Abstract
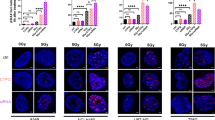
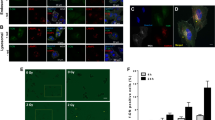
Drug metabolizing transgene products, which activate bioreductive cytotoxins, can be used to target treatment-resistant hypoxic tumors. The prodrug AQ4N is bioreduced in hypoxic cells by cytochrome P450s (CYPs) to the cytotoxin AQ4. Previously we have shown that intra-tumoral injection of CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 transgenes with AQ4N and radiation inhibits tumor growth. Here we examine the ability of other CYPs, in particular CYP1A1, to metabolize AQ4N, and to enhance radiosensitization. Metabolism of AQ4N was assessed using microsomes prepared from baculovirus-infected cells transfected with various CYP isoforms. AQ4N metabolism was most efficient with CYP1A1 (66.7 nmol/min/pmol) and 2B6 (34.4 nmol/min/pmol). Transient transfection of human CYP1A1±CYP reductase (CYPRED) was investigated in hypoxic RIF-1 mouse cells in vitro using the alkaline comet assay. There was a significant increase in DNA damage following transient transfection of CYP1A1 compared to non-transfected cells; inclusion of CYPRED provided no additional effect. In vivo, a single intra-tumoral injection of a CYP1A1 construct in combination with AQ4N (100 mg/kg i.p.) and 20 Gy X-rays caused a 16-day delay in tumor regrowth compared to tumors receiving AQ4N plus radiation and empty vector (P=0.0344). The results show the efficacy of a CYP1A1-mediated GDEPT strategy for bioreduction of AQ4N.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hockel M, Vaupel P . Biological consequences of tumor hypoxia. Semin Oncol 2001; 28: 36–41. asonc0280036e [pii].
Vaupel P, Harrison L . Tumor hypoxia: causative factors, compensatory mechanisms, and cellular response. Oncologist 2004; 9(Suppl 5): 4–9. 9/suppl_5/4 [pii]; 10.1634/theoncologist.9-90005-4 [doi].
Gandara DR, Lara Jr PN, Goldberg Z, Le QT, Mack PC, Lau DH et al. Tirapazamine: prototype for a novel class of therapeutic agents targeting tumor hypoxia. Semin Oncol 2002; 29: 102–109. asonc02901e0102 [pii].
Brown JM, Siim BG . Hypoxia-specific cytotoxins in Cancer Therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol 1996; 6: 22–36. 10.1053/SRAO0060022 [doi]; 00600022 [pii].
Stratford IJ, Williams KJ, Cowen RL, Jaffar M . Combining bioreductive drugs and radiation for the treatment of solid tumors. Semin Radiat Oncol 2003; 13: 42–52. 10.1053/srao.2003.50008 [doi]; S1053429603500078 [pii].
Patterson LH, Murray GI . Tumour cytochrome P450 and drug activation. Curr Pharm Des 2002; 8: 1335–1347.
Patterson LH, McKeown SR, Ruparelia K, Double JA, Bibby MC, Cole S et al. Enhancement of chemotherapy and radiotherapy of murine tumours by AQ4N, a bioreductively activated anti-tumour agent. Br J Cancer 2000; 82: 1984–1990. S0007092000911637 [pii]; 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1163 [doi].
Patterson LH, McKeown SR . AQ4N: a new approach to hypoxia-activated cancer chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 2000; 83: 1589–1593. 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1564 [doi]; S0007092000915647 [pii].
Patterson LH, McKeown SR, Robson T, Gallagher R, Raleigh SM, Orr S . Antitumour prodrug development using cytochrome P450 (CYP) mediated activation. Anticancer Drug Des 1999; 14: 473–486.
Friery OP, Gallagher R, Murray MM, Hughes CM, Galligan ES, McIntyre IA et al. Enhancement of the anti-tumour effect of cyclophosphamide by the bioreductive drugs AQ4N and tirapazamine. Br J Cancer 2000; 82: 1469–1473. S0007092099911321 [pii]; 10.1054/bjoc.1999.1132 [doi].
Gallagher R, Hughes CM, Murray MM, Friery OP, Patterson LH, Hirst DG et al. The chemopotentiation of cisplatin by the novel bioreductive drug AQ4N. Br J Cancer 2001; 85: 625–629. 10.1054/bjoc.2001.1975 [doi]; S0007092001919755 [pii].
Newell DR, Searle KM, Westwood NB, Burtles SS, Cancer Research UK Phase I/II Clinical Trials Committee. Professor Tom Connors and the development of novel cancer therapies by the Phase I/II Clinical Trials Committee of Cancer Research UK. Br J Cancer 2003; 89: 437–454. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601106 [doi]; 6601106 [pii].
Benghiat A, Steward WP, Loadman PM, Middleton D, Talbot D . Phase I dose escalation study of AQ4N, a selective hypoxic cell cytotoxin, with fractionated radiotherapy – first report. American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting, Orlando, Florida, March 27–31, 2004.
Cowen RL, Williams KJ, Chinje EC, Jaffar M, Sheppard FC, Telfer BA et al. Hypoxia targeted gene therapy to increase the efficacy of tirapazamine as an adjuvant to radiotherapy: reversing tumor radioresistance and effecting cure. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 1396–1402.
Jounaidi Y, Waxman DJ . Combination of the bioreductive drug tirapazamine with the chemotherapeutic prodrug cyclophosphamide for P450/P450-reductase-based cancer gene therapy. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 3761–3769.
