Abstract
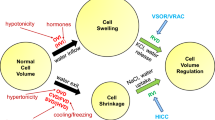
Restoration of cell volume after cell swelling in mammalian cells is achieved by the loss of solutes (K+, Cl−, and organic osmolytes) and the subsequent osmotically driven efflux of water. This process is generally known as regulatory volume decrease (RVD). One pathway for the swelling induced loss of Cl− (and also organic osmolytes) during RVD is the volume-regulated anion channel (VRAC). In this review, we discuss the physiological role and cellular control of VRAC. We will first highlight evidence that VRAC is more than a volume regulator and that it participates in other fundamental cellular processes such as cell proliferation and apoptosis. The second part concentrates on the Rho/Rho kinase/myosin phosphorylation cascade and on compartmentalization in caveolae as modulators of the signal transduction cascade that controls VRAC gating in vascular endothelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nilius, B., Eggermont, J., Voets, T., Buyse, G., Manolopoulos, V., and Droogmans, G. (1997) Properties of volume-regulated anion channels in mammalian cells. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 68, 69–119.
Okada, Y. (1997) Volume expansion sensing outward rectifier Cl− channel: fresh start to the molecular identity and volume sensor. Am. J. Physiol. 273, C755-C789.
Strange, K., Emma, F. and Jackson, P. S. (1996) Cellular and molecular physiology of volumesensitive anion channels. Am. J. Physiol. 270, C711-C730.
Grunder, S., Thiemann, A., Pusch, M. and Jentsch, T. J. (1992) Regions involved in the opening of CIC-2 chloride channel by voltage and cell volume. Nature 360, 759–762.
Thiemann, A., Grunder, S., Pusch, M. and Jentsch, T. J. (1992) A chloride channel widely expressed in epithelial and non-epithelial cells. Nature 356, 57–60.
Strange K. (1998) Molecular identity of the outwardly rectifying, swelling-activated anion channel: time to re-evaluate pICln. J. Gen. Physiol. 111, 617–622.
Clapham, D. E. (1998) The list of potential volume-sensitive chloride currents continues to swell (and shrink). J. Gen. Physiol. 111, 623–624.
Clapham, D. (2001) How to lose your hippocampus by working on chloride channels. Neuron 29, 1–3.
Okada, Y., Oiki, S., Hazama, A. and Morishima, S. (1998) Criteria for the molecular identification of the volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying Cl∟ channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 112, 365–367.
Jackson, P. S., Morrison, R. and Strange, K. (1994) The volume-sensitive organic osmolyte-anion channel VSOAC is regulated by nonhydrolytic ATP binding. Am. J. Physiol. 267, C1203-C1209.
Duan, D. and Hume, J. R. (2000) NO and the regulation of VSOACs. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 528, 2.
Chou, C. Y., Shen, M. R. and Wu, S. N. (1995) Volume-sensitive chloride channels associated with human cervical carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 55, 6077–6083.
Duan, D., Winter, C., Cowley, S., Hume, J. R. and Horowitz, B. (1997) Molecular identification of a volume regulated chloride channel. Nature 390, 417–421.
Duan, D., Cowley, S., Horowitz, B. and Hume, J. R. (1999) A serine residue in CIC-3 links phosphorylation-dephosphorylation to chloride channel regulation by cell volume. J. Gen. Physiol. 113, 57–70.
Duan, D., Zhong, J., Hermoso, M., Satterwhite, C. M., Rossow, C. F., Hatton, W. J., et al. (2001) Functional inhibition of native volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion channels in muscle cells and Xenopus oocytes by anti-CIC-3 antibody. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 531, 437–444.
Li, X. H., Shimada, K., Showalter, L. A. and Weinman, S. A. (2000) Biophysical properties of CIC-3 differentiate it from swelling-activated chloride channels in Chinese hamster ovary-K1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 35,994–35,998.
Weylandt, K.-H., Valverde, M. A., Nobles, M., Raguz, S., Amey, J. S., Diaz, M., et al. (2001) Human CIC-3 is not the swelling-activated chloride channel involved in cell volume regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 17,461–17,467.
Friedrich, T., Breiderhoff, T. and Jentsch, T. J. (1999) Mutational analysis demonstrates that CIC-4 and CIC-5 directly mediate plasma membrane currents. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 896–902.
Stobrawa, S. M., Breiderhoff, T., Takamori, S., Engel, D., Schweizer, M., Zdebik, et al. (2001) Disruption of CIC-3, a chloride channel expressed on synaptic vesicles, leads to a loss of the hippocampus. Neuron 29, 185–196.
