Abstract
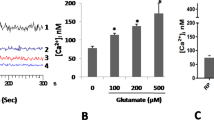
Growth factors can be divided into two classes which act through distinct signal transduction pathways1. One class including epidermal growth factor, platelet derived growth factor and fibroblast growth factor activates receptor tyrosine kinases2,3, and the second class, including thrombin4,5, bombesin6,7, bradykinin7 and vasopressin7,8 activates a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C through GTP-binding proteins9 which can be inactivated by pertussis toxin10. In Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts, thrombin-induced mitogenicity seems to correlate well with phospholipase C activation and both events are sensitive to pertussis toxin1,5,11. Thrombin12,13, like the other mitogens in this class14–16, simultaneously inhibits adenylate cyclase. This involves an inhibitory G protein (Gi), a well established pertussis toxin substrate17,18. The relative contributions of the two signalling pathways to mitogenicity has not been evaluated so far. We report here that the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine), a contracting agent19 and mitogen for smooth muscle cells20, activates phospholipase C, inhibits adenylate cyclase and stimulates DNA synthesis in fibroblasts. These events are sensitive to pertussis toxin. We show that the mitogenicity of 5-hydroxytryptamine can be uncoupled from phospholipase C activation that is mediated by 5-HT2 receptors, but correlates perfectly with inhibition of adenylate cyclase through 5-HT1B receptors. We propose that inhibition of adenylate cyclase or activation of an undefined effector system by Gi is important in 5-hydroxytryptamine induced DNA synthesis and contributes to the strong mitogenicity of the other members of this family of growth factors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chambard, J. C., Paris, S., L'Allemain, G. & Pouysségur, J. Nature 326, 800–803 (1987).
Yarden, Y. & Ullrich, A. Biochemistry 27, 3113–3119 (1988).
Huang, S. S. & Huang, J. S. J. biol. Chem. 261, 9568–9571 (1986).
Carney, D. H., Scott, D. L., Gordon, E. A. & La Belle, E. F. Cell 42, 479–488 (1985).
Paris, S. & Pouysségur, J. EMBO J. 5, 55–60 (1986).
Brown, K. D., Blay, J., Irvine, R. F., Heslop, J. P. & Berridge, M. J. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 123, 377–384 (1984).
Vicentini, L. M. & Villereal, M. L. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 123, 663–670 (1984).
Kirk, C. J., Michell, R. H. & Hems, D. A. Biochem. J. 194, 155–165 (1981).
Gomperts, B. D. Nature 306, 64–66 (1983).
Cockroft, S. Trends biochem. Sci. 12, 75–78 (1987).
Paris, S., Chambard, J. C. & Pouysségur, J. J. biol. Chem. (in the press).
Aktories, K. & Jakobs, K. H. Eur. J. Biochem. 145, 333–338 (1984).
Magnaldo, I., Pouysségur, J. & Paris, S. Biochem. J. 253, 711–713 (1988).
Murayama, T. & Ui, M. J. biol. Chem. 260, 7226–7233 (1985).
Murayama, T. & Ui, M. J. biol. Chem. 262, 5522–5529 (1987).
Vanderwel, M., Lum, D. S. & Haslam, R. J. FEBS Lett. 164, 340–344 (1983).
Katada, T. & Ui, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 3129–3133 (1982).
Bokoch, G. M., Katada, T., Northup, J. K., Hewlett, E. L. & Gilman, A. G. J. biol Chem. 258, 2072–2075 (1983).
De Chafloy de Courcelles, D., Leysen, J. E., De Clerck, F., Van Belle, H. & Janssen, P. A. J. J. biol. Chem. 260, 7603–7608 (1985).
Nemecek, G. M., Coughlin, S. R., Handley, D. A. & Moskowitz, M. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 674–678 (1986).
Fozard, J. R. Trends Pharmac. Sci. 8, 501–506 (1987).
Hoyer, D. Trends pharmac. Sci 9, 89–94 (1988).
Leysen, J. E., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Van Nueten, J. M. & Laduron, P. M. Molec. Pharmac. 21, 301–314 (1982).
Meeker, R. B. & Harden, T. K. Molec Pharmac. 22, 310–319 (1982).
Hoyer, D., Pazos, A., Probst, A. & Palacios, J. M. Brain Res. 376, 85–96 (1986).
Sills, M. A., Wolfe, B. B. & Frazer, A. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 231, 480–487 (1984).
Tricklebank, M. D., Middlemiss, D. N. & Neill, J. Neuropharmac. 25, 877–881 (1986).
Pastan, I. H., Johnson, G. S. & Anderson, W. B. A. Rev. Biochem. 44, 491–522 (1975).
Rozengurt, E. Science 234, 161–166 (1986).
Stryer, L. & Bourne, H. A. Rev. cell Biol. 2, 391–419 (1986).
Pouysségur, J. in G-proteins (eds Birnbaumer, L. & Iyengar, R.) (Academic, in the press).
Letterio, J. J., Coughlin, S. R. & Williams, L. T. Science 234, 1117–1119 (1987).
Zachary, I., Millar, J., Nånberg, E., Higgins, T. & Rozengurt, E. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 146, 456–463 (1987).
Lefkowitz, R. J. & Caron, M. G. J. biol. Chem. 263, 4993–4996 (1988).
Peralta, E. G., Ashkenazi, A., Winslow, J. W., Ramachandran, J. & Capon, D. J. Nature 334, 434–437 (1988).
Seuwen, K., Lagarde, A. & Pouysségur, J. EMBO J. 7, 161–168 (1988).
Berridge, M. J., Downes, C. P. & Hanley, M. R. Biochem. J. 206, 587–595 (1982).
Kavanaugh, W. M., Williams, L. T., Ives, H. E. & Coughlin, S. R. Molec. Endocrinology 2, 599–605 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seuwen, K., Magnaldo, I. & Pouysségur, J. Serotonin stimulates DNA synthesis in fibroblasts acting through 5–HT1B receptors coupled to a Gi-protein. Nature 335, 254–256 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/335254a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/335254a0
This article is cited by
-
Serotonin: good or bad for bone
BoneKEy Reports (2012)
-
Decreased Hepatic 5-HT1A Receptors During Liver Regeneration and Neoplasia in Rats
Neurochemical Research (2008)
-
Molecular signaling involved in regulating feeding and other mitivated behaviors
Molecular Neurobiology (2007)
-
Molecular signaling involved in regulating feeding and other mitivated behaviors
Molecular Neurobiology (2007)
-
The recombinant 5‐HT1A receptor: G protein coupling and signalling pathways
British Journal of Pharmacology (1999)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.