Abstract
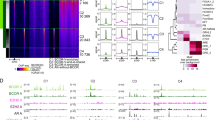
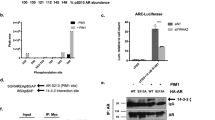
Recent reports suggest that the β-catenin-T-cell factor (Tcf) (BCT) signaling pathway is important in the progression of prostate cancer. Evidence suggests that the androgen receptor (AR) can repress BCT-mediated transcription both in prostate cancer and colon cancer cells (Chesire and Isaacs, 2002). In this study, we validate such findings and show that repression of BCT signaling is facilitated by competition between the AR and Tcf. Measurements of the Tcf transcriptional reporter (TOPFLASH) indicated that AR+DHT-mediated repression can inhibit BCT transcription in the presence of WT and exogenous activating β-catenin (Δ1–130 bp). Transient transfections in SW480 cells (APCmut/mut) showed that this mode of repression is functionally independent of APC-mediated β-catenin ubiquitination. Using a recently developed red flourescent protein (HcRed), we demonstrate novel observations about the nuclear distribution of Tcf. Furthermore, with the use of red (HcRed-AR and HcRed-Tcf) and green fusion proteins (β-catenin-EGFP), we provide morphological evidence of a reciprocal balance of nuclear β-catenin-EGFP (BC-EGFP). By cotransfecting in LNCaP prostate tumor cells and using quantitative imaging software, we demonstrated a 62.0% colocalization of HcRed-AR and BC-EGFP in the presence of DHT and 63.3% colocalization of HcRed-Tcf/BC-EGFP in the absence of DHT. Costaining for activated RNA Pol II (phosphoserine 2) and HcRed-Tcf suggested that Tcf foci contain transcriptional ‘hotspots’ validating that these sites have the capacity for transcriptional activity. Given this apparent androgen-dependent competition for nuclear BC-EGFP, we chose to assess our hypothesis by in vivo and in vitro binding assays. SW480 cells transiently transfected with an AR expression construct, treated with DHT and immunoprecipitated for Tcf showed less associated β-catenin when compared to Tcf precipitates from untreated cells. Furthermore, by treating cells with DHT+Casodex, we were able to abrogate the androgen-sensitive AR/β-catenin interaction, in addition to relieving transcriptional repression of the TOPFLASH reporter. In vitro binding assays, with increasing amounts of ARS35, resulted in decreased TcfS35 association with immunoprecipitated recombinant β-catenin-HIS. These data suggest that in steady-state conditions, AR has the ability to compete out Tcf binding for β-catenin. Finally, using SW480 cells, we show that AR-mediated repression of the BCT pathway has implications for cell cycle progression and in vitro growth. Using FACs analysis, we observed a 26.1% increase in accumulation of cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, while in vitro growth assays showed a 35% reduction in viable cells transfected with AR+DHT treatment. Together, our data strongly suggest that a reciprocal balance of nuclear β-catenin facilitates AR-mediated repression of BCT-driven transcription and cell growth.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker N, Morin PJ and Clevers H . (2000). Adv. Cancer Res., 77, 1–24.
Barnes DM and Gillett CE . (1998). Breast Cancer Res. Treat., 52, 1–15.
Cairns P, Okami K, Halachmi S, Halachmi N, Esteller M, Herman JG, Jen J, Isaacs WB, Bova GS and Sidransky D . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 4997–5000.
Carlsson P, Waterman ML and Jones KA . (1993). Genes Dev., 7, 2418–2430.
Catalano MG, Pfeffer U, Raineri M, Ferro P, Curto A, Capuzzi P, Corno F, Berta L and Fortunati N . (2000). Int. J. Cancer, 86, 325–330.
Chen RH and McCormick F . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 4445–4449.
Chesire DR, Ewing CM, Gage WR and Isaacs WB . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 2679–2694.
Chesire DR, Ewing CM, Sauvageot J, Bova GS and Isaacs WB . (2000). Prostate, 45, 323–334.
Chesire DR and Isaacs WB . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 8453–8469.
Damm K, Thompson CC and Evans RM . (1989). Nature, 339, 593–597.
Davies MA, Koul D, Dhesi H, Berman R, McDonnell TJ, McConkey D, Yung WK and Steck PA . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 2551–2556.
