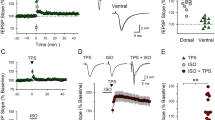
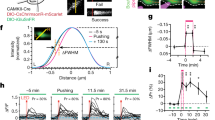
Abstract
LONG-term potentiation (LTP) refers to a persisting enhancement of neurotransmission that follows high-frequency activation of certain synapses1. Although both pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms contribute to LTP2,3, it is believed that the enhanced release of neurotransmitter that accompanies this process results from the production of a diffusible messenger in postsynaptic neurons which traverses the synaptic cleft and alters the function of presynaptic terminals4,5. One candidate for such a messenger is arachidonic acid, a metabolite produced by phospholipase A2 which augments synaptic transmission when coupled with presynaptic stimulation5. However, the effects of arachidonic acid require activation of the postsynaptic receptor for N-methyl-D-aspartate6. Previously we found that platelet-activating factor (1 O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine), another phospholipase A2-derived messenger7, selectively enhances excitatory postsynaptic currents in hippocampal neurons by a presynaptic mechanism8. We now present evidence that platelet-activating factor, acting at a receptor localized to synaptic regions, participates in LTP in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices and may serve as part of a retrograde signalling cascade..
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuba, K. & Kumamoto, E. Prog. Neurobiol. 34, 197–269 (1990).
Bekkers, J. M. & Stevens, C. F. Nature 346, 724–728 (1990).
Manabe, T., Renner, P. & Nicoll, R. A. Nature 355, 50–55 (1992).
Kandel, E. R. & O'Dell, T. J. Science 258, 243–245 (1992).
Williams, J. H., Errington, M. L., Lynch, M. A. & Bliss, T. V. P. Nature 341, 739–742 (1989).
O'Dell, T. J., Hawkins, R. D., Kandel, E. R. & Arancio, O. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 11285–11289 (1991).
Bazan, N. G. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 559, 1–16 (1989).
Clark, G. D., Happel, L. T., Zorumski, C. F. & Bazan, N. G. Neuron 9, 1211–1216 (1992).
Marcheselli, V. L., Rossowska, M. J., Domingo, M. T., Braquet, P. & Bazan, N. G. J. biol. Chem. 265, 9140–9145 (1990).
Marcheselli, V. L., & Bazan, N. G. J. Neurosci. Res. (in the press).
Del Cerro, S. D., Arai, A. & Lynch, G. Behavl neural Biol. 54, 213–217 (1990).
Arai, A. & Lynch, G. Eur. J. Neurosci. 4, 411–419 (1992).
Schuman, E. M. & Madison, D. V. Science 254, 1503–1506 (1991).
Zhuo, M., Small, S. A., Kandel, E. R. & Hawkins, R. D. Science 260, 1946–1950 (1993).
Bredt, D. S. et al. Neuron 7, 615–624 (1991).
Gribkoff, V. K. & Lum-Ragan, J. T. J. Neurophysiol. 68, 639–642 (1992).
Li, Y. G., Errington, M. L., Williams, J. H. & Bliss, T. V. P. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 18, 343 (1992).
Izumi, Y., Clifford, D. B. & Zorumski, C. F. Science 257, 1273–1276 (1992).
Lynch, M. A., Errington, M. L. & Bliss, T. V. P. Neuroscience 30, 693–701 (1989).
Braquet, P., Touqui, L., Shen, T. Y. & Vargaftig, B. B. Pharmac. Rev. 39, 97–145 (1987).
Kato, K., Uruno, K., Saito, K. & Kato, H. Brain Res. 563, 94–100 (1991).
Wieraszko, A., Li, G., Kornecki, E., Hogan, M. V. & Ehrlich, Y. H. Neuron 10, 553–557 (1993).
Miller, B., Sarantis, M., Traynelis, S. F. & Attwell, D. Nature 355, 722–725 (1992).
Doucet, J. P. & Bazan, N. G. Molec. Neurobiol. 6, 407–424 (1992).
Yue, T-L., Lysko, P. G. & Feuerstein, G. J. Neurochem. 54, 1809–1811 (1990).
Prescott, S. M., Zimmerman, G. A. & Mclntyre, T. M. J. biol. Chem. 265, 17381–17384 (1990).
Bazan, N. G. & Cluzel, J. M. in Emerging Strategies in Neuroprotection (eds Marangos, P. J., & Lai, H.) 238–251 (Birkhauser, Boston, 1992).
Bito, H. et al. Neuron 9, 285–294 (1992).
Lynch, M. A. & Voss, K. L. J. Neurochem. 56, 113–118 (1991).
Kato, K., Clifford, D. B. & Zorumski, C. F. Neuroscience 53, 39–47 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kato, K., Clark, G., Bazan, N. et al. Platelet-activating factor as a potential retrograde messenger in CA1 hippocampal long-term potentiation. Nature 367, 175–179 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/367175a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/367175a0
This article is cited by
-
Ginkgolide B improved postoperative cognitive dysfunction by inhibiting microgliosis-mediated neuroinflammation in the hippocampus of mice
BMC Anesthesiology (2022)
-
Homozygous Expression of Mutant ELOVL4 Leads to Seizures and Death in a Novel Animal Model of Very Long-Chain Fatty Acid Deficiency
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)
-
Emerging Trends in Retrograde Signaling
Molecular Neurobiology (2016)
-
Superior Neuroprotective Efficacy of LAU-0901, a Novel Platelet-Activating Factor Antagonist, in Experimental Stroke
Translational Stroke Research (2012)
-
Low Molecular Weight Phospholipases A2 in Mammalian Brain and Neural Cells: Roles in Functions and Dysfunctions
Molecular Neurobiology (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.