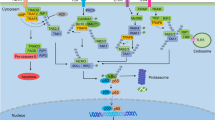
Abstract
The NF-κB2/p100 and bcl-3 genes are involved in chromosomal translocations described in chronic lymphocytic leukemias (CLL) and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-κB) protects cancer cells against apoptosis. Therefore, we investigated whether this transcription factor could modulate the expression of the Bcl-2 antiapoptotic protein. Bcl-2 promoter analysis showed multiple putative NF-κB binding sites. Transfection assays of bcl-2 promoter constructs in HCT116 cells showed that NF-κB can indeed transactivate bcl-2. We identified a κB site located at position −180 that can only be bound and transactivated by p50 or p52 homodimers. As p50 and p52 homodimers are devoid of any transactivating domains, we showed that they can transactivate the bcl-2 promoter through association with Bcl-3. We also observed that stable overexpression of p100 and its processed product p52 can induce endogenous Bcl-2 expression in MCF7AZ breast cancer cells. Finally, we demonstrated that, in breast cancer and leukemic cells (CLL), high NF-κB2/p100 expression was associated with high Bcl-2 expression. Our data suggest that Bcl-2 could be an in vivo target gene for NF-κB2/p100.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA, Lowe SW . Apoptosis: a link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell 2002; 108: 153–164.
Reed JC . Dysregulation of apoptosis in cancer. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 2941–2953.
Beg AA, Baltimore D . An essential role for NF-kappaB in preventing TNF-alpha-induced cell death. Science 1996; 274: 782–784.
Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Kafri T, Green DR, Verma IM . Suppression of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB. Science 1996; 274: 787–789.
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Baldwin AS . TNF- and cancer therapy induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Science 1996; 274: 784–787.
Bargou RC, Emmerich F, Krappmann D, Bommert K, Mapara MY, Arnold W et al. Constitutive nuclear factor-kappaB-RelA activation is required for proliferation and survival of Hodgkin's disease tumor cells. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 2961–2969.
Bentires-Alj M, Hellin AC, Ameyar M, Chouaib S, Merville MP, Bours V . Stable inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB in cancer cells does not increase sensitivity to cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 811–815.
Baldwin AS . The NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 1996; 14: 649–681.
Rayet B, Gélinas C . Aberrant rel/nfkb genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene 1999; 18: 6938–6947.
Garg A, Aggarwal BB . Nuclear transcription factor-kappaB as a target for cancer drug development. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1053–1068.
Neri A, Chang CC, Lombardi L, Salina M, Corradini P, Maiolo AT et al. B cell lymphoma-associated chromosomal translocation involves candidate oncogene lyt-10, homologous to NF-kappaB p50. Cell 1991; 67: 1075–1087.
Franzoso G, Carlson L, Poljak L, Shores EW, Epstein S, Leonardi A et al. Mice deficient in nuclear factor (NF)-kappa B/p52 present with defects in humoral responses, germinal center reactions, and splenic microarchitecture. J Exp Med 1998; 187: 147–159.
Fujita T, Nolan GP, Liou HC, Scott ML, Baltimore D . The candidate proto-oncogene bcl-3 encodes a transcriptional coactivator that activates through NF-kappaB p50 homodimers. Genes Dev 1993; 7: 1354–1363.
Bours V, Franzoso G, Azarenko V, Park S, Kanno T, Brown K et al. The oncoprotein Bcl-3 directly transactivates through kappaB motifs via association with DNA binding p50B homodimers. Cell 1993; 72: 729–739.
Ohno H, Takimoto G, Mc Keithan T . The candidate proto oncogene bcl-3 is related to genes implicated in cell lineage determination and cell cycle control. Cell 1990; 60: 991–997.
Franzoso G, Carlson L, Scharton-Kersten T, Shores EW, Epstein S, Grinberg A et al. Critical role for the Bcl-3 oncoprotein in T-cell mediated immunity, splenic microarchitecture, and germinal center reactions. Immunity 1997; 6: 479–490.
