Abstract
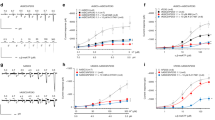
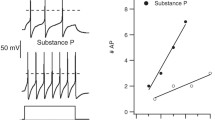
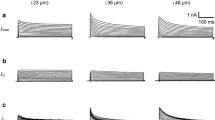
The properties and functional expression of the purinergic receptors in small (nociceptive) neurons acutely isolated from the DRG of rat were studied using whole-cell patch-clamp recording. The responses of small DRG neurons to ATP exhibited diverse kinetics and could be subdivided into three types: rapid, slow and mixed kinetics responses. Their affinities to agonists allowed to identify the responsible receptors as P2X3 (“fast”) and heteromeric P2X2/3 (“slow”) subtypes. The expression of different responses dramatically varied both on the neuron-to-neuron and animal-to-animal basis. Out of 744 neurons tested 24% of cells demonstrated predominance of functional P2X2/3 receptors, 44% had mixed representation and in 32% of cells P2X3 receptors dominated. All the animals tested (110) could be subdivided into 3 groups: in 19% of animals the response of each cell to ATP was mediated by P2X2/3 receptors, both types of ATP-evoked currents were found in 58% of animals and only in 23% of the animals P2X3 receptors dominated. Our results argue with exclusive role of P2X3 receptors in purinergic signaling in primary nociceptive neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abbracchio, M. P. and Burnstock, G. 1998. Purinergic signalling: Pathophysiological roles. J. Pharmacol. 78:113–145.
Juranyi, Z., Orso, E., Janossy, A., Szalay, K. S., Sperlagh, B., Windisch, K., Vinson, G. P., and Vizi, E. S. 1997. ATP and [3H]noradrenaline release and the presence of ecto-Ca(2+)-ATPases in the capsule-glomerulosa fraction of the rat adrenal gland. J. Endocrinol. 153:105–114.
Sperlagh, B., Kittel, A., Lajtha, A., and Vizi, E. S. 1995. ATP acts as fast neurotransmitter in rat habenula: Neurochemical and enzymecytochemical evidence. Neuroscience 66:915–920.
Bardoni, R., Goldstein, P. A., Lee, C. J., Gu, J. G., and Mac-Dermott, A. B. 1997. ATP P2X receptors mediate fast synaptic transmission in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 17:5297–5304.
Ralevic, V. and Burnstock, G. 1998. Receptors for Purines and Pyrimidines. Pharmacol. Rev. 50:413–492.
Illes, P. Nieber K. and Norenberg W. 1996. Electrophysiological effects of ATP on brain neurones. J. Auton. Pharmacol. 16:407–411.
Zimmermann, H. 1994. Signalling via ATP in the nervous system. Trends. Neurosci. 17:420–426.
Robertson, S. J. 1998. Tissue distribution and functional contribution of P2X receptors in the CNS. Drug Delop. Res. 45:336–341.
MacKenzie, A. B., Surprenant, A., and North, R. A. 1999. Functional and molecular diversity of purinergic ion channel receptors. Ann NY Acad Sci. 868:716–729.
Edwards, F. A., Gibb, A. J., and Colquhoun, D. 1992. ATP receptor-mediated currents in the central nervous system. Nature 359:144–147.
Nieber, K., Poelchen, W., and Illes, P. 1997. Role of ATP in fast excitatory synaptic potentials in locus coeruleus neurones of the rat. nes of the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 122:423–431.
Pankratov, Yu., Castro, E., Miras-Portugal, M. T., and Krishtal, O. 2001. A purinergic component of the excitatory post-synaptic current mediated by P2X receptors in the CA1 neurons of the rat hippocampus. Europ. J. Neurosci. 10:3898–3902.
Surprenant, A. 1996. Functional properties of native and cloned P2X receptors. Ciba Found Symp. 198:208–219.
Buell, G., Collo, G., and Rassendren, F. 1996. P2X receptors: an emerging channel family. Eur. J. Neurosci. 8:2221–2228.
Ding, Y., Cesare, P., Drew, L., Nikitaki, D., and Wood, J. N. 2000. ATP, P2X receptors and pain pathways. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 81:289–294.
Hamilton, S. G. and McMahon, S. B. 2000. ATP as a peripheral mediator of pain. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 81:187–194.
Burnstock, G. 2000. P2X receptors in sensory neurones. Br. J. Anaesth. 84:476–488.
