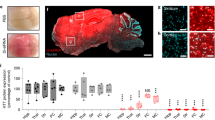
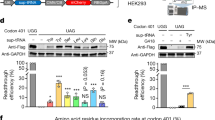
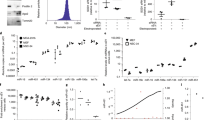
Abstract
RNA interference is now established as an important biological strategy for gene silencing, but its application to mammalian cells has been limited by nonspecific inhibitory effects of long dsRNA on translation. Here, we describe a viral-mediated delivery mechanism that results in specific silencing of targeted genes through expression of small interfering RNA (siRNA). We establish proof of principle by markedly diminishing expression of exogenous and endogenous genes in vitro and in vivo in brain and liver, and further apply this strategy to a model system of a major class of neurodegenerative disorders, the polyglutamine diseases, to show reduced polyglutamine aggregation in cells. This viral-mediated strategy should prove generally useful in reducing expression of target genes to model biological processes or to provide therapy for dominant human diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cogoni, C., Romano, N. & Macino, G. Suppression of gene expression by homologous transgenes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 65, 205–209 (1994).
Baulcombe, D.C. RNA as a target and an initiator of post-transcriptional gene silencing in transgenic plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 32, 79–88 (1996).
Kennerdell, J.R. & Carthew, R.W. Use of dsRNA-mediated genetic interference to demonstrate that frizzled and frizzled 2 act in the wingless pathway. Cell 95, 1017–1026 (1998).
Timmons, L. & Fire, A. Specific interference by ingested dsRNA. Nature 395, 854 (1998).
Waterhouse, P.M., Graham, M.W. & Wang, M.B. Virus resistance and gene silencing in plants can be induced by simultaneous expression of sense and antisense RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 13959–13964 (1998).
Wianny, F. & Zernicka-Goetz, M. Specific interference with gene function by double-stranded RNA in early mouse development. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 70–75 (2000).
Yang, S., Tutton, S., Pierce, E. & Yoon, K. Specific double-stranded RNA interference in undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 7807–7816 (2001).
Svoboda, P., Stein, P., Hayashi, H. & Schultz, R.M. Selective reduction of dormant maternal mRNAs in mouse oocytes by RNA interference. Development 127, 4147–4156 (2000).
Caplan, N.J., Parrish, S., Imani, F., Fire, A. & Morgan, R.A. Specific inhibition of gene expression by small double-stranded RNAs in invertebrate and vertebrate systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 9742–9747 (2001).
Elbashir, S.M. et al. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 411, 494–498 (2001).
Brummelkamp, T.R., Bernards, R. & Agami, R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 296, 550–553 (2002).
Lee, N.S. et al. Expression of small interfering RNAs targeted against HIV-1 rev transcripts in human cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 500–505 (2002).
Miyagishi, M. & Taira, K. U6 promoter-driven siRNAs with four uridine 3′ overhangs efficiently suppress targeted gene expression in mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 497–500 (2002).
Paul, C.P., Good, P.D., Winer, I. & Engelke, D.R. Effective expression of small interfering RNA in human cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 505–508 (2002).
Manche, L., Green, S.R., Schmedt, C. & Mathews, M.B. Interactions between double-stranded RNA regulators and the protein kinase DAI. Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 5238–5248 (1992).
Minks, M.A., West, D.K., Benvin, S. & Baglioni, C. Structural requirements of double-stranded RNA for the activation of 2', 5′-oligo(A) polymerase and protein kinase of interferon-treated HeLa cells. J. Biol. Chem. 254, 10180–10183 (1979).
Nykänen, A., Haley, B. & Zamore, P.D. ATP requirements and small interfering RNA structure in the RNA interference pathway. Cell 107, 309–321 (2001).
Xia, H., Mao, Q. & Davidson, B.L. The HIV tat protein transduction domain improves the biodistribution of β-glucuronidase expressed from recombinant viral vectors. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 640–644 (2001).
Anderson, R.D., Haskell, R.E., Xia, H., Roessler, B.J. & Davidson, B.L. A simple method for the rapid generation of recombinant adenovirus vectors. Gene Ther. 7, 1034–1038 (2000).
Okabe, M., Ikawa, M., Kominami, K., Nakanishi, T. & Nishimune, Y. 'Green mice' as a source of ubiquitous green cells. FEBS Lett. 407, 313–319 (1997).
Ooboshi, H. et al. Augmented adenovirus-mediated gene transfer to atherosclerotic vessels. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 17, 1786–1792 (1997).
Stein, C.S., Ghodsi, A., Derksen, T. & Davidson, B.L. Systemic and central nervous system correction of lysosomal storage in mucopolysaccharidosis type VII mice. J. Virol. 73, 3424–3429 (1999).
Margolis, R.L. & Ross, C.A. Expansion explosion: new clues to the pathogenesis of repeat expansion neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 7, 479–482 (2001).
Davidson, B.L. et al. Recombinant adeno-associated type 2, 4 and 5 vectors: transduction of variant cell types and regions in the mammalian CNS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3428–3432 (2000).
Brooks, A.I. et al. Functional correction of established CNS deficits in an animal model of lysosomal storage disease using feline immunodeficiency virus-based vectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 6216–6221 (2002).
Chai, Y., Koppenhafer, S.L., Bonini, N.M. & Paulson, H.L. Analysis of the role of heat shock protein (Hsp) molecular chaperones in polyglutamine disease. J. Neurosci. 19, 10338–10347 (1999).
Moulder, K.L., Onodera, O., Burk, J.R., Strittmatter, W.J. & Johnson, E.M. Jr. Generation of neuronal intranuclear inclusion by polyglutamine–GFP: analysis of inclusion clearance and toxicity as a function of polyglutamine length. J. Neurosci. 19, 705–715 (1999).
Zamore, P.D., Tuschl, T., Sharp, P.A. & Bartel, D.P. RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 101, 25–33 (2000).
Bernstein, E., Caudy, A.A., Hammond, S.M. & Hannon, G.J. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409, 363–366 (2001).
Hamilton, A.J. & Baulcombe, D.C. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 286, 950–952 (1999).
Hammond, S.M., Bernstein, E., Beach, D. & Hannon, G.J. An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-transcriptional gene silencing in Drosophila cells. Nature 404, 293–296 (2000).
Blömer, U. et al. Highly efficient and sustained gene transfer in adult neurons with a lentivirus vector. J. Virol. 71, 6641–6649 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the NIH (HD 44093) and the Roy J. Carver Trust. The authors thank P.B. McCray, Jr. and M.J. Welsh for critical review of the work, and C. McLennan, J. Lindbloom, N. Kiewiet, and A. Espie-Ziemann for assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, H., Mao, Q., Paulson, H. et al. siRNA-mediated gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 20, 1006–1010 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt739
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt739
This article is cited by
-
Molecular Characterization of U6 Promoters from Orange-Spotted Grouper (Epinephelus coioides) and Its Application in DNA Vector-Based RNAi Technology
Marine Biotechnology (2023)
-
A practical approach to RNA interference for studying gene function in a refractory social insect (on a limited budget)
Insectes Sociaux (2023)
-
A recombinant adenoviral vector with a specific tropism to CD4-positive cells: a new tool for HIV-1 inhibition
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2022)
-
Programmably tiling rigidified DNA brick on gold nanoparticle as multi-functional shell for cancer-targeted delivery of siRNAs
Nature Communications (2021)
-
A small interfering RNA (siRNA) database for SARS-CoV-2
Scientific Reports (2021)