Bond, T. D., Ambikapathy, S., Mohammad, S. and Valverde M. A. (1998) Osmosensitive Cl− currents and their relevance to regulatory volume decrease in human intestinal T84 cells: outwardly vs. inwardly rectifying currents. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 511, 45–54.
Nilius, B., Sehrer, J., Desmet, P., Vandriessche, W. and Droogmans, G. (1995) Volume regulation in a toad epithelial cell line: role of coactivation of K+and Cl-chennels. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 487, 367–378.
Davies, P. F. (1995) Flow-mediated endothelial mechanotransduction. Physiol. Rev. 75, 519–560.
Nakao, M., Ono, K., Fujisawa, S. and Iijima, T. (1999) Mechanical stress-induced Ca2+ entry and Cl− current in cultured human aortic endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 276, C238–249.
Barakat, A. I., Leaver, E. V., Pappone, P. A., and Davies, P. F. (1999) A flow-activated chlorideselective membrane current in vascular endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 85, 820–828.
Nilius, B., Viana, F. and Droogmans, G. (1997) Ion channels in vascular endothelium. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 59, 145–170.
Voets, T., Droogmans, G., and Nilius, B. (1996) Membrane currents and the resting membrane potential in cultured bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 497, 95–107.
Doughty, J. M., Boyle, J. P. and Langton, P. D. (2001) Blockade of chloride channels reveals relaxations of rat small mesenteric arteries to raised potassium. Br. J. Pharmacol. 132, 293–301.
Nelson, M., Conway, M., Knot, H. and Brayden, J. (1997) Chloride channel blockers inhibit myogenic tone in rat cerebral arteries. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 502, 259–264.
Nelson, M. T. (1998) Bayliss, myogenic tone and volume-regulated chloride channels in arterial smooth muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 507, 629.
Maertens, C., Droogmans, G., Chakraborty, P. and Nilius, B. (2001) Inhibition of volume-regulated anion channels in cultured endothelial cells by the anti-oestrogens clomiphene and nafoxidine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 132, 135–142.
Voets, T., Szücs, G., Droogmans, G. and Nilius, B. (1995) blockers of volume-activated Cl-currents inhibit endothelial cell proliferation. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 431, 132–134.
Rouzaire-Dubois, B. and Dubois, J. M. (1998) K+channel block-induced mammalian neuroblastoma cell swelling: a possible mechanism to influence proliferation. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 510, 93–102.
Shen, M., Droogmans, G., Eggermont, J., Voets, T., Ellory, J. C. and Nilius, B. (2000) Differential expression of volume-regulated anion channels during cell cycle progression of human cervical cancer cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 529, 385–394.
Wondergem, R., Gong, W., Monen, S. H., Dooley, S. N., Gonce, J. L., Conner, T. D., et al. (2001) Blocking swelling-activated chloride current inhibits mouse liver cell proliferation. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 532, 661–672.
Doroshenko, P., Sabanov, V. and Doroshenko, N. (2001) Cell cycle-related changes in regulatory volume decrease and volume-sensitive chloride conductance in mouse fibroblasts. J. Cell. Physiol. 187, 65–72.
Manolopoulos, V. G., Liekens, S., Koolwijk, P., Voets, T., Peters, E., Droogmans, G., et al. (2000) Inhibition of angiogenesis by blockers of volume-regulated anion channels. Gen. Pharmacol. 34, 107–116.
Lang, F., Lepple Wienhues, A., Paulmichl, M., Szabo, I., Siemen, D. and Gulbins, E. (1998) Ion channels, cell volume, and apoptotic cell death. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 8, 285–292.
Okada, Y., Maeno, E., Shimizu, T., Dezaki, K., Wang, J. and Morishima, S. (2001) Receptor-mediated control of regulatory volume decrease (RVD) and apoptotic volume decrease (AVD). J. Physiol. (Lond.) 532, 3–16.
Yu, S. P. and Choi, D. W. (2000) Ions, cell volume, and apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9360–9362.
Szabo, I., LeppleWienhues, A., Kaba, K. N., Zoratti, M., Gulbins, E. and Lang, F. (1998) Tyrosine kinase-dependent activation of a chloride channel in CD95-induced apoptosis in T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6169–6174.
Maeno, E., Ishizaki, Y., Kanaseki, T., Hazama, A. and Okada, Y. (2000) Normotonic cell shrinkage because of disordered volume regulation is an early prerequisite to apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9487–9492.