Schwarz EM, Krimpenfort P, Berns A, Verma IM . Immunological defects in mice with a targeted disruption in Bcl-3. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 187–197.
Tiong Ong S, Hackbarth ML, Degenstein LC, Baunoch DA, Anastasi J, McKeithan T . Lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and altered immunoglobulin production in Bcl-3 transgenic mice. Oncogene 1998; 16: 2333–2433.
Pan J, McEver RP . Regulation of the human P-selectin promoter by Bcl-3 and specific homodimeric members of the NF-kappa B/Rel family. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 23077–23083.
Westerheide SD, Mayo MW, Anest V, Hanson JL, Baldwin AS . The putative oncoprotein Bcl-3 induces Cyclin D1 to stimulate G1 transition. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 8428–8436.
Mitchell TC, Hildeman D, Kedl RM, Teague TK, Schaefer BC, White J et al. Immunological adjuvants promote activated T cell survival via induction of Bcl-3. Nat Immunol 2001; 2: 397–402.
Tsujimoto Y, Croce CM . Analysis of the structure, transcripts, and protein products of bcl-2, the gene involved in human follicular lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986; 83: 5214–5218.
Seto M, Jaeger U, Hockett RD, Graninger W, Bennett S, Goldman P et al. Alternative promoters and exons, somatic mutation and deregulation of the Bcl-2-Ig fusion gene in lymphoma. EMBO J 1988; 7: 123–131.
Chen HM, Boxer LM . Pi 1 binding sites are negative regulators of bcl-2 expression in pre-B cells. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15: 3840–3847.
Heckman C, Mochon E, Arcinas M, Boxer LM . The WT1 protein is a negative regulator of the normal bcl-2 allele in t(14;18) lymphomas. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 19609–19614.
Dong L, Wang W, Wang F, Stoner M, Reed JC, Harigai M et al. Mechanisms of transcriptional activation of bcl-2 gene expression by 17beta-estradiol in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 32099–32107.
Mayo MW, Wang CY, Drouin SS, Madrid LV, Marshall AF, Reed JC et al. WT1 modulates apoptosis by transcriptionally upregulating the bcl-2 proto-oncogene. EMBO J 1999; 18: 3990–4003.
Young RL, Korsmeyer SJ . A negative regulatory element in the bcl-2 5′-untranslated region inhibits expression from an upstream promoter. Mol Cell Biol 1993; 13: 3686–3697.
Bours V, Burd PR, Brown K, Villalobos J, Park S, Ryseck RP et al. A novel mitogen inducible gene product related to p50/p105-NF-kappaB participates in transactivation through a kappaB site. Mol Cell Biol 1992; 12: 685–695.
Kurland JF, Kodym R, Story MD, Spurgers KB, McDonnell TJ, Meyn RE . NF-kB1 (p50) homodimers contribute to transcription of the bcl-2 oncogene. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 45380–45386.
Cogswell PC, Guttridge DC, Funkhouser WK, Baldwin AS . Selective activation of NF-kappaB subunits in human breast cancer: potential roles for NF-kappaB2/p52 and for Bcl-3. Oncogene 2000; 19: 1123–1131.
Dejardin E, Bonizzi G, Bellahcene A, Castronovo V, Merville M-P, Bours V . Highly expressed p100/p52 (NFKB2) sequesters other NF-kappaB related proteins in the cytoplasm of human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 1995; 11: 1835–1841.
Stehlik C, de Martin R, Kumabashiri I, Schmid JA, Binder BR, Lipp J . Nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB-regulated X chromosome-linked iap gene expression protects endothelial cells from tumor necrosis factor alpha induced apoptosis. J Exp Med 1998; 188: 211–216.
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin AS . NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase 8 activation. Science 1998; 281: 1680–1683.
