Abstract
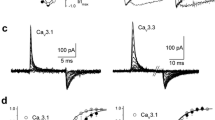
Inorganic ions have been used widely to investigate biophysical properties of high voltage-activated calcium channels (HVA: Cav1 and Cav2 families). In contrast, such information regarding low voltage-activated calcium channels (LVA: Cav3 family) is less documented. We have studied the blocking effect of Cd2+, Co2+ and Ni2+ on T-currents expressed by human Cav3 channels: Cav3.1, Cav3.2, and Cav3.3. With the use of the whole-cell configuration of the patch-clamp technique, we have recorded Ca2+ (2 mM) currents from HEK−293 cells stably expressing recombinant T-type channels. Cd2+ and Co2+ block was 2- to 3-fold more potent for Cav3.2 channels (EC50 = 65 and 122 μM, respectively) than for the other two LVA channel family members. Current-voltage relationships indicate that Co2+ and Ni2+ shift the voltage dependence of Cav3.1 and Cav3.3 channels activation to more positive potentials. Interestingly, block of those two Cav3 channels by Co2+ and Ni2+ was drastically increased at extreme negative voltages; in contrast, block due to Cd2+ was significantly decreased. This unblocking effect was slightly voltage-dependent. Tail-current analysis reveals a differential effect of Cd2+ on Cav3.3 channels, which can not close while the pore is occupied with this metal cation. The results suggest that metal cations affect differentially T-type channel activity by a mechanism involving the ionic radii of inorganic ions and structural characteristics of the channels pore.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike N., Kanaide H., Kuga T., Nakamura M., Sadoshima J., Tomoike H. 1989. Low-voltage-activated calcium current in rat aorta smooth muscle cells in primary culture. J. Physiol. 416:141–160
Akaike N., Kostyuk P.O., Osipchuk Y.V. 1989. Dihydropyridine-sensitive low-threshold calcium channels in isolated rat hypothalamic neurones. J. Physiol. 412:181–195
Arnoult C., Villaz M., Florman H.M. 1998. Pharmacological properties of the T-type Ca2+ current of mouse spermatogenic cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 53:1104–1111
Beedle A.M., Hamid J., Zamponi G.W. 2002. Inhibition of transiently expressed low- and high-voltage-activated calcium channels by trivalent metal cations. J. Membrane Biol. 187:225–238
Biagi B.A., Enyeart J.J. 1990. Gadolinium blocks low- and high-threshold calcium currents in pituitary cells. Am. J. Physiol 259:C515–C520
Bootman M.D., Lipp P., Berridge M.J. 2001. The organisation and functions of local Ca2+ signals. J. Cell Sci. 114:2213–2222
Brown A.M., Tsuda Y., Wilson D.L. 1983. A description of activation and conduction in calcium channels based on tail and turn-on current measurements in the snail. J. Physiol. 344:549–583
Castelli L., Tanzi F., Taglietti V., Magistretti J. 2003. Cu2+, Co2+, and Mn2+ modify the gating kinetics of high-voltage-activated Ca2+ channels in rat palaeocortical neurons. J. Membrane Biol. 195:121–136
Chow R.H. 1991. Cadmium block of squid calcium currents. Macroscopic data and a kinetic model. J. Gen. Physiol 98:751–770
Cribbs L.L., Gomora J.C., Daud A.N., Lee J.H., Perez-Reyes E. 2000. Molecular cloning and functional expression of Ca(v)3.1c, a T-type calcium channel from human brain. FEBS Lett. 466:54–58
Cribbs L.L., Lee J.H., Yang J., Satin J., Zhang Y., Daud A., Barclay J., Williamson M.P., Fox M., Rees M., Perez-Reyes E. 1998. Cloning and characterization of alpha1H from human heart, a member of the T-type Ca2+ channel gene family. Circ. Res. 83:103–109
Elinder F., Arhem P. 2003. Metal ion effects on ion channel gating. Q. Rev. Biophys. 36:373–427
Frazier C.J., Serrano J.R., George E.G., Yu X., Viswanathan A., Perez-Reyes E., Jones S.W. 2001. Gating kinetics of the alpha1I T-type calcium channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 118:457–470
Gomora J.C., Daud A.N., Weiergraber M., Perez-Reyes E. 2001. Block of cloned human T-type calcium channels by succinimide antiepileptic drugs. Mol. Pharmacol. 60:1121–1132
Gomora J.C., Murbartian J., Arias J.M., Lee J.H., Perez-Reyes E. 2002. Cloning and expression of the human T-type channel Ca(v)3.3: insights into prepulse facilitation. Biophys. J. 83:229–241
Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. 1967. Surface density of calcium ions and calcium spikes in the barnacle muscle fiber membrane. J. Gen. Physiol. 50:583–601
