Summary
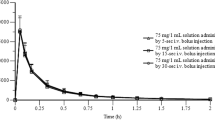
Previous studies have shown that aspirin interacts with orally administered diclofenac sodium, causing reduced peak concentrations, lower levels and decreased areas under curves. In this study, diclofenac sodium was administered orally and intravenously with and without aspirin, to 6 healthy female volunteers. After intravenous dosing both plasma levels and areas under curves were significantly reduced although none of the rate constants was affected. The volume of distribution of diclofenac was increased as was the plasma clearance. Oral administration with aspirin also resulted in lower plasma levels, particularly peak levels, and areas under curves. Comparison of AUC's for both modes of administration with and without aspirin suggested that lower levels after oral administration were not due to impaired absorption. These observations are best explained by decreased protein binding and increased biliary excretion of diclofenac in the presence of salicylate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geiger UP, Degen PH, Sioufi A (1975) Quantitative assay of diclofenac in biological material by gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 111: 293–298
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1975) Pharmacokinetics. Vol. 1. Drugs and the pharmaceutical sciences. Marcel Dekker, New York
Jeremy R, Towson J (1970) Interaction between aspirin and indomethacin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Med J Aust 2: 127–129
Metzler CM (1969) A user's manual for NONLIN, Technical Report 7292/69/7292/005. Upjohn Company, Kalamazoo, MI
Müller FO, Hundt HKL, Müller DG (1977) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic implications of long-term administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Int J Clin Pharmacol 15: 397–402
Riess W, Stierlin H, Degen P, Faigle JW, Gerardin A, Moppert J, Sallmann A, Schmid K, Schweizer A, Sulc M, Theobald W, Wagner J (1978) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of the anti-inflammatory agent Voltaren. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl 22: 17–29
Rubin A, Rodda BF, Warrick P, Gruber jr M, Ridolfo AS (1973) Interactions of aspirin with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in man. Arthritis Rheum. 16: 635–645
Segre FJ, Chaplin M, Forchielli F, Runkel R, Savelius H (1974) Naproxen-aspirin interaction in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 15: 374–379
Willis JV, Kendall MJ, Flinn RM, Thornhill DP, Welling PG (1979) The pharmacokinetics of diclofenac sodium following intravenous and oral administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 16: 405–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willis, J.V., Kendall, M.J. & Jack, D.B. A study of the effect of aspirin on the pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous diclofenac sodium. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18, 415–418 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636795
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636795