Krikos A, Laherty CD, Dixit VM . Transcriptional activation of the tumor necrosis factor alpha-inducible zinc finger protein, A20, is mediated by kappaB elements. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 17971–17976.
Jones PL, Ping D, Boss JM . Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1beta regulate the murine manganese superoxide dismutase gene through a complex intronic enhancer involving C/EBP-beta and NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 6970–6981.
Dixon EP, Stephenson DT, Clemens JA, Little SP . Bcl-Xshort is elevated following severe global ischemia in rat brains. Brain Res 1997; 776: 222–229.
Chen F, Demers LM, Vallyathan V, Lu Y, Castranova V, Shi X . Involvement of 5′-flanking kappaB-like sites within bcl-x gene in silica-induced Bcl-x expression. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 35591–35595.
Grumont RJ, Rourke IJ, Gerondakis S . Rel-dependent induction of A1 transcription is required to protect B cells from antigen receptor ligation induced apoptosis. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 400–411.
Tamatani M, Che YH, Matsuzaki H, Ogawa S, Okado H, Miyake S et al. Tumor necrosis factor induces Bcl-2 and Bcl-x expression through NFkappaB activation in primary hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 8531–8538.
Tsukahara T, Kannagi M, Ohashi T, Kato H, Arai M, Nunez G et al. Induction of Bcl-x(L) expression by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax through NF-kappaB in apoptosis-resistant T-cell transfectants with Tax. J Virol 1999; 73: 7981–7987.
Wang CY, Guttridge DC, Mayo MW, Baldwin AS . NF-kappaB induces expression of the Bcl-2 homologue A1/Bfl1 to preferentially suppress chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 5923–5929.
Zong WX, Edelstein LC, Chen C, Bash J, Gelinas C . The prosurvival Bcl-2 homologue Bfl-1/A1 is a direct transcriptional target of NF-kappaB that blocks TNFalpha induced apoptosis. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 382–387.
Bentires-Alj M, Dejardin E, Viatour P, Van Lint C, Froesch B, Reed JC et al. Inhibition of the NF-kappaB transcription factor increases Bax expression in cancer cell lines. Oncogene 2001; 20: 2805–2813.
Rowe M, Peng-Pilon M, Huen DS, Hardy R, Croom-Carter D, Lundge-ren E et al. Upregulation of bcl-2 by the Epstein–Barr virus latent membrane protein LMP1: a B-cell-specific response that is delayed relative to NF-kappaB activation and to induction if cell surface markers. J Virol 1994; 68: 5602–5612.
Feng Z, Porter AG . NF-kappaB/Rel proteins are required for neuronal differentiation of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 30341–30344.
Feuillard J, Schuhmacher M, Kohanna S, Asso-Bonnet M, Ledeur F, Joubert-Caron R et al. Inducible loss of NF-kappaB activity is associated with apoptosis and Bcl-2 down regulation in Epstein–Barr virus-transformed B lymphocytes. Blood 2000; 95: 2068–2075.
Davis RE, Brown KD, Siebenlist U, Staudt LM . Constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity is required for survival of activated B cell like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J Exp Med 2001; 194: 1861–1874.
Catz SD, Johnson JL . Transcriptional regulation of bcl-2 by nuclear factor kB and its significance in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2001; 20: 7342–7351.
Heckman CA, Mehew JW, Boxer LM . NF-kappaB activates Bcl-2 expression in t(14;18) lymphoma cells. Oncogene 2002; 21: 3898–3908.
Claudio E, Brown K, Park S, Wang H, Siebenlist U . BAFF-induced NEMO independent processing of NF-kappaB2 in maturing B cells. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 958–965.
Aviram A, Rabizadeh E, Zimra Y, Yeshoron M, Shaklai M, Bairey O . Expression of bcl-2 and bax in cells isolated from B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients at different stages of the disease. Eur J Haematol 2000; 64: 80–84.