Souktani, R., Berdeaux, A., Ghaleh, B., Giudicelli, J. F., Guize, L., Le Heuzey, et al. (2000) Induction of apoptosis using sphingolipids activates a chloride current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 279, C158-C165.
Hughes, F. M., Jr., Bortner, C. D., Purdy, G. D. and Cidlowski, J. A. (1997) Intracellular K+ suppresses the activation of apoptosis in lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 30,567–30,576.
Voets, T., Manolopoulos, V., Eggermont, J., Ellory, C., Droogmans, G. and Nilius, B. (1998) Regulation of a swelling-activated chloride current in bovine endothelium by protein tyrosine phosphorylation and G proteins. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 506, 341–352.
Bond, T., Basavappa, S., Christensen, M. and Strange, K. (1999) ATP dependence of the I-C1,I-swell channel varies with rate of cell swelling— evidence for two modes of channel activation. J. Gen. Physiol. 113, 441–456.
Nilius, B., Oike, M., Zahradnik, I. and Droogmans, G. (1994) Activation of a C1-current by hypotonic volume increase in human endothelial cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 103, 787–805.
Lewis, R. S., Ross, P. E., and Cahalan, M. D. (1993) Chloride channels activated by osmotic stress in T lymphocytes. J. Gen. Physiol. 101, 801–826.
Doroshenko, P. and Neher, E. (1992) Volume-sensitive chloride conductance in bovine chromaffin cell membrane. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 449, 197–218.
Voets, T., Droogmans, G., Raskin, G., Eggermont, J. and Nilius, B. (1999) Reduced intracellular ionic strength as the initial trigger for activation of endothelial volume-regulated anion channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 5298–5303.
Nilius, B., Prenen, J., Voets, T., Eggermont, J. and Droogmans, G. (1998) Activation of volume-regulated chloride currents by reduction of intracellular ionic strength in bovine endothelial cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 506, 353–361.
Sabirov, R. Z., Prenen, J., Tomita, T., Droogmans, G. and Nilius, B. (2000) Reduction of ionic strength activates single volume-regulated anion channels (VRAC) in endothelial cells. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 439, 315–320.
Jung, K., Veen, M. and Altendorf, K. (2000) K+ and ionic strength directly influence the autophosphorylation activity of the putative turgor sensor KdpD of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 40,142–40,147.
Sorota, S. (1995) Tyrosine protein kinase inhibitors prevent activation of cardiac swelling-induced chloride current. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 431, 178–185.
Lepple-Wienhues, A., Szabo, I., Laun, T., Kaba, N. K., Gulbins, E. and Lang, F. (1998) The tyrosine kinase p56(lck) mediates activation of swelling-induced chloride channels in lymphocytes. J. Cell Biol. 141, 281–286.
Tilly, B. C., van den Berghe, N., Tertoolen, L. G., Edixhoven,M. J. and de Jonge, H. R. (1993) Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is involved in osmoregulation of ionic conductances. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 19,919–19,922.
Du, X. Y. and Sorota, S. (1999) Protein kinase C stimulates swelling-induced chloride current in canine atrial cells. Pflugers Arch Eur. J. Physiol. 437, 227–234.
Duan, D., Fermini, B. and Nattel, S. (1995) Alpha-adrenergic control of volume-regulated Cl-currents in rabbit atrial myocytes—characterization of a novel ionic regulatory mechanism. Circ. Res. 77, 379–393.
Chou, C. Y., Shen, M. R., Hsu, K. S., Huang, H. Y. and Lin, H. C. (1998) Involvement of PKC-alpha in regulatory volume decrease responses and activation of volume-sensitive chloride channels in human cervical cancer HT-3 cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 512, 435–448.
Trouet, D., Carton, I., Hermans, D., Droogmans G., Nilius, B. and Eggermont, J. (2001) The inhibition of volume-regulated anion channels by cSrc tyrosine kinase targeted to caveolae is mediated by the Src homology domains. Am. J. Physiol. 281, C248-C256.
Somlyo, A. P. and Somlyo, A. V. (2000) Signal transduction by G-proteins, Rho-kinase and protein phosphatase to smooth muscle and non-muscle myosin II. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 522, 177–185.
Bishop, A. L. and Hall, A. (2000) Rho GTPases and their effector proteins. Biochem. J. 348, 241–255.
Mackay, D. J. G. and Hall, A. (1998) Rho GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 20,685–20,688.
