Abstract
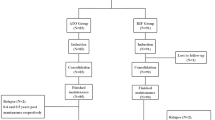
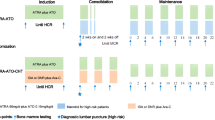
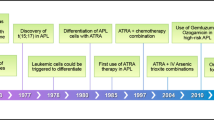
Twenty cases of patients with relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) were entered into this study for evaluating the clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics of low-dose arsenic trioxide (As2O3). As2O3 was given at a daily dose of 0.08 mg/kg intravenously for 28 days. Pharmacokinetic study was carried out in eight patients. 16/20 (80%) patients achieved CR. The occurrence of some toxic events including gastrointestinal disturbance, facial edema and cardiac toxicity seemed reduced in the low-dose group than those in the standard-dose group. Differentiation changes were observed in peripheral blood, as well as in bone marrow (BM). Pharmacokinetic study showed that the plasma concentration increased soon after administration of As2O3 with the peak values of 1.535–3.424 μmol/l. After infusion, the plasma concentration was around 0.1–0.5 μmol/l. The arsenic concentration of the plasma of BM aspirates 24 h after administration in five patients was close to the level needed for differentiation-inducing effect. The estimated 2-year OS and RFS were 61.55 ± 15.79% and 49.11 ± 15.09% respectively, with no difference as compared with those in patients treated with conventional dose (P = 0.2865 and 0.7146, respectively). In conclusion, we demonstrated that low-dose As2O3 had the same effect as the conventional dosage and the mechanism of low-dose arsenic seemed to primarily induce differentiation of APL cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tallman MS . Therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia: all-trans retinoic acid and beyond Leukemia 1998 12: (Suppl. 1) S37–S40
Chen Z, Wang ZY, Chen SJ . Acute promyelocytic leukemia: cellular and molecular basis of differentiation and apoptosis Pharmacol Ther 1997 76: 141–149
Andre C, Guillemin MC, Zhu J, Koken MH, Quignon F, Herve L, Chelbi-Alix MK, Dhumeaux D, Wang ZY, Degos L, Chen Z, de Thé H . The PML and PML/RARalpha domains: from autoimmunity to molecular oncology and from retinoic acid to arsenic Exp Cell Res 1996 229: 253–260
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM, Qiu QY, Zhu J, Tang W, Sun GL, Yang KQ, Chen Y, Zhou L, Fang ZW, Wang YT, Ma J, Zhang P, Zhang TD, Chen SJ, Chen Z, Wang ZY . Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): II. Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients Blood 1997 89: 3354–3360
Hu J, Shen ZX, Sun GL, Chen SJ, Wang ZY, Chen Z . Long-term survival and prognostic study in acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with all-trans-retinoic acid, chemotherapy, and As203: an experience of 120 patients at a single institution Int J Hematol 1999 70: 248–260
Slack JL, Rusiniak ME . Current issues in the management of acute promyelocytic leukemia Ann Hematol 2000 79: 227–238
Soignet SL, Maslak P, Wang ZG, Jhanwar S, Calleja E, Dardashti LJ, Corso D, DeBlasio A, Gabrilove J, Scheinberg DA, Pandolfi PP, Warrell RP Jr . Complete remission after treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide N Engl J Med 1998 339: 1341–1348
Kitamura K, Kiyoi H, Yoshida H, Tobita T, Takeshita A, Ohno R, Naoe T . New retinoids and arsenic compounds for the treatment of refractory acute promyelocytic leukemia: clinical and basic studies for the next generation Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1997 40: (Suppl) S36–S41
Chen GQ, Shi XG, Tang W, Xiong SM, Zhu J, Cai X, Han ZG, Ni JH, Shi GY, Jia PM, Liu MM, He KL, Niu C, Ma J, Zhang P, Zhang TD, Paul P, Naoe T, Kitamura K, Miller W, Waxman S, Wang ZY, de The H, Chen SJ, Chen Z . Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): I. As2O3 experts dose-dependent dual effects on APL cells Blood 1997 89: 3345–3353
Tang W, Chen G, Shi G . Double effects of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) on acute promyelocytic leukemic cell line Chung Hua I Hsueh Tsa Chih 1997 77: 509–512
Huang SY, Chang CS, Tang JL, Tien HF, Kuo TL, Huang SF, Yao YT, Chou WC, Chung CY, Wang CH, Shen MC, Chen YC . Acute and chronic arsenic poisoning associated with treatment of acute promyelocytic leukaemia Br J Haematol 1998 103: 1092–1095
Niu C, Yan H, Yu T, Sun HP, Liu JX, Li XS, Wu W, Zhang FQ, Chen Y, Zhou L, Li JM, Zeng XY, Yang RR, Yuan MM, Ren MY, Gu FY, Cao Q, Gu BW, Su XY, Chen GQ, Xiong SM, Zhang Td, Waxman S, Wang ZY, Chen SJ . Studies on treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide: remission induction, follow-up, and molecular monitoring in 11 newly diagnosed and 47 relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia patients Blood 1999 94: 3315–3324