Thomas A, Pepper C, Hoy T, Bentley P . Bcl-2 and bax expression and chlorambucil-induced apoptosis in the T-cells and leukaemic B-cells of untreated B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia patients. Leukemia Res 2000; 24: 813–821.
Faderl S, Keating MJ, Do KA, Kantarjan HM, O'Brien S, Garcia-Manero G et al. Expression profile of 11 proteins and their prognostic significance in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Leukemia 2002; 16: 1045–1052.
Furman RR, Asgary Z, Mascarenhas JO, Liou HC, Schattner EJ . Modulation of NF-kappaB activity and apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. J Immunol 2000; 164: 2200–2206.
Romano MF, Lamberti A, Turco MC, Venuta S . CD40 and B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell response to fludarabine: the influence of NF-kappaB/Rel transcription factors on chemotherapy-induced apoptosis? Leukemia Lymphoma 2000; 36: 255–262.
Coope HJ, Atkinson PG, Huhse B, Belich M, Janzen J, Holman MJ et al. CD40 regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 to p52. EMBO J 2002; 21: 5375–5385.
Munzert G, Kirchner D, Stobbe H, Bergmann L, Schmid RM, Dohner H et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1 gene overexpression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: analysis of NF-kappaB/Rel-regulated inhibitors of apoptosis. Blood 2002; 100: 3749–3756.
Sovak MA, Bellas RE, Kim DW, Zanieski GJ, Rogers AE, Traish AM et al. Aberrant nuclear factor-kappaB/Rel expression and the pathogenesis of breast cancer. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 2952–2960.
Nakshatri H, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Martin DA, Goulet RJ, Sledge GW . Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB during progression of breast cancer to hormone-independent growth. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 3629–3639.
Wood KM, Roff M, Hay RT . Defective IkappaBalpha in Hodgkin cell lines with constitutively active NF-kappaB. Oncogene 1998; 16: 2131–2139.
Krappmann D, Emmerich F, Kordes U, Scharschmidt E, Dorken B, Scheidereit C . Molecular mechanisms of constitutive NF-kappaB/Rel activation in Hodgkin/Reed–Sternberg cells. Oncogene 1999; 18: 943–953.
Wu M, Lee H, Bellas RE, Schauer SL, Arsura M, Katz D et al. Inhibition of NF-kappaB/Rel induces apoptosis of murine B cells. EMBO J 1996; 15: 4682–4690.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr U Siebenlist (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA) for his helpful comments on the manuscript, Dr L Boxer (Stanford, CA, USA) for the Bcl-2 Luc plasmids, Dr Hagemeijer (Leuven, Belgium) and Dr Lambert (CHU Liège, Belgium) for CLL samples. We are most thankful to Professor J Gielen (University of Liège, Belgium) for his continuous support during this work. M-P Merville, A Chariot and L de Leval are Research Associates at the National Foundation for Scientific Research (FNRS, Belgium). P Viatour, M Bentires-Alj and V Deregowski are supported by Télévie fellowships (FNRS, Belgium). This research was supported by grants from the ‘Centre Anti-Cancéreux’ (University of Liège, Belgium) and the FRSM (FNRS, Belgium).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viatour, P., Bentires-Alj, M., Chariot, A. et al. NF-κB2/p100 induces Bcl-2 expression. Leukemia 17, 1349–1356 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402982
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402982
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Paradoxical effects of statins on endothelial and cancer cells: the impact of concentrations
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Multiple roles for Bcl-3 in mammary gland branching, stromal collagen invasion, involution and tumor pathology
Breast Cancer Research (2022)
-
Calcium-binding protein S100P is a new target gene of MACC1, drives colorectal cancer metastasis and serves as a prognostic biomarker
British Journal of Cancer (2022)
-
Biological significance of monoallelic and biallelic BIRC3 loss in del(11q) chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression
Blood Cancer Journal (2021)
-
Simvastatin Prevents Long-Term Cognitive Deficits in Sepsis Survivor Rats by Reducing Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration
Neurotoxicity Research (2020)