Abstract
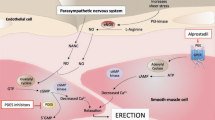
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in penile vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) plays a key role in promoting penile erection. Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) in VSMC breaks down cGMP to counter this effect. Sildenafil (Viagra), vardenafil (Levitra) and tadalafil (Cialis), treatments for erectile dysfunction, inhibit PDE5 action. Many men with erectile dysfunction have improved erectile function after plasma inhibitor concentration falls below therapeutic levels. Maximum effect plus onset and duration of action of inhibitor determines its efficacy. The rate and extent of cellular drug accumulation and efflux of drug from smooth muscle cells plus persistence of drug effects in these cell impact these parameters. We propose possible molecular mechanisms that could account for prolonged action of PDE5 inhibitors including (1) persistence of biochemical effects after inhibitor is cleared from cells, and (2) retention of drug in VSMC beyond plasma clearance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnett AL . Nitric oxide regulation of penile erection: biology and therapeutic implications. J Androl 2002; 23: S20–S26.
Burnett AL . The role of nitric oxide in erectile dysfunction: implications for medical therapy. J Clin Hypertens 2006; 8: 53–62.
Hofmann F . The biology of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 1–4.
Lincoln TM, Dey N, Sellak H . Invited review: cGMP-dependent protein kinase signaling mechanisms in smooth muscle: from the regulation of tone to gene expression. J Appl Physiol 2001; 91: 1421–1430.
Sausbier M, Schubert R, Voigt V, Hirneiss C, Pfeifer A, Korth M et al. Mechanisms of NO/cGMP-dependent vasorelaxation. Circ Res 2000; 87: 825–830.
Francis SH, Corbin JD . Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition: the molecular biology of erectile function and dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am 2005; 32: 419–429.
Corbin JD, Francis SH . Molecular biology and pharmacology of PDE-5-inhibitor therapy for erectile dysfunction. J Androl 2003; 24: S38–S41.
Gopal VK, Francis SH, Corbin JD . Allosteric sites of phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). A potential role in negative feedback regulation of cGMP signaling in corpus cavernosum. Eur J Biochem/FEBS 2001; 268: 3304–3312.
Francis SH, Zoraghi R, Kotera J, Ke H, Bessay EP, Blount MA et al. Phosphodiesterase 5: molecular characteristics relating to structure, function, and regulation. In: Beavo JA, Francis SH, Houslay MD (ed). Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterases in Health and Disease. CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2006, pp 131–164.
Corbin JD, Francis SH . Cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase-5: target of sildenafil. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 13729–13732.
Corbin JD, Turko IV, Beasley A, Francis SH . Phosphorylation of phosphodiesterase-5 by cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinase alters its catalytic and allosteric cGMP-binding activities. Eur J Biochem/FEBS 2000; 267: 2760–2767.
Blount MA, Beasley A, Zoraghi R, Sekhar KR, Bessay EP, Francis SH et al. Binding of tritiated sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil to the phosphodiesterase-5 catalytic site displays potency, specificity, heterogeneity, and cGMP stimulation. Mol Pharmacol 2004; 66: 144–152.
Corbin JD, Blount MA, Weeks II JL, Beasley A, Kuhn KP, Ho YS et al. [3H]sildenafil binding to phosphodiesterase-5 is specific, kinetically heterogeneous, and stimulated by cGMP. Mol Pharmacol 2003; 63: 1364–1372.
Corbin JD, Francis SH . Pharmacology of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors. Int J Clin Pract 2002; 56: 453–459.
Kuthe A . Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors in male sexual dysfunction. Curr Opin Urol 2003; 13: 405–410.
Stief CG . Phosphodiesterase inhibitors in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Drugs Today 2000; 36: 93–99.
Francis SH, Corbin JD . Molecular mechanisms and pharmacokinetics of phosphodiesterase-5 antagonists. Curr Urol Rep 2003; 4: 457–465.
Sandner P, Hutter J, Tinel H, Ziegelbauer K, Bischoff E . PDE5 inhibitors beyond erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2007; 19: 533–543.
Salem EA, Kendirci M, Hellstrom WJ . Udenafil, a long-acting PDE5 inhibitor for erectile dysfunction. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2006; 7: 661–669.
Moncada I, Jara J, Subira D, Castano I, Hernandez C . Efficacy of sildenafil citrate at 12 h after dosing: re-exploring the therapeutic window. Eur Urol 2004; 46: 357–360; discussion 360–351.
Gingell C, Sultana SR, Wulff MB, Gepi-Attee S . Duration of action of sildenafil citrate in men with erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 2004; 1: 179–184.
Youn JM, Feldman RA, Auerbach SM, Kaufman JM, Garcia CS, Shen W et al. Tadalafil improved erectile function at twenty-four and thirty-six hours after dosing in men with erectile dysfunction: US trial. J Androl 2005; 26: 310–318.
