Abstract
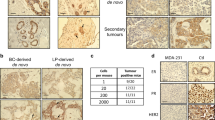
The human DF3/MUC1 mucin-like glycoprotein is aberrantly overexpressed by most carcinomas of the breast and other epithelia. The contribution of MUC1 overexpression to the malignant phenotype is, however, not known. In the present studies, we have stably expressed MUC1 in rat 3Y1 fibroblasts. MUC1-positive cells were selected from independent transfections. The results demonstrate that, as found in human carcinomas, MUC1 is expressed on the cell surface and as a complex with β-catenin in the nucleus of the transfectants. Colony formation in soft agar demonstrates that cells expressing MUC1, but not the empty vector, exhibit anchorage-independent growth. The results also show that MUC1 expression confers tumor formation in nude mice. These findings provide the first evidence that MUC1 induces cellular transformation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C and Darnell Jr JE . (1999). Cell, 98, 295–303.
Gendler S, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Duhig T, Rothbard J and Burchell JA . (1988). J. Biol. Chem., 263, 12820–12823.
Guilford P, Hopkins J, Harraway J, McLeod M, McLeod N, Harawira P, Taite H, Scoular R, Miller A and Reeve AE . (1998). Nature, 392, 402–405.
Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A, Ward E and Thun M . (2003). CA Cancer J. Clin., 53, 5–26.
Kintner C . (1992). Cell, 69, 225–236.
Kondo K, Kohno N, Yokoyama A and Hiwada K . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 2014–2019.
Kufe D, Inghirami G, Abe M, Hayes D, Justi-Wheeler H and Schlom J . (1984). Hybridoma, 3, 223–232.
Li Y, Bharti A, Chen D, Gong J and Kufe D . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 7216–7224.
Li Y, Chen W, Ren J, Yu W, Li Q, Yoshida K and Kufe D . (2003). Cancer Biol. Ther., 2, 187–193.
Li Y, Kuwahara H, Ren J, Wen G and Kufe D . (2001a). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 6061–6064.
Li Y, Ren J, Yu W-H, Li G, Kuwahara H, Yin L, Carraway KL and Kufe D . (2001b). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 35239–35242.
Ligtenberg M, Buijs F, Vos H and Hilkens J . (1992). Cancer Res., 52, 223–232.
Ren J, Li Y and Kufe D . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 17616–17622.
Shiozaki H, Oka H, Inoue M, Tamura S and Monden M . (1996). Cancer, 77, 1605–1613.
Siddiqui J, Abe M, Hayes D, Shani E, Yunis E and Kufe D . (1988). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 85, 2320–2323.
Vleminckx K, Vakaet LJ, Mareel M, Fiers W and van Roy F . (1991). Cell, 66, 107–119.
Yamamoto M, Bharti A, Li Y and Kufe D . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 12492–12494.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grant CA97098 awarded by the National Cancer Institute. The authors acknowledge Kamal Chauhan for excellent technical support. DK has a financial interest in ILEX.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Liu, D., Chen, D. et al. Human DF3/MUC1 carcinoma-associated protein functions as an oncogene. Oncogene 22, 6107–6110 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206732
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206732
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MUC1 is a potential target to overcome trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer therapy
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
MUC1-C regulates lineage plasticity driving progression to neuroendocrine prostate cancer
Nature Communications (2020)
-
AGR2-induced glucose metabolism facilitated the progression of endometrial carcinoma via enhancing the MUC1/HIF-1α pathway
Human Cell (2020)
-
MUC1-C represses the RASSF1A tumor suppressor in human carcinoma cells
Oncogene (2019)
-
MUC1-C activates polycomb repressive complexes and downregulates tumor suppressor genes in human cancer cells
Oncogene (2018)