Abstract
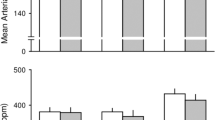
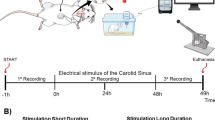
This study was conducted to show the effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model. Fifteen 12-week-old male Wistar Kyoto rats were used. The intracavernous pressure and arterial blood pressure were simultaneously monitored through electric cavernous nerve stimulation before and after the administration of sildenafil (2 mg/kg). Statistical analysis was performed on maximal intracavernous pressure (MIP), mean arterial blood pressure (MAP), the MIP/MAP and detumescence time. MAP decreased significantly by about 20 mmHg after sildenafil administration. The MIP/MAP increased significantly after sildenafil administration. The effect of sildenafil on the MIP/MAP was marked especially at lower (2–3 Hz) frequencies. The detumescence time significantly increased after sildenafil administration. We have shown that sildenafil is effective for enhancing erection at lower frequencies and prolonging penile erection in rats. After the administration of sildenafil, penile erection would be induced by weak stimuli that will not cause penile erection under normal conditions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boolell M et al. Sildenafil: an orally active type 5 cyclic GMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the treatment of penile erectile dysfunction Int J Impot Res 1996 8: 47–52
Goldstein I et al. Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction New Engl J Med 1998 338: 1397–1404
Quinlan DM et al. The rat as a model for the study of penile erection J Urol 1989 141: 656–661
Mills TM, Wiedmeier VT, Stopper VS . Androgen maintenance of erectile function in the rat penis Biol Reprod 1992 46: 342–348
Martinez-Pineiro L et al. Rat model for the study of penile erection: pharmacologic and electrical-stimulation parameters Eur Urol 1994 25: 62–70
Zvara P et al. Nitric oxide mediated erectile activity is a testosterone dependent event: a rat erection model Int J Impot Res 1995 7: 209–219
Penson DF et al. Androgen and pituitary control of penile nitric oxide synthase and erectile function in the rat Biol Reprod 1996 55: 567–574
ƶusman RM et al. Overall cardiovascular profile of sildenafil citrate Am J Cardiol 1999 83: 35C–44C
Walker DK et al. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of sildenafil in mouse, rat, rabbit, dog and man Xenobiotica 1999 29: 297–310
Jackson G et al. Effects of sildenafil citrate on human hemodynamics Am J Cardiol 1999 83: 13C–20C
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueno, N., Iwamoto, Y., Segawa, N. et al. The effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model. Int J Impot Res 14, 251–255 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900860
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900860
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Yohimbine enhances the effect of sildenafil on erectile process in rats
International Journal of Impotence Research (2008)
-
Animal models in urological disease and sexual dysfunction
British Journal of Pharmacology (2006)