Porst H, Padma-Nathan H, Giuliano F, Anglin G, Varanese L, Rosen R . Efficacy of tadalafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction at 24 and 36 h after dosing: a randomized controlled trial. Urol 2003; 62: 121–125; discussion 125–126.
Shabsigh R, Seftel AD, Rosen RC, Porst H, Ahuja S, Deeley MC et al. Review of time of onset and duration of clinical efficacy of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors in treatment of erectile dysfunction. Urol 2006; 68: 689–696.
Thomas MK, Francis SH, Corbin JD . Characterization of a purified bovine lung cGMP-binding cGMP phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem 1990; 265: 14964–14970.
Turko IV, Francis SH, Corbin JD . Potential roles of conserved amino acids in the catalytic domain of the cGMP-binding cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 6460–6466.
Boolell M, Allen MJ, Ballard SA, Gepi-Attee S, Muirhead GJ, Naylor AM et al. Sildenafil: an orally active type 5 cyclic GMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the treatment of penile erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 1996; 8: 47–52.
Ballard SA, Gingell CJ, Tang K, Turner LA, Price ME, Naylor AM . Effects of sildenafil on the relaxation of human corpus cavernosum tissue in vitro and on the activities of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes. J Urol 1998; 159: 2164–2171.
Turko IV, Ballard SA, Francis SH, Corbin JD . Inhibition of cyclic GMP-binding cyclic GMP-specific phosphodiesterase (type 5) by sildenafil and related compounds. Mol Pharmacol 1999; 56: 124–130.
Gupta M, Kovar A, Meibohm B . The clinical pharmacokinetics of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction. J Clin Pharmacol 2005; 45: 987–1003.
Valiquette L, Montorsi F, Hellstrom WJ, Giuliano F, Homering M, Taylor T et al. Penetration and maintenance of erection with vardenafil: a time-from-dosing analysis. Can J Urol 2005; 12: 2687–2698; discussion 2699.
Barber R, Butcher RW . The quantitative relationship between intracellular concentration and egress of cyclic AMP from cultured cells. Mol Pharmacol 1981; 19: 38–43.
Mercapide J, Santiago E, Alberdi E, Martinez-Irujo JJ . Contribution of phosphodiesterase isoenzymes and cyclic nucleotide efflux to the regulation of cyclic GMP levels in aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochem Pharmacol 1999; 58: 1675–1683.
Jiang H, Colbran JL, Francis SH, Corbin JD . Direct evidence for cross-activation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase by cAMP in pig coronary arteries. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 1015–1019.
Bessay EP, Zoraghi R, Blount MA, Grimes KA, Beasley A, Francis SH et al. Phosphorylation of phosphodiesterase-5 is promoted by a conformational change induced by sildenafil, vardenafil, or tadalafil. Front Biosci 2007; 12: 1899–1910.
Francis SH, Chu DM, Thomas MK, Beasley A, Grimes K, Busch JL et al. Ligand-induced conformational changes in cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases and cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Methods 1998; 14: 81–92.
Francis SH, Grimes KA, Liu L, Thompson WJ, Corbin JD . Phosphorylation of isolated human PDE5 regulatory domain increases cGMP-binding affinity and induces an apparent conformational change. J Biol Chem 2001; 277: 47581–47587.
Smith JA, Francis SH, Walsh KA, Kumar S, Corbin JD . Autophosphorylation of type Ibeta cGMP-dependent protein kinase increases basal catalytic activity and enhances allosteric activation by cGMP or cAMP. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 20756–20762.
Busch JL, Bessay EP, Francis SH, Corbin JD . A conserved serine juxtaposed to the pseudosubstrate site of type I cGMP-dependent protein kinase contributes strongly to autoinhibition and lower cGMP affinity. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 34048–34054.
Hofmann F, Gensheimer HP, Gobel C . Autophosphorylation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase is stimulated only by occupancy of one of the two cGMP binding sites. FEBS Lett 1983; 164: 350–354.
Hofmann F, Gensheimer HP, Gobel C . cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Autophosphorylation changes the characteristics of binding site 1. Eur J Biochem 1985; 147: 361–365.
Chu DM, Francis SH, Thomas JW, Maksymovitch EA, Fosler M, Corbin JD . Activation by autophosphorylation or cGMP binding produces a similar apparent conformational change in cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 14649–14656.
Corbin JD, Doskeland SO . Studies of two different intrachain cGMP-binding sites of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 1983; 258: 11391–11397.
Broderick KE, Zhang T, Rangaswami H, Zeng Y, Zhao X, Boss GR et al. Guanosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (cGMP)/cGMP-dependent protein kinase induce interleukin-6 transcription in osteoblasts. Mol Endocrinol 2007; 21: 1148–1162.
Pilz RB, Broderick KE . Role of cyclic GMP in gene regulation. Front Biosci 2005; 10: 1239–1268.
Lu Z, Liu D, Hornia A, Devonish W, Pagano M, Foster DA . Activation of protein kinase C triggers its ubiquitination and degradation. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 839–845.
