Abstract
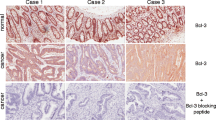
Since the role of the Bcl-2 gene family has beenonly poorly investigated in colorectal cancer, we haveexamined the expression of the apoptosis blockersBcl-xL and Bcl-2, as well as the proapoptoticfactors Bax and Bak. Northern blot analysis andimmunohistochemistry were performed on normal andcancerous colonic tissue from 12 patients. In colorectalcancer, Bcl-xL immunoreaction was strongerthan in normal controls, and 83% of the cancers had increasedBcl-xL mRNA expression. The mediandensitometric Bcl-xL values were 3.4-foldhigher in carcinomas (P < 0.005). In contrast to thenormal colon, colorectal carcinomas often lack any Bcl-2 immunostaining,and Bcl-2 mRNA was not detectable by Northern blotseither. Bax was not obviously altered in colorectalcancer, either at the protein level or at the mRNA level compared to the normal control colon. BakmRNA expression exhibited a wide variation incarcinomas, but was somewhat decreased in comparison tothe controls. Of these members of the Bcl-2 gene family, Bcl-xL seems to play a major role incolorectal tumori genesis and disease progression. Anagonistic effect might have caused the tendency forreduced Bak expression. The Bcl-2/Bax regulation systemof cell homeostasis seems to be of lesserimportance.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Steel GG: Growth Kinetics of Tumors. London, Oxford University Press, 1977
Sarraf CE, Bowen ID: Proportion of mitotic and apoptotic cells in a range of untreated experimental tumors. Cell Tissue Kinet 21:45-49, 1988
Deschner EE: Kinetics of normal, preneoplastic, and neoplastic colon epithelium. San Diego, Academic Press 1990, p 41
Reed JC: Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 124:1-6, 1994
Vaux DL: Toward an understanding of the molecular mechanisms of physiological cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:786 -789, 1993
Thompson CB: Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267:1456 -1462, 1995
Boise LH, Gottschalk AR, Quintáns J, Thompson CB: Bcl-2 and Bcl-2-related proteins in apoptosis regulation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 200:107-121, 1995
Cheng EH-Y, Levine B, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Hardwick JM: Bax-independent inhibition of apoptosis by BCL-xL. Nature 379:554 -556, 1996
Gottschalk AR, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Quintáns J: Identi-fi cation of immunosuppressant-induced apoptosis in a murine B-cell line and its prevention by Bcl-xL but not Bcl-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:7350 -7354, 1994
Shimizu S, Eguchi Y, Kosaka H, Kamiike W, Matsuda H, Tsujimoto Y: Prevention of hypoxia-induced cell death by Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. Nature 374:811-813, 1995
Nakayama K-I, Nakayama K, Negishi I, Kuida K, Shinkai Y, Louie MC, Fields LE, Lucas PJ, Stewart V, Alt FW, Loh DY: Disappearance of the lymphoid system in Bcl-2 homozygous mutant chimeric mice. Science 261:1584 -1588, 1993
Veis DJ, Sorenson CM, Shutter JR, Korsmeyer SJ: Bcl-2 defi cient mice demonstrate fulminant lymphoid apoptosis, polycystic kidneys and hypopigmented hair. Cell 75:229 -240, 1993
Kamada S, Shimono A, Shinto Y, Tsujimura T, Takahashi T, Noda T, Kiramura Y, Kondoh H, Tsujimoto Y: Bcl-2 defi-ciency in mice leads to pleiotropic abnormalities: Accelerated lymphoid cell death in thymus and spleen, polycystic kidney, hair hypopigmentation, and distorted small intestine. Can Res 55:354 -359, 1995
Motoyama N, Wang F, Roth KA, Sawa H, Nakayama K-I, Nakayama K, Nigishi I, Serju S, Zhang Q, Fujii S, Loh DY: Massive cell death of immature hematopoietic cells and neurons in Bcl-x-defi cient mice. Science 267:1506 -1510, 1995
Krajewska M, Moss SF, Krajewski S, Song K, Holt PR, Reed JC: Elevated expression of BCL-x and reduced Bak in primary colorectal adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 56:2422-2427, 1996
Tsujimoto Y, Finger LR, Yunis J, Nowell PC, Croce CM: Cloning of the chromosome s breakpoint of neoplastic B-cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science 226:1097- 1099, 1984
Kaklamanis L, Mortensen N, Tsiotos P, Doussis-Anagnostopoulou I, Biddolph S, Whitehouse R, Harris AL, Gatter KC: Early expression of Bcl-2 protein in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence of colorectal neoplasia. J Pathol 179:10 -14, 1996
Oefner D, Riehemann K, Maier H, Riedmann B, Nehoda H, Tötsch M, Böcker W, Jasani B, Schmid KW: Immunohistochemically detectable Bcl-2 expression in colorectal carcinoma: Correlation with tumor stage and patient survival. Br J Cancer 72:981-985, 1995
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ: Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivowith a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerate s programmed cell death. Cell 74:609 -619, 1993
Sinicrope FA, San Bao Ruan, Cleary KR, Stephens LC, Lee JJ, Levin B: Bcl-2 and p53 oncoprotein expression during colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 55:237-241, 1995
Yin XM, Oltval ZN, Korsmeyer SJ: BH1 and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis and heterodimerization with Bax. Nature 369:321-323, 1994
Baretton GB, Diebold J, Christoforis G, Vogt M, Müller C, Dopfer K, Schneiderbanger K, Schmidt M, Löhrs U: Apoptosis and immunohistochemical Bcl-2 expression in colorectal ade-nomas and carcinomas. Cancer 77:255-264, 1996
Chittenden T, Harrington EA, O'Connor R, Flemington C, Lutz RJ, Evan GI, Guild BC: Induction of apoptosis by the Bcl-2 homologue Bak. Nature 374:733-736, 1995
Kiefer MC, Brauer MJ, Powers VC, Wu JJ, Umansky SR, Tomei LD, Barr PJ: Modulation of apoptosis by the widely distributed Bcl-2 homologue Bak. Nature 374:736 -739, 1995
Boise LH, González-García M, Postema CE, Ding L, Lindsten T, Turka LA, Mao X, Nuñez G, Thompson CB: Bcl-x, a Bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell 74:597-608, 1993
Moss SF, Agarwal B, Arber N, Guan RJ, Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Holt PR: Increased intestinal Bak expression results in apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 223:199 -203, 1996
Potten CS, Wilson JW, Booth C: Regulation and signifi cance of apoptosis in the stem cells of the gastrointestinal epithelium. Stem Cells 15:82-93, 1997
Watson AJM, Merritt AJ, Jones LS, Askew JN, Anderson E, Becciolini A, Balzi M, Potten CS, Hickman JA: Evidence for reciprocity of Bcl-2 and p53 expression in human colorectal adenomas and carcinomas. Br J Cancer 73:889 -895, 1996
Pereira H, Silva S, Juliã o R, Garcia P, Perpé tua F: Prognostic markers for colorectal cancer: Expression of p53 and Bcl-2. World J Surg 21:210 -213, 1997
Bedi A, Pasricha PJ, Akhtar AJ, Barber JP, Bedi GC, Giardie llo FM, Zehnbauer BA, Hamilton SR, Jones RJ: Inhibition of apoptosis during development of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 55:1811-1816, 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maurer, C.A., Friess, H., Buhler, S.S. et al. Apoptosis Inhibiting Factor Bcl-xL Might Be the Crucial Member of the Bcl-2 Gene Family in Colorectal Cancer. Dig Dis Sci 43, 2641–2648 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026695025990
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026695025990