Easwaran V, Pishvaian M, Salimuddin and Byers S . (1999). Curr. Biol., 9, 1415–1418.
Giannini AL, Vivanco MM and Kypta RM . (2000). Exp. Cell. Res., 255, 207–220.
Gleave M, Hsieh JT, Gao CA, von Eschenbach AC and Chung LW . (1991). Cancer Res., 51, 3753–3761.
Helmbrecht K, Kispert A, von Wasielewski R and Brabant G . (2001). Endocrinology, 142, 5261–5266.
Ikonen T, Palvimo JJ and Janne OA . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 29821–29828.
Janne OA, Moilanen AM, Poukka H, Rouleau N, Karvonen U, Kotaja N, Hakli M and Palvimo JJ . (2000). Biochem. Soc. Trans., 28, 401–405.
Knop M, Barr F, Riedel CG, Heckel T and Reichel C . (2002). Biotechniques, 33, 592–594, 596–598 passim.
Knudsen KE, Cavenee WK and Arden KC . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 2297–2301.
Miller LD, Park KS, Guo QM, Alkharouf NW, Malek RL, Lee NH, Liu ET and Cheng SY . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 6626–6639.
Mulholland DJ, Cheng H, Reid K, Rennie PS and Nelson CC . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 17933–17943.
Pawlowski JE, Ertel JR, Allen MP, Xu M, Butler C, Wilson EM and Wierman ME . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 20702–20710.
Persad S, Troussard AA, McPhee TR, Mulholland DJ and Dedhar S . (2001). J. Cell. Biol., 153, 1161–1174.
Polakis P . (2001). Cell, 105, 563–566.
Quigley CA, De Bellis A, Marschke KB, el-Awady MK, Wilson EM and French FS . (1995). Endocr. Rev., 16, 271–321.
Rivera OJ, Song CS, Centonze VE, Lechleiter JD, Chatterjee B and Roy AK . (2003). Mol. Endocrinol., 17, 128–140.
Saitoh M, Takayanagi R, Goto K, Fukamizu A, Tomura A, Yanase T and Nawata H . (2002). Mol. Endocrinol., 16, 694–706.
Sap J, Munoz A, Schmitt J, Stunnenberg H and Vennstrom B . (1989). Nature, 340, 242–244.
Schulman IG, Juguilon H and Evans RM . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 3807–3813.
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Oren M, Levina E and Ben-Ze'ev A . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 5947–5954.
Simcha I, Shtutman M, Salomon D, Zhurinsky J, Sadot E, Geiger B and Ben-Ze'ev A . (1998). J. Cell. Biol., 141, 1433–1448.
Snoek R, Rennie PS, Kasper S, Matusik RJ and Bruchovsky N . (1996). J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 59(3–4), 243–250.
Song LN, Herrell R, Byers S, Shah S, Wilson EM and Gelmann EP . (2003). Mol. Cell. Biol., 23, 1674–1687.
Tomura A, Goto K, Morinaga H, Nomura M, Okabe T, Yanase T, Takayanagi R and Nawata H . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 28395–28401.
Truica CI, Byers S and Gelmann EP . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 4709–4713.
Yang F, Li X, Sharma M, Sasaki CY, Longo DL, Lim B and Sun Z . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 11336–11344.
Yeh S, Chang HC, Miyamoto H, Takatera H, Rahman M, Kang HY, Thin TH, Lin HK and Chang C . (1999). Keio. J. Med., 48, 87–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulholland, D., Read, J., Rennie, P. et al. Functional localization and competition between the androgen receptor and T-cell factor for nuclear β-catenin: a means for inhibition of the Tcf signaling axis. Oncogene 22, 5602–5613 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206802
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206802
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Delineating the role of nuclear receptors in colorectal cancer, a focused review
Discover Oncology (2024)
-
Tubular β-catenin alleviates mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death in acute kidney injury
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
The Glypican proteoglycans show intrinsic interactions with Wnt-3a in human prostate cancer cells that are not always associated with cascade activation
BMC Molecular and Cell Biology (2021)
-
TCF7 is suppressed by the androgen receptor via microRNA-1-mediated downregulation and is involved in the development of resistance to androgen deprivation in prostate cancer
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2017)
-
Nuclear expression of TCF4/TCF7L2 is correlated with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2016)