Abstract
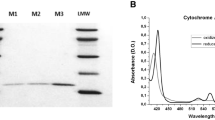
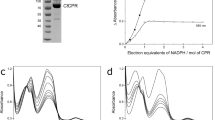
Cytochrome P450 (P450) enzymes are important in the metabolism of steroids, vitamins, carcinogens, drugs and other compounds. Two of the commonly used assays in this field are the measurements of total P450 and NADPH–P450 reductase in biological preparations. A detailed protocol is presented for the measurement of P450 by its spectral properties, along with a protocol for measuring NADPH–P450 reductase by its NADPH–cytochrome c reduction activity. Each assay can be completed in 5–10 min. Detailed explanations for the rationale of particular sequences in the protocols are provided, along with potential confounding problems.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams, J.A. et al. Drug–drug interactions for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase substrates: a pharmacokinetic explanation for typically observed low exposure (AUCi/AUC) ratios. Drug Metab. Dispos. 32, 1201–1208 (2004).
Guengerich, F.P. Human cytochrome P450 enzymes. In Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry 3rd ed. (ed. Ortiz de Montellano, P.R.) Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, 377–530 (2005).
Wienkers, L.C. & Heath, T.G. Predicting in vivo drug interactions from in vitro drug discovery data. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 4, 825–833 (2005).
Ortiz de Montellano, P.R. ed., Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry 3rd ed., Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York (2005).
Sohl, C.D., Cheng, Q. & Guengerich, F.P. Chromatographic assays of drug oxidation by human cytochrome P450 3A4. Nat. Protoc. 4, 1252–1257 (2009).
Cheng, Q., Sohl, C.D. & Guengerich, F.P. High–throughput fluorescence assay of cytochrome P450 3A4. Nat. Protoc. 4, 1258–1261 (2009).
Klingenberg, M. Pigments of rat liver microsomes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 75, 376–386 (1958).
Omura, T. & Sato, R. A new cytochrome in liver microsomes. J. Biol. Chem. 237, 1375–1376 (1962).
Omura, T. & Sato, R. The carbon monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes. I. Evidence for its hemoprotein nature. J. Biol. Chem. 239, 2370–2378 (1964).
Omura, T. & Sato, R. Isolation of cytochromes P-450 and P-420. Methods Enzymol. 10, 556–561 (1967).
Guengerich, F.P. Reduction of cytochrome b 5 by NADPH–cytochrome P450 reductase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 440, 204–211 (2005).
Phillips, A.H. & Langdon, R.G. Hepatic triphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome c reductase: isolation, characterization, and kinetic studies. J. Biol. Chem. 237, 2652–2660 (1962).
Coon, M.J., Haugen, D.A., Guengerich, F.P., Vermilion, J.L. & Dean, W.L. Liver microsomal membranes: reconstitution of the hydroxylation system containing cytochrome P-450. In The Structural Basis of Membrane Function (eds., Hatefi, Y. & Djavadi-Ohaniance, L.) Academic Press, New York, 409–427 (1976).
Gillam, E.M.J. Extending the capabilities of nature's most versatile catalysts: directed evolution of mammalian xenobiotic-metabolizing P450s. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 464, 176–186 (2007).
Guengerich, F.P. & Bartleson, C.J. Analysis and characterization of enzymes and nucleic acids. In Principles and Methods of Toxicology 5th edn. (ed. Hayes, A.W.) CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1981–2048 (2007).
Yasukochi, Y. & Masters, B.S.S. Some properties of a detergent-solubilized NADPH–cytochrome c (cytochrome P-450) reductase purified by biospecific affinity chromatography. J. Biol. Chem. 251, 5337–5344 (1976).
Stark, K., Dostalek, M. & Guengerich, F.P. Expression and purification of orphan cytochrome P450 4X1 and oxidation of anandamide. FEBS J. 275, 3706–3717 (2008).
Parikh, A., Gillam, E.M.J. & Guengerich, F.P. Drug metabolism by Escherichia coli expressing human cytochromes P450. Nat. Biotechnol. 15, 784–788 (1997).
