Abstract
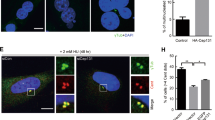
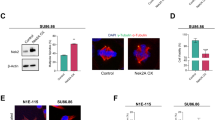
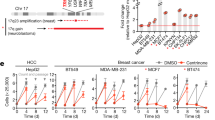
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) has been proposed to function as a master regulator of centrosome duplication. Using mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) in which Cdk2 has been genetically deleted, we show here that CDK2 is not required for normal centrosome duplication, maturation and bipolar mitotic spindle formation. In contrast, Cdk2 deficiency completely abrogates aberrant centrosome duplication induced by a viral oncogene. Mechanistically, centrosome overduplication in MEFs wild-type for Cdk2 involves the formation of supernumerary immature centrosomes. These results indicate that normal and abnormal centrosome duplication have significantly different requirements for CDK2 activity and point to a role of CDK2 in licensing centrosomes for aberrant duplication. Furthermore, our findings suggest that CDK2 may be a suitable therapeutic target to inhibit centrosome-mediated chromosomal instability in tumor cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht-Buehler G, Bushnell A . (1980). Exp Cell Res 126: 427–437.
Aleem E, Kiyokawa H, Kaldis P . (2005). Nat Cell Biol 7: 831–836.
Alvarez-Salas LM, Cullinan AE, Siwkowski A, Hampel A, DiPaolo JA . (1998). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 1189–1194.
Berthet C, Aleem E, Coppola V, Tessarollo L, Kaldis P . (2003). Curr Biol 13: 1775–1785.
Bornens M . (2002). Curr Opin Cell Biol 14: 25–34.
Brinkley BR . (2001). Trends Cell Biol 11: 18–21.
Chen Z, Indjeian VB, McManus M, Wang L, Dynlacht BD . (2002). Dev Cell 3: 339–350.
Delattre M, Gonczy P . (2004). J Cell Sci 117: 1619–1630.
Doxsey S . (2002). Mol Cell 10: 439–440.
Duensing A, Geng Y, Sicinski P, Munger K, Duensing S . (2004a). Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 45: 2596.
Duensing S . (2005). Cell Biol Int 29: 352–359.
Duensing S, Duensing A, Lee DC, Edwards KM, Piboonniyom S, Manuel E et al. (2004b). Oncogene 23: 8206–8215.
Duensing S, Lee LY, Duensing A, Basile J, Piboonniyom S, Gonzalez S et al. (2000). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 10002–10007.
Fisk HA, Winey M . (2001). Cell 106: 95–104.
Guarguaglini G, Duncan PI, Stierhof YD, Holmstrom T, Duensing S, Nigg EA . (2005). Mol Biol Cell 16: 1095–1107.
Hinchcliffe EH, Li C, Thompson EA, Maller JL, Sluder G . (1999). Science 283: 851–854.
Hinchcliffe EH, Sluder G . (2001). Genes Dev 15: 1167–1181.
Lacey KR, Jackson PK, Stearns T . (1999). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 2817–2822.
Mason DX, Jackson TJ, Lin AW . (2004). Oncogene 23: 9238–9246.
Matsumoto Y, Hayashi K, Nishida E . (1999). Curr Biol 9: 429–432.
Matsumoto Y, Maller JL . (2004). Science 306: 885–888.
Meijer L, Leclerc S, Leost M . (1999). Pharmacol Ther 82.
Meraldi P, Lukas J, Fry AM, Bartek J, Nigg EA . (1999). Nat Cell Biol 1: 88–93.
Munger K, Howley PM . (2002). Virus Res 89: 213–228.
Mussman JG, Horn HF, Carroll PE, Okuda M, Tarapore P, Donehower LA et al. (2000). Oncogene 19: 1635–1646.
Nigg EA . (2002). Nature Rev Cancer 2: 1–11.
Okuda M, Horn HF, Tarapore P, Tokuyama Y, Smulian AG, Chan PK et al. (2000). Cell 103: 127–140.
Ortega S, Prieto I, Odajima J, Martin A, Dubus P, Sotillo R et al. (2003). Nat Genet 35: 25–31.
Salisbury JL, Whitehead CM, Lingle WL, Barrett SL . (1999). Biol Cell 91: 451–460.
Tetsu O, McCormick F . (2003). Cancer Cell 3: 233–245.
Wheatley DN, Wang AM, Strugnell GE . (1996). Cell Biol Int 20: 73–81.
Wong C, Stearns T . (2003). Nat Cell Biol 5: 539–544.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to K Munger, P Hinds, Y Chang and P Moore for sharing reagents. This work was supported by NIH/NCI Grant CA112598 (to SD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duensing, A., Liu, Y., Tseng, M. et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is dispensable for normal centrosome duplication but required for oncogene-induced centrosome overduplication. Oncogene 25, 2943–2949 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209310
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209310
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MPS1 is involved in the HPV16-E7-mediated centrosomes amplification
Cell Division (2021)
-
Opposing post-translational modifications regulate Cep76 function to suppress centriole amplification
Oncogene (2016)
-
Ubiquitin, the centrosome, and chromosome segregation
Chromosome Research (2016)
-
A p27Kip1 mutant that does not inhibit CDK activity promotes centrosome amplification and micronucleation
Oncogene (2012)
-
Such small hands: the roles of centrins/caltractins in the centriole and in genome maintenance
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2012)