Burnstock, G. 1996. A unifying purinergic hypothesis for the initiation of pain. Lancet 347:1604–1605.
Bradbury, E. J., Burnstock, G., and McMahon, S. B. 1998. The Expression of P2X3 Purinoreceptors in Sensory Neurons: Effects of Axotomy and Glial-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 12:256–268.
Lewis, C., Neidhart, S., Holy, C., North, R. A., Buell, G., and Surprenant, A. 1995. Coexpression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits can account for ATP-gated currents in sensory neurons. Nature 377:432–435.
Barden, J. A. and Bennett, M. R. 2000. Distribution of P2X purinoceptor clusters on individual rat dorsal root ganglion cells. Neurosci Lett. 287:183–186.
Rothlin, C. V., Katz, E., Verbitsky, M., and Elgoyhen, A. B. 1999. The alpha9 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor shares pharmacological properties with type A gamma-aminobutyric acid, glycine, and type 3 serotonin receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 55:248–254.
Burgard, E. C., Niforatos, W., van Biesen, T., Lynch, K. J., Touma, E., Metzger, R. E., Kowaluk, E. A., and Jarvis, M. F. 1999. P2X receptor-mediated ionic currents in dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 82:1590–1598.
Bland-Ward, P. A. and Humphrey, P. P. 2000. P2X receptors mediate ATP-induced primary nociceptive neurone activation. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 81:146–151.
Ueno, S., Tsuda, M., Iwanaga, T., and Inoue, K. 1999. Cell typespecific ATP-activated responses in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 126:429–436.
Liu, M., King, B. F., Dunn, P. M., Rong, W., Townsend-Nicholson, A., and Burnstock, G. 2001. Coexpression of P2X(3) and P2X(2) Receptor Subunits in Varying Amounts Generates Heterogeneous Populations of P2X Receptors That Evoke a Spectrum of Agonist Responses Comparable to That Seen in Sensory Neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 296:1043–1050.
Le, K. T., Paquet, M., Nouel, D., Babinski, K., and Seguela, P. 1997. Primary structure and expression of a naturally truncated human P2X ATP receptor subunit from brain and immune system. FEBS Lett. 418:195–199.
Wildman, S. S., King, B. F., and Burnstock, G. 1997. Potentiation of ATP-responses at a recombinant P2x2 receptor by neurotransmitters and related substances. Br J. Pharmacol. 120:221–224.
Wang, C. Z., Namba, N., Gonoi, T., Inagaki, N., and Seino, S. 1996. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a fourth P2X receptor subtype widely expressed in brain and peripheral tissues including various endocrine tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 220:196–202.
Piper, A. S. and Docherty, R. J. 2000. One-way cross-desensitization between P2X purinoceptors and vanilloid receptors in adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J. Physiol. 523 Pt 3:685–696.
Yiangou, Y., Facer, P., Birch, R., Sangameswaran, L., Eglen, R., and Anand, P. 2000. P2X3 receptor in injured human sensory neurons. NeuroReport 11:993–996.
Petruska, J. C., Cooper, B. Y., Johnson, R. D., and Gu, J. G. 2000. Distribution patterns of different P2x receptor phenotypes in acutely dissociated dorsal root ganglion neurons of adult rats [In Process Citation]. Exp. Brain Res. 134:126–132.
Petruska, J. C., Cooper, B. Y., Johnson, R. D., and Gu, J. G. 2000. Distribution patterns of different P2x receptor phenotypes in acutely dissociated dorsal root ganglion neurons of adult rats. Exp. Brain Res. 134:126–132.
Akaike N., Inoue M., and Krishtal O. A. 2001. “Concentrationclamp” study of g-aminobutyric acid-induced chloride current kinetics in frog sensory neurons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 379:171–185.
Zhang, M., Zhong, H., Vollmer, C., and Nurse, C. A. 2000. Corelease of ATP and ACh mediates hypoxic signalling at rat carotid body chemoreceptors. J. Physiol. 525(Pt. 1):143–158.
Rong, W., Burnstock, G., and Spyer, K. M. 2000. P2X purinoceptor-mediated excitation of trigeminal lingual nerve terminals in an in vitro intra-arterially perfused rat tongue preparation. J. Physiol (Lond) 524(Pt. 3):891–902.
