Abstract
Purpose. The microcomputer program, MicroPharm-K (MP-K) was developed for pharmacokinetic modeling, including analysis of experimental data and estimation of relevant parameters, and simulation. The intention was to provide a user-friendly, interactive, event-driven program for PC computers.
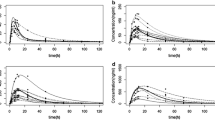
Methods. The data are ascribed to a predefined model from a library including various routes of administration, oral or intra-venous, bolus or infusion, and various compartmental interpretations, 1 to 3. Single and multiple administrations are supported. The program provides initial estimates of the parameters in most cases, and the parameters are then fitted to the model by non linear model fitting using either the Simplex, Evol, Gauss-Newton, Levenberg-Marquardt or Fletcher-Powell algorithms. The non linear model fitting is based on the maximum likelihood method, and the criterion to minimize is either the weighted least squares (Chi2 criterion) or the extended least squares. Graphical representations of non-fitted or curve-fitted data are immediately available (including log-scale representation), as well as pharmacokinetic typical parameters such as area under the curve, clearance, volumes, time-rate constants, transfer rate constants, etc.
Results. Simulated and experimental data were analysed and the results were similar to those obtained by other programs.
Conclusions. This non linear fitting program has been proved in our laboratory to be a very effective package for pharmacokinetic studies, including estimation and simulation. Because it is easy-to-use and runs on basic computers, the program could also be used for educational purposes.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. Gex-Fabry, L. P. Balant. Considerations on data analysis using computer methods and currently available software for personal computers. In P. G. Welling and L. P. Balant (eds.), Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, Vol. 110, Pharmacokinetics of Drugs, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 1994.
C. M. Metzler. Extended least squares (ELS) for pharmacokinetic models. J. Pharm. Sci. 76:565–571 1987.
W. H. Press, B. P. Flannery, S. A. Teukolsky, W. T. Vetterling. Numerical recipes in Pascal, The art of scientific computing, Cambridge University Press, New York, 1992.
P. Koeppe, C. Hamann. A program for non-linear regression analysis to be used on desk-top computers. Comput. Progr. Biomed. 12:121–128 (1980).
K. Yamaoka, Y. Tanigawara, T. Nakagawa, T. Uno. A pharmacokinetic analysis program (Multi) for microcomputer. J. Pharmaco-Biodyn. 4:879–885 1981.
G. Thomas, J. C. Thalabard, C. Girre. A program for the integrated Michaelis-Menten equation. Trends Pharm. Sci. 8:292–294.
H. Akaike. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 19:716–723 1974.
E. M. Landaw, J. J. Di Stefano. Multiexponential, multicompartmental, and non-compartmental modeling: II. Data analysis and statistical considerations. Am. J. Physiol. 246:R665–R667 1984.
M. Gibaldi, D. Perrier. Pharmacokinetics, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, 1975.
R. Gomeni. SIPHAR users manual, SIMED SA, Paris 1987.
N. Holford. MKMODEL: An extended least squares modelling program—Users Manual, Biosoft, Cambridge, England, 1986.
J. L. Valentine, S. Hunter. INTRAV and ORAL: basic interactive computer programs for estimating pharmacokinetic parameters. J. Pharm. Sci. 74:113–119 1985.
C. M. Metzler, G. L. Elfring, A. J. McEwen. A package of computer programs to pharmacokinetic modeling. Biometrics 30:562 (1974).
D. R. Lu, F. Mao. An interactive program for pharmacokinetic modeling. J. Pharm. Sci. 82:537–542 1993.
I. D. Cockshott, J. Haywood. Extended least squares curve fitting: a comparison of SIPHAR and MKMODEL. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 13:461–480 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Urien, S. MicroPharm-K, a Microcomputer Interactive Program for the Analysis and Simulation of Pharmacokinetic Processes. Pharm Res 12, 1225–1230 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016280430580
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016280430580