Abstract
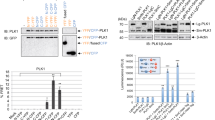
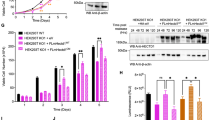
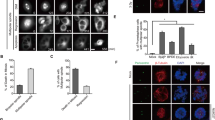
Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1), the best characterized member of the mammalian polo-like kinase family, is well regulated throughout the cell cycle at the protein expression level. Moreover, it is known that Plk1 kinase activity is also regulated at the post-translational level through phosphorylation. However, the upstream kinases of Plk1 have not been identified. Although the involvement of the p38 MAP kinase pathway in cellular responses to stress has been well documented, the role of this pathway in normal cell cycle progression is unclear. Here, we show that phosphorylated p38 and MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) are colocalized with Plk1 to the spindle poles during prophase and metaphase. Specific depletion of various members of the p38 MAP kinase pathway by the use of RNA interference revealed that the pathway is required for mitotic progression under normal growth conditions. Furthermore, MK2 directly phosphorylates Ser326 of Plk1. Ectopic expression of Plk1-S326A completely blocked cells at mitosis, likely due to the defect of bipolar spindle formation and subsequent activation of the spindle checkpoint. Only Plk1-S326E, but not the Plk1-S326A, efficiently rescued the p38 or MK2-depletion-induced mitotic defects, further solidifying the requirement of S326 phosphorylation during mitotic progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MK2:
-
MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 2
- Plk1:
-
polo-like kinase 1
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
References
Barr FA, Sillje HH, Nigg EA . (2004). Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 429–440.
Campos CB, Bedard PA, Linden R . (2002). Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase during normal mitosis in the developing retina. Neuroscience 112: 583–591.
Cha H, Wang X, Li H, Fornace AJ . (2007). A functional role for p38 MAPK in modulating mitotic transit in the absence of stress. J Biol Chem 282: 22984–22992.
Eckerdt F, Yuan J, Strebhardt K . (2005). Polo-like kinases and oncogenesis. Oncogene 24: 267–276.
Fan L, Yang X, Du J, Marshall M, Blanchard K, Ye X . (2005). A novel role of p38 alpha MAPK in mitotic progression independent of its kinase activity. Cell Cycle 4: 1616–1624.
Golsteyn RM, Schultz SJ, Bartek J, Ziemiecki A, Ried T, Nigg EA . (1994). Cell cycle analysis and chromosomal localization of human Plk1, a putative homologue of the mitotic kinases Drosophila polo and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc5. J Cell Sci 107 (Part 6): 1509–1517.
Knecht R, Elez R, Oechler M, Solbach C, von Ilberg C, Strebhardt K . (1999). Prognostic significance of polo-like kinase (PLK) expression in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res 59: 2794–2797.
Knecht R, Oberhauser C, Strebhardt K . (2000). PLK (polo-like kinase), a new prognostic marker for oropharyngeal carcinomas. Int J Cancer 89: 535–536.
Li H, Wang Y, Liu X . (2008). Plk1-dependent phosphorylation regulates functions of DNA topoisomerase IIalpha in cell cycle progression. J Biol Chem 283: 6209–6221.
Lindon C, Pines J . (2004). Ordered proteolysis in anaphase inactivates Plk1 to contribute to proper mitotic exit in human cells. J Cell Biol 164: 233–241.
Liu X, Erikson RL . (2002). Activation of Cdc2/cyclin B and inhibition of centrosome amplification in cells depleted of Plk1 by siRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 8672–8676.
Liu X, Erikson RL . (2003). Polo-like kinase (Plk)1 depletion induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 5789–5794.
Lowery DM, Lim D, Yaffe MB . (2005). Structure and function of Polo-like kinases. Oncogene 24: 248–259.
Manke IA, Nguyen A, Lim D, Stewart MQ, Elia AE, Yaffe MB . (2005). MAPKAP kinase-2 is a cell cycle checkpoint kinase that regulates the G2/M transition and S phase progression in response to UV irradiation. Mol Cell 17: 37–48.
Mikhailov A, Shinohara M, Rieder CL . (2004). Topoisomerase II and histone deacetylase inhibitors delay the G2/M transition by triggering the p38 MAPK checkpoint pathway. J Cell Biol 166: 517–526.
Mulvihill DP, Petersen J, Ohkura H, Glover DM, Hagan IM . (1999). Plo1 kinase recruitment to the spindle pole body and its role in cell division in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Biol Cell 10: 2771–2785.
Olson JM, Hallahan AR . (2004). p38 MAP kinase: a convergence point in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med 10: 125–129.
Petersen J, Hagan IM . (2005). Polo kinase links the stress pathway to cell cycle control and tip growth in fission yeast. Nature 435: 507–512.
Shirayama M, Zachariae W, Ciosk R, Nasmyth K . (1998). The Polo-like kinase Cdc5p and the WD-repeat protein Cdc20p/fizzy are regulators and substrates of the anaphase promoting complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J 17: 1336–1349.
Sui G, Soohoo C, Affar EB, Gay F, Shi Y, Forrester WC et al. (2002). A DNA vector-based RNAi technology to suppress gene expression in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 5515–5520.
Takai N, Hamanaka R, Yoshimatsu J, Miyakawa I . (2005). Polo-like kinases (Plks) and cancer. Oncogene 24: 287–291.
Tang J, Erikson RL, Liu X . (2006a). Checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) is required for mitotic progression through negative regulation of polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 11964–11969.
Tang J, Erikson RL, Liu X . (2006b). Ectopic expression of Plk1 leads to activation of the spindle checkpoint. Cell Cycle 5: 2484–2488.
Zarubin T, Han J . (2005). Activation and signaling of the p38 MAP kinase pathway. Cell Res 15: 11–18.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Raymond Erikson, in whose laboratory the preliminary experiments were performed, for generously providing many cell lines and plasmids. We appreciate Eleanor Erikson, Xiaoyi Zhang and Hongchang Li for helpful discussions and critical reading of the paper. XL is a recipient of the Howard Temin Award from the National Cancer Institute (K01 CA114401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Yang, X. & Liu, X. Phosphorylation of Plk1 at Ser326 regulates its functions during mitotic progression. Oncogene 27, 6635–6645 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.262
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.262
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MAPKAPK2: the master regulator of RNA-binding proteins modulates transcript stability and tumor progression
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
SAPK pathways and p53 cooperatively regulate PLK4 activity and centrosome integrity under stress
Nature Communications (2013)
-
B-Myb switches from Cyclin/Cdk-dependent to Jnk- and p38 kinase-dependent phosphorylation and associates with SC35 bodies after UV stress
Cell Death & Disease (2013)
-
PI 3-kinase-dependent phosphorylation of Plk1–Ser99 promotes association with 14-3-3γ and is required for metaphase–anaphase transition
Nature Communications (2013)
-
TrkC Promotes Survival and Growth of Leukemia Cells Through Akt-mTOR-Dependent Up-Regulation of PLK-1 and Twist-1
Molecules and Cells (2013)