Vulchanova, L., Riedl, M. S., Shuster, S. J., Stone, L. S., Hargreaves, K. M., Buell, G., Surprenant, A., North, R. A., and Elde, R. 1998. P2X3 is expressed by DRG neurons that terminate in inner lamina II. Eur J. Neurosci. 10:3470–3478.
Chen, C. C., Akopian, A. N., Sivilotti, L., Colquhoun, D., Burnstock, G., and Wood, J. N. 1995. A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature 377:428–431.
Hamilton, S. G., Wade, A., and McMahon, S. B. 1999. The effects of inflammation and inflammatory mediators on nociceptive behaviour induced by ATP analogues in the rat. Br J. Pharmacol. 126:326–332.
Cockayne, D. A., Hamilton, S. G., Zhu, Q. M., Dunn, P. M., Zhong, Y., Novakovic, S., Malmberg, A. B., Cain, G., Berson, A., Kassotakis, L., Hedley, L., Lachnit, W. G., Burnstock, G., McMahon, S. B., and Ford, A. P. 2000. Urinary bladder hyporeflexia and reduced pain-related behaviour in P2X3-deficient mice. Nature 407:1011–1015.
Cook, S. P., Vulchanova, L., Hargreaves, K. M., Elde, R., and McCleskey, E. W. 1997. Distinct ATP receptors on painsensing and stretch-sensing neurons. Nature 387:505–508.
Petruska, J. C., Mena, N., Nakatsuka, T., Cooper, B. Y., Johnson, R. D., and Gu, J. G. 2000. P2X1 receptor subunit immunoreactivity and ATP-evoked fast currents in adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. NeuroReport 11:3589–3592.
Xiang, Z., Bo, X., and Burnstock, G. 1998. Localization of ATP-gated P2X receptor immunoreactivity in rat sensory and sympathetic ganglia. Neurosci. Lett. 256:105–108.
Collo, G., North, R. A., Kawashima, E., Merlo-Pich, E., Neidhart, S., Surprenant, A., and Buell, G. 1996. Cloning OF P2X5 and P2X6 receptors and the distribution and properties of an extended family of ATP-gated ion channels. J. Neurosci. 16: 2495-2507.
Virginio, C., North, R. A., and Surprenant, A. 1998. Calcium permeability and block at homomeric and heteromeric P2X2 and P2X3 receptors, and P2X receptors in rat nodose neurones. J. Physiol. 510(Pt. 1):27–35.
Cook, S. P., Rodland, K. D., and McCleskey, E. W. 1998. A memory for extracellular Ca2+ by speeding recovery of P2X receptors from desensitization. J. Neurosci. 18:9238–9244.
Cook, S. P. and McCleskey, E. W. 1997. Desensitization, recovery and Ca(2+)-dependent modulation of ATP-gated P2X receptors in nociceptors. Neuropharmacol. 36:1303–1308.
Wildman, S. S., Brown, S. G., King, B. F., and Burnstock, G. 1999. Selectivity of diadenosine polyphosphates for rat P2X receptor subunits. Eur J. Pharmacol. 367:119–123.
Chow, Y. W. and Wang, H. L. 1998. Functional modulation of P2X2 receptors by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Neurochem. 70:2606–2612.
Koshimizu, T., Tomic, M., Koshiomizu, M., and Stojikovic, S. S. 1998. Identification of amino acid residues contributing to desensitization of the P2X2 receptor channel. J. Biol Chem. 273:12853–12857.
Evans, R. J., Lewis, C., Virginio, C., Lundstrom, K., Buell, G., Surprenant, A., and North, R. A. 1996. Ionic permeability of, and divalent cation effects on, two ATP-gated cation channels (P2X receptors) expressed in mammalian cells. J. Physiol. (Lond) 497:413–422.
Souslova, V., Cesare, P., Ding, Y., Akopian, A. N., Stanfa, L., Suzuki, R., Carpenter, K., Dickenson, A., Boyce, S., Hill, R., Nebenuis-Oosthuizen, D., Smith, A. J., Kidd, E. J., and Wood, J. N. 2000. Warm-coding deficits and aberrant inflammatory pain in mice lacking P2X3 receptors. Nature 407: 1015-1017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pankratov, Y.V., Lalo, U.V., Dashkin, A.N. et al. Heterogeneity of the Functional Expression of P2X3 and P2X2/3 Receptors in the Primary Nociceptive Neurons of Rat. Neurochem Res 26, 993–1000 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012344803672
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012344803672