Essler, M., Amano, M., Kruse, H. J., Kaibuchi, K., Weber, P. C. and Aepfelbacher, M. (1998) Thrombin inactivates myosin light chain phosphatase via rho and its target rho kinase in human endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 21,867–21,874.
van Nieuw Amerongen, G. P., van Delft, S., Vermeer, M. A., Collard, J. G. and van Hinsbergh, V. W. (2000) Activation of RhoA by thrombin in endothelial hyperpermeability: role of Rho kinase and protein tyrosine kinases. Circ. Res. 87, 335–340.
Gohla, A., Harhammer, R. and Schultz, G. (1998) The G-protein G13 but not G12 mediates signaling from lysophosphatidic acid receptor via epidermal growth factor receptor to Rho. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 4653–4659.
Watanabe, N., Kato, T., Fujita, A., Ishizaki, T. and Narumiya, S. (1999) Cooperation between mDial and ROCK in Rho-induced actin reorganisation. Nature Cell Biol. 1, 136–143.
Nilius, B., Voets, T., Prenen, J., Barth, H., Aktories, K., Kaibuchi, K., et al. (1999) Role of Rho and Rho kinase in the activation of volume-regulated anion channels in bovine endothelial cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 516, 67–74.
Nilius, B., Prenen, J., Walsh, M. P., Carton, I., Bollen, M., Droogmans, G., et al. (2000) Myosin light chain phosphorylation-dependent modulation of volume-regulated anion channels in macrovascular endothelium. FEBS Lett. 466, 346–350.
Manolopoulos, G. V., Prenen, J., Droogmans, G. and Nilius, B. (1997) Thrombin potentiates volume activated chloride currents in pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 433, 845–847.
Kaibuchi, K., Kuroda, S. and Amano, M. (1999) Regulation of the cytoskeleton and cell adhesion by the Rho family GTPases in mammalian cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 459–486.
Eggermont, J., Carton, I., Trouet, D., Hermans, D., Droogmans, G. and Nilius, B. (2001) The RhoA signaling pathway exerts a permissive, not a causative effect on the activation of the volume-regulated anion channel (VRAC) in macrovascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 15, A845.
Janmey, P. A. (1998) The cytoskeleton and cell signaling: component localization and mechanical coupling. Physiol. Rev. 78, 763–781.
Koyama, T., Oike, M. and Ito, Y. (2001) Involvement of Rho-kinase and tyrosine kinase in hypotonic stress-induced ATP release in bovine aortic endothelial cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 532, 759–769.
Trouet, D., Nilius, B., Jacobs, A., Remacle, C., Droogmans, G. and Eggermont, J. (1999) Caveolin-1 modulates the activity of the volume-regulated chloride channel. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 520, 113–119.
Anderson (1993) Potocytosis of small molecules and ions by caveolae. Trends Cell Biol. 3, 69–72.
Okamoto, T., Schlegel, A., Scherer, P. E. and Lisanti, M. P. (1998) Caveolins, a family of scaffolding proteins for organizing “preassembled signaling complexes” at the plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 5419–5422.
Trouet, D., Hermans, D., Droogmans, G., Nilius, B. and Eggermont, J. (2001) Inhibition of volume-regulated anion channels by dominant-negative caveolin-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 284, 461–465.
Smart, E. J., Graf, G. A., McNiven, M. A., Sessa, W. C., Engelman, J. A., Scherer, et al. (1999) Caveolins, liquid-ordered domains, and signal transduction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 7289–7304.
Scheiffele, P., Verkade, P., Fra, A. M., Virta, H., Simons, K. and Ikonen, E. (1998) Caveolin-1 and-2 in the exocytic pathway of MDCK cells. J. Cell Biol. 140, 795–806.
Rizzo, V., Sung, A., Oh, P. and Schnitzer, J. E. (1998) Rapid mechanotransduction in situ at the luminal cell surface of vascular endothelium and its caveolae. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 26,323–26,329.
Doroshenko, P. (1991) Second messengers mediating activation of chloride current by intracellular GTP gamma S in bovine chromaffin cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 436, 725–738.
Cannon, C. L., Basavappa, S. and Strange, K. (1998) Intracellular ionic strength regulates the volume sensitivity of a swelling-activated anion channel. Am. J. Physiol. 275, C416-C422.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eggermont, J., Trouet, D., Carton, I. et al. Cellular function and control of volume-regulated anion channels. Cell Biochem Biophys 35, 263–274 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:35:3:263
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:35:3:263