Guengerich, F.P. Destruction of heme and hemoproteins mediated by liver microsomal reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-cytochrome P-450 reductase. Biochemistry 17, 3633–3639 (1978).
Matsubara, T., Koike, M., Touchi, A., Tochino, Y. & Sugeno, K. Quantitative determination of cytochrome P-450 in rat liver homogenate. Anal. Biochem. 75, 596–603 (1976).
Johannesen, K.A.M. & DePierre, J.W. Measurements of cytochrome P-450 in the presence of large amounts of contaminating hemoglobin and methemoglobin. Anal. Biochem. 86, 725–732 (1978).
Song, W.C. & Brash, A.R. Purification of an allene oxide synthase and identification of the enzyme as a cytochrome P-450. Science 253, 781–784 (1991).
Lau, S.M.C., Harder, P.A. & O'Keefe, D.P. Low carbon monoxide affinity allene oxide synthase is the predominant cytochrome P450 in many plant tissues. Biochemistry 32, 1945–1950 (1993).
Sandhu, P., Guo, Z., Baba, T., Martin, M.V., Tukey, R.H. & Guengerich, F.P. Expression of modified human cytochrome P450 1A2 in Escherichia coli: stabilization, purification, spectral characterization, and catalytic activities of the enzyme. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 309, 168–177 (1994).
Harada, N. Novel properties of human placental aromatase as cytochrome P-450: purification and characterization of a unique form of aromatase. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 103, 106–113 (1988).
Gartner, C.A., Thompson, S.J., Rettie, A.E. & Nelson, S.D. Human aromatase in high yield and purity by perfusion chromatography and its characterization by difference spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Protein Expr. Purif. 22, 443–454 (2001).
Ghosh, D., Griswold, J., Erman, M. & Pangborn, W. Structural basis for androgen specificity and oestrogen synthesis in human aromatase. Nature 457, 219–223 (2009).
Dignam, J.D. & Strobel, H.W. Preparation of homogeneous NADPH–cytochrome P-450 reductase from rat liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 63, 845–852 (1975).
Vermilion, J.L. & Coon, M.J. Identification of the high and low potential flavins of liver microsomal NADPH–cytochrome P-450 reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 253, 8812–8819 (1978).
Roerig, D.L., Mascaro, L., Jr. & Aust, S.D. Microsomal electron transport: tetrazolium reduction by rat liver microsomal NADPH–cytochrome c reductase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 153, 475–479 (1972).
Vermilion, J.L. & Coon, M.J. Purified liver microsomal NADPH–cytochrome P-450 reductase: spectral characterization of oxidation-reduction states. J. Biol. Chem. 253, 2694–2704 (1978).
Guengerich, F.P. & Martin, M.V. Purification of cytochrome P-450, NADPH–cytochrome P-450 reductase, and epoxide hydratase from a single preparation of rat liver microsomes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys, 205, 365–379 (1980).
Acknowledgements
The research on cytochrome P450 and NADPH–P450 reductase in this laboratory is supported by United States Public Health Service Grant no. R37 CA090426. We thank K. Trisler for her assistance in preparation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.P.G. and M.V.M. optimized the assays. F.P.G. wrote most of the paper, with the assistance of M.V.M. and C.D.S. Q.C. checked the protocols and participated in some of the optimization steps.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guengerich, F., Martin, M., Sohl, C. et al. Measurement of cytochrome P450 and NADPH–cytochrome P450 reductase. Nat Protoc 4, 1245–1251 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.121
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.121
This article is cited by
-
Heterologous expression in E. coli and functional characterization of the tomato CPR enzymes
Applied Biological Chemistry (2023)
-
Engineered cytochrome P450 for direct arylalkene-to-ketone oxidation via highly reactive carbocation intermediates
Nature Catalysis (2023)
-
Identification and characterization of cytochrome P450 CYP77A59 of loquat (Rhaphiolepis bibas) responsible for biosynthesis of phenylacetonitrile, a floral nitrile compound
Planta (2023)
-
Overexpression of chaperones GroEL/ES from Escherichia coli enhances indigo biotransformation production of cytochrome P450 BM3 mutant
Biotechnology Letters (2023)
-
Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) biodegradation by Purpureocillium lilacinum strain BA1S
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.