
Anastassiadis T, Deacon SW, Devarajan K, Ma H, Peterson JR (2011) Comprehensive assay of kinase catalytic activity reveals features of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol 29:1039–1045
Steinberg S (2008) Structural basis of protein kinase C isoform function. Physiol Rev 88:1341–1378
Penela P, Ribas C, Mayor F Jr (2003) Mechanisms of regulation of the expression and function of G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Cell Signal 15:973–981
Moser E, Kargl J, Whistler JL, Waldhoer M, Tschische P (2010) G protein-coupled receptor-associated sorting protein 1 regulates the postendocytic sorting of seven-transmembrane-spanning G protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacology 86:22–29
Shi Y, Sheng R, Zhong T, Xu Y, Chen X, Yang D, Sun Y, Yang F, Hu Y, Zhou N (2012) Identification and characterization of ZEL-H16 as a novel agonist of the histamine H3 receptor. PLoS One 7(8):e42185
Fujimoto K, Ohta K, Kangawa K, Kikkawa U, Ogino S, Fukui H (1999) Identification of protein kinase C phosphorylation sites involved in phorbol ester-induced desensitization of the histamine H1 receptor. Mol Pharmacol 55:735–742
Feng B, Li Z, Wang JB (2011) Protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation of the μ-opioid receptor and its effects on receptor signaling. Mol Pharmacol 79:768–775
Namkung Y, Sibley DR (2004) Protein kinase C mediates phosphorylation, desensitization, and trafficking of the D2 dopamine receptor. J Biol Chem 279:49533–49541
Namkung Y, Dipace C, Javitch JA, Sibley DR (2009) G protein-coupled receptor kinase-mediated phosphorylation regulates post-endocytic trafficking of the D2 dopamine receptor. J Biol Chem 284:15038–15051
Haas HL, Sergeeva OA, Selbach O (2008) Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol Rev 88:1183–1241
Lin JY, Chung KK, de Castro D, Funk GD, Lipski J (2004) Effects of muscarinic acetylcholine activation on membrane currents and intracellular messengers in medium spiny neurons of the rat striatum. Eur J Neurosci 20:1219–1230
Shen W, Hamilton SE, Nathanson NM, Surmeier DJ (2005) Cholinergic suppression of KCNQ channel currents enhances excitability ofstriatal medium spiny neurons. J Neurosci 25:7449–7458
Blomeley CP, Kehoe LA, Bracci E (2009) Substance P mediates excitatory interactions between striatal projection neurons. J Neurosci 29:4953–4963
Szot P, White SS, Greenup JL, Leverenz JB, Peskind ER, Raskind MA (2005) α1-Adrenoreceptor in human hippocampus: binding and receptor subtype mRNA expression. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 139:367–371
Luo F, Tang H, Li BM, Li SH (2014) Activation of α1-adrenoceptors enhances excitatory synaptic transmission via a pre- and postsynaptic protein kinase C-dependent mechanism in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats. Eur J Neurosci 39:1281–1293
Passani MB, Blandina P (2011) Histamine receptors in the CNS as targets for therapeutic intervention. Trends Pharmacol Sci 32:242–249
Berlin M, Boyce CW, Ruiz M de L (2011) Histamine H3 receptor as a drug discovery target. J Med Chem 54:26–53
Tiligada E, Kyriakidis K, Chazot PL, Passani MB (2011) Histamine pharmacology and new CNS drug targets. CNS Neurosci Ther 17:620–628
Acknowledgments
Supported by Cinvestav and Conacyt (Grant 128205 to J.-A.A.-M.). We thank Raul Gonzalez-Pantoja for excellent technical assistance. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funding sources were not involved at all in the study design, collection, analysis and interpretation of data, writing of the manuscript or the decision to submit this report.
Author Contributions
W. M.-L., U. G.-H. and J.-A.A.-M. designed the study; W. M.-L., N. R.-R. and J. E.-S. conducted experiments; W. M.-L., N. R.-R., U. G.-H. and J.-A.A.-M. performed data analysis. W. M.-L., U. G.-H. and J.-A.A.-M. wrote the manuscript. All authors revised and approved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montejo-López, W., Rivera-Ramírez, N., Escamilla-Sánchez, J. et al. Heterologous, PKC-Mediated Desensitization of Human Histamine H3 Receptors Expressed in CHO-K1 Cells. Neurochem Res 41, 2415–2424 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1954-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1954-5