Raleigh SM, Wanogho E, Burke MD, McKeown SR, Patterson LH . Involvement of human cytochromes P450 (CYP) in the reductive metabolism of AQ4N, a hypoxia activated anthraquinone di-N-oxide prodrug. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1998; 42: 763–767. S0360301698003083 [pii].
Raleigh SM, Wanogho E, Burke MD, Patterson LH . Rat cytochromes P450 (CYP) specifically contribute to the reductive bioactivation of AQ4N, an alkylaminoanthraquinone-di-N-oxide anticancer prodrug. Xenobiotica 1999; 29: 1115–1122.
McCarthy HO, Yakkundi A, McErlane V, Hughes CM, Keilty G, Murray M et al. Bioreductive GDEPT using cytochrome P450 3A4 in combination with AQ4N. Cancer Gene Ther 2003; 10: 40–48. 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700522 [doi]; 7700522 [pii].
McErlane V, Yakkundi A, McCarthy HO, Hughes CM, Patterson LH, Hirst DG et al. A cytochrome P450 2B6 meditated gene therapy strategy to enhance the effects of radiation or cyclophosphamide when combined with the bioreductive drug AQ4N. J Gene Med 2005; 7: 851–859. 10.1002/jgm.728 [doi].
Twentyman PR, Brown JM, Gray JW, Franko AJ, Scoles MA, Kallman RF . A new mouse tumor model system (RIF-1) for comparison of end-point studies. J Natl Cancer Inst 1980; 64: 595–604.
Swaine DJ, Loadman PM, Bibby MC, Graham MA, Patterson LH . High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of AQ4N, an alkylaminoanthraquinone N-oxide. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 2000; 742: 239–245.
Moulder JE, Rockwell S . Hypoxic fractions of solid tumors: experimental techniques, methods of analysis, and a survey of existing data. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1984; 10: 695–712.
Murata R, Shibamoto Y, Sasai K, Oya N, Shibata T, Takagi T et al. Reoxygenation after single irradiation in rodent tumours of different types and sizes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1996; 34: 859–865.
Chen L, Yu LJ, Waxman DJ . Potentiation of cytochrome P450/cyclophosphamide-based cancer gene therapy by coexpression of the P450 reductase gene. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 4830–4837.
Ding S, Yao D, Burchell B, Wolf CR, Friedberg T . High levels of recombinant CYP3A4 expression in Chinese hamster ovary cells are modulated by coexpressed human P450 reductase and hemin supplementation. Arch Biochem Biophys 1997; 348: 403–410. S0003986197904057 [pii].
Patterson LH . Rationale for the use of aliphatic N-oxides of cytotoxic anthraquinones as prodrug DNA binding agents: a new class of bioreductive agent. Cancer Metastasis Rev 1993; 12: 119–134.
Hukkanen J, Hakkola J, Anttila S, Piipari R, Karjalainen A, Pelkonen O et al. Detection of mRNA encoding xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome P450s in human bronchoalveolar macrophages and peripheral blood lymphocytes. Mol Carcinog 1997; 20: 224–230. 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2744(199710)20:2<224::AID-MC9>3.0.CO;2-M [pii].
Hukkanen J, Pelkonen O, Hakkola J, Raunio H . Expression and regulation of xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes in human lung. Crit Rev Toxicol 2002; 32: 391–411.
Hakkola J, Pasanen M, Pelkonen O, Hukkanen J, Evisalmi S, Anttila S et al. Expression of CYP1B1 in human adult and fetal tissues and differential inducibility of CYP1B1 and CYP1A1 by Ah receptor ligands in human placenta and cultured cells. Carcinogenesis 1997; 18: 391–397.
Hakkola J, Pasanen M, Hukkanen J, Pelkonen O, Maenpaa J, Edwards RJ et al. Expression of xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome P450 forms in human full-term placenta. Biochem Pharmacol 1996; 51: 403–411. 0006295295021841 [pii].
Pasanen M . The expression and regulation of drug metabolism in human placenta. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 1999; 38: 81–97. S0169409X99000083 [pii].
Wei C, Cacavale RJ, Kehoe JJ, Thomas PE, Iba MM . CYP1A2 is expressed along with CYP1A1 in the human lung. Cancer Lett 2001; 164: 25–32. S0304383500007126 [pii].
Leung YK, Lau KM, Mobley J, Jiang Z, Ho SM . Overexpression of cytochrome P450 1A1 and its novel spliced variant in ovarian cancer cells: alternative subcellular enzyme compartmentation may contribute to carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 3726–3734. 65/9/3726 [pii]; 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3771 [doi].
Baumhakel M, Kasel D, Rao-Schymanski RA, Bocker R, Beckurts KT, Zaigler M et al. Screening for inhibitory effects of antineoplastic agents on CYP3A4 in human liver microsomes. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2001; 39: 517–528.
Harris JW, Rahman A, Kim BR, Guengerich FP, Collins JM . Metabolism of taxol by human hepatic microsomes and liver slices: participation of cytochrome P450 3A4 and an unknown P450 enzyme. Cancer Res 1994; 54: 4026–4035.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from Cancer Research UK. AQ4N was kindly supplied by KuDOS Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yakkundi, A., McErlane, V., Murray, M. et al. Tumor-selective drug activation: a GDEPT approach utilizing cytochrome P450 1A1 and AQ4N. Cancer Gene Ther 13, 598–605 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700933
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700933