Chen GQ, Zhu J, Shi XG, Ni JH, Zhong HJ, Si GY, Jin XL, Tang W, Li XS, Xong SM, Shen ZX, Sun GL, Ma J, Zhang P, Zhang TD, Gazin C, Naoe T, Chen SJ, Wang ZY, Chen Z . In vitro studies on cellular and molecular mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia: As2O3 induces NB4 cell apoptosis with downregulation of Bcl-2 2 expression and modulation of PML-RAR alpha/PML proteins Blood 1996 88: 1052–1061
Zhu J, Guo WM, Yao YY, Zhao WL, Pan L, Cai X, Ju B, Sun GL, Wang HL, Chen SJ, Chen GQ, Caen J, Chen Z, Wang ZY . Tissue factors on acute promyelocytic leukemia and endothelial cells are differently regulated by retinoic acid, arsenic trioxide and chemotherapeutic agents Leukemia 1999 13: 1062–1070
Tallman MS . The thrombophilic state in acute promyelocytic leukemia Semin Thromb Hemost 1999 25: 209–215
Shao W, Fanelli M, Ferrara FF, Riccioni R, Rosenauer A, Davison K, Lamph WW, Waxman S, Pelicci PG, Lo Coco F, Avvisati G, Testa U, Peschle C, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Nervi C, Miller WH Jr . Arsenic trioxide as an inducer of apoptosis and loss of PML/RAR alpha protein in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells J Natl Cancer Inst 1998 90: 124–133
Sternsdorf T, Puccetti E, Jensen K, Hoelzer D, Will H, Ottmann OG, Ruthardt M . PIC-1/SUMO-1-modified PML-retinoic acid receptor alpha mediates arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia Mol Cell Biol 1999 19: 5170–5178
Lallemand-Breitenbach V, Guillemin MC, Janin A, Daniel MT, Degos L, Kogan SC, Bishop JM, de Thé H . Retinoic acid and arsenic synergize to eradicate leukemic cells in a mouse model of acute promyelocytic leukemia J Exp Med 1999 189: 1043–1052
Koken MH, Daniel MT, Gianni M, Zelent A, Licht J, Buzyn A, Minard P, Degos L, Varet B, de Thé H . Retinoic acid, but not arsenic trioxide, degrades the PLZF/RA Ralpha fusion protein, without inducing terminal differentiation or apoptosis, in a RA-therapy resistant t(11;17)(q23;q21) APL patient Oncogene 1999 18: 1113–1118
Jing Y, Dai J, Chalmers-Redman RM, Tatton WG, Waxman S . Arsenic trioxide selectively induces acute promyelocytic leukemia cell apoptosis via a hydrogen peroxide-dependent pathway Blood 1999 94: 2102–2111
Wang ZG, Rivi R, Delva L, Konig A, Scheinberg DA, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Gabrilove JL, Warrell RP Jr . Pandolfi PP. Arsenic trioxide and melarsoprol induce programmed cell death in myeloid leukemia cell lines and function in a PML and PML-RARalpha independent manner Blood 1998 92: 1497–1504
Zhu XH, Shen YL, Jing YK, Cai X, Jia PM, Huang Y, Tang W, Shi GY, Sun YP, Dai J, Wang ZY, Chen SJ, Zhang TD, Waxman S, Chen Z, Chen GQ . Apoptosis and growth inhibition in malignant lymphocytes after treatment with arsenic trioxide at clinically achievable concentrations J Natl Cancer Inst 1999 91: 772–778
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Clyde Wu Foundation of Shanghai Institute of Hematology. The authors thank all members of Shanghai Institute of Hematology for providing patient samples and clinical data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., Shen, ZX., Yan, H. et al. Studies on the clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics of low-dose arsenic trioxide in the treatment of relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia: a comparison with conventional dosage. Leukemia 15, 735–741 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402106
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402106
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Combinatorial Effect of Arsenic and Herbal Compounds in Telomerase-Mediated Apoptosis Induction in Liver Cancer
Biological Trace Element Research (2023)
-
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: A History over 60 Years—From the Most Malignant to the most Curable Form of Acute Leukemia
Oncology and Therapy (2019)
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics and safety profile of single agent arsenic trioxide by continuous slow-rate infusion in patients with newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2018)
-
The evolving use of arsenic in pharmacotherapy of malignant disease
Annals of Hematology (2013)
-
Management of elderly patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia: progress and problems
Annals of Hematology (2013)