Kuo WL, Duke CJ, Abe MK, Kaplan EL, Gomes S, Rosner MR . ERK7 expression and kinase activity is regulated by the ubiquitin–proteosome pathway. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 23073–23081.
Wyatt TA, Lincoln TM, Pryzwansky KB . Vimentin is transiently co-localized with and phosphorylated by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in formyl-peptide-stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 21274–21280.
Pryzwansky KB, Wyatt TA, Lincoln TM . Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase is targeted to intermediate filaments and phosphorylates vimentin in A23187-stimulated human neutrophils. Blood 1995; 85: 222–230.
Pryzwansky KB, Wyatt TA, Nichols H, Lincoln TM . Compartmentalization of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in formyl-peptide stimulated neutrophils. Blood 1990; 76: 612–618.
Murthy KS, Zhou H, Grider JR, Makhlouf GM . Inhibition of sustained smooth muscle contraction by PKA and PKG preferentially mediated by phosphorylation of RhoA. Am J Physiol 2003; 284: G1006–G1016.
Golin-Bisello F, Bradbury N, Ameen N . STa and cGMP stimulate CFTR translocation to the surface of villus enterocytes in rat jejunum and is regulated by protein kinase G. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2005; 289: C708–C716.
Zhu CB, Hewlett WA, Francis SH, Corbin JD, Blakely RD . Stimulation of serotonin transport by the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor sildenafil. Eur J Pharmacol 2004; 504: 1–6.
Blount MA, Zoraghi R, Bessay EP, Beasley A, Francis SH, Corbin JD . Conversion of phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) catalytic site to higher affinity by PDE5 inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007; 323: 730–737.
Bessay EP, Blount MA, Zoraghi R, Beasley A, Grimes KA, Francis SH et al. Phosphorylation increases conversion of phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) catalytic site to higher affinity by PDE5 inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2008, In press.
Silhavy TJ, Szmelcman S, Boos W, Schwartz M . On the significance of the retention of ligand by protein. Proc Natl Aacd Sci USA 1975; 72: 2120–2124.
Corbin JD, Sugden PH, West L, Flockhart DA, Lincoln TM, McCarthy D . Studies on the properties and mode of action of the purified regulatory subunit of bovine heart adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 1978; 253: 3997–4003.
Kotera J, Francis SH, Grimes KA, Rouse A, Blount MA, Corbin JD . Allosteric sites of phosphodiesterase-5 sequester cyclic GMP. Front Biosci 2004; 9: 378–386.
Kotera J, Grimes KA, Corbin JD, Francis SH . cGMP-dependent protein kinase protects cGMP from hydrolysis by phosphodiesterase-5. Biochem J 2003; 372: 419–426.
Corbin JD, Kotera J, Gopal VK, Cote RH, Francis SH . Regulation of cyclic nucleotide levels by sequestration. In: Bradshaw RH (ed). Handbook of Signaling. Academic Press: New York, 2004, pp 465–470.
Belfiore CJ, Yang RS, Chubb LS, Lohitnavy M, Lohitnavy OS, Andersen ME . Hepatic sequestration of chlordecone and hexafluoroacetone evaluated by pharmacokinetic modeling. Toxicology 2007; 234: 59–72.
Borzelleca JF, Lester D . Acute toxicity of some perhalogenated acetones. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1965; 7: 592–597.
Gillies PJ, Rickard RW . Toxicokinetics of [14C]hexafluoroacetone in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1984; 73: 23–29.
Belfiore A, Costantino A, Frasca F, Pandini G, Mineo R, Vigneri P et al. Overexpression of membrane glycoprotein PC-1 in MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells is associated with inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Endocrinol 1996; 10: 1318–1326.
Willis RC, Furlong CE . Purification and properties of a ribose-binding protein from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 1974; 249: 6926–6929.
Wolfe L, Francis SH, Landiss LR, Corbin JD . Interconvertible cGMP-free and cGMP-bound forms of cGMP-dependent protein kinase in mammalian tissues. J Biol Chem 1987; 262: 16906–16913.
Richarme G, Kepes A . Release of glucose from purified galactose-binding protein of Escherichia coli upon addition of galactose. Eur J Biochem/FEBS 1974; 45: 127–133.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH DK40029.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francis, S., Morris, G. & Corbin, J. Molecular mechanisms that could contribute to prolonged effectiveness of PDE5 inhibitors to improve erectile function. Int J Impot Res 20, 333–342 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2008.4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2008.4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effect of low-dose tadalafil once daily on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and erectile dysfunction: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2022)
-
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors: back and forward from cardiac indications
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2016)
-
Erectile properties of the Rho-kinase inhibitor SAR407899 in diabetic animals and human isolated corpora cavernosa
Journal of Translational Medicine (2012)
-
PDE-5 and NOS II mRNA expression in menopausal women: a molecular biology study
World Journal of Urology (2011)