Hamill O.P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pfludgers Arch. 391:85–100
Herrington J., Lingle C.J. 1992. Kinetic and pharmacological properties of low voltage-activated Ca2+ current in rat clonal (GH3) pituitary cells. J. Neurophysiol. 68:213–232
Jeong S.W., Park E.G., Park J.Y., Lee J.W., Lee J.H. 2003. Divalent metals differentially block cloned T-type calcium channels. Neuroreport 14:1537–1540
Jones S.W., Marks T.N. 1989. Calcium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. I. Activation kinetics and pharmacology. J. Gen. PhysioL. 94:151–167
Kaneda M., Akaike N. 1989. The low-threshold Ca current in isolated amygdaloid neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 497:187–190
Kim M.S., Morii T., Sun L.X., Imoto K., Mori Y. 1993. Structural determinants of ion selectivity in brain calcium channel. FEBS Lett. 318:145–148
Kim D., Song I., Keum S., Lee T., Jeong M.J., Kim S.S., McEnery M.W., Shin H.S. 2001. Lack of the burst firing of thalamocortical relay neurons and resistance to absence seizures in mice lacking alpha (1G) T-type Ca2+ channels. Neuron 31:35–45
Lacinova L., Klugbauer N., Hofmann F. 2000. Regulation of the calcium channel alpha (1G) subunit by divalent cations and organic blockers. Neuropharmacology 39:1254–1266
Lansman J.B., Hess P., Tsien R.W. 1986. Blockade of current through single Cd2+, Mg2+, and Ca2+ Voltage and concentration dependence of calcium entry into the pore. J. Gen. Physiol 88:321–347
Lee J.H., Daud A.N., Cribbs L.L., Lacerda A.E., Pereverzev A., Klockner U., Schneider T., Perez-Reyes E. 1999a. Cloning and expression of a novel member of the low voltage-activated T-type calcium channel family. J. Neurosci. 19:1912–1921
Lee J.H., Gomora J.C., Cribbs L.L., Perez-Reyes E. 1999b. Nickel block of three cloned T-type calcium channels: low concentrations selectively block alpha1H. Biophys. J. 77:3034–3042
Magistretti J., Brevi S., de Curtis M. 2001. Ni2+ slows the activation kinetics of high-voltage-activated Ca2+ currents in cortical neurons: evidence for a mechanism of action independent of channel-pore block. J. Membrane Biol. 179:243–262
Marty A., Neher. E. 1995. Tight-seal whole-cell recording. In: Sakmann B., Neher E. (eds) Single Channel Recording. Plenum Press, New York
McFarlane M.B., Gilly W.F. 1998. State-dependent nickel block of a high-voltage-activated neuronal calcium channel. J. Neurophysiol. 80:1678–1685
Mitterdorfer J., Grabner M., Kraus R.L., Hering S., Prinz H., Glossmann H., Striessnig J. 1998. Molecular basis of drug interaction with L-type channels. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 30:319–334
Mlinar B., Enyeart J.J. 1993a. Block of current through T-type calcium channels by trivalent metal cations and nickel in neural rat and human cells. J. Physiol. 469:639–652
Nachshen D.A. 1984. Selectivity of the Ca binding site in synaptosome Ca channels. Inhibition of Ca influx by multivalent metal cations. J. Gen. Physiol. 83:941–967
Obejero-Paz C.A., Gray I.P., Jones S.W. 2004. Y3+ Block Remonstrates an intracellular activation gate for the {alpha} 1G T-type Ca2+ channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 124:631–640
Perchenet L., Benardeau A., Ertel E.A. 2000. Pharmacological properties of Ca(V)3.2, a low voltage-activated Ca2+ channel cloned from human heart. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 361:590–599
Perez-Reyes E. 2003. Molecular physiology of low-voltage-activated t-type calcium channels. Physiol. Rev. 83:117–161
Perez-Reyes E., Cribbs L.L., Daud A., Lacerda A.E., Barclay J., Williamson M.P., Fox M., Rees M., Lee J.H. 1998. Molecular characterization of a neuronal low-voltage-activated T-type calcium channel. Nature 391:896–900
Schrier A.D., Wang H., Talley E.M., Perez-Reyes E., Barrett P.Q. 2001. alpha1H T-type Ca2+ channel is the predominant subtype expressed in bovine and rat zona glomerulosa. Am. J. Physiol 280:C265–C272
Serrano J.R., Dashti S.R., Perez-Reyes E., Jones S.W. 2000. Mg2+ block unmasks Ca2+ Ba2+ selectively of alpha1G T-type calcium channels. Biophys. J. 79:3052–3062
Swandulla D., Armstrong C.M. 1989. Calcium channel block by cadmium in chicken sensory neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:1736–1740
Takahashi K., Akaike N. 1991. Calcium antagonist effects on low-threshold (T-type) calcium current in rat isolated hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 256:169–175
Talley E.M., Cribbs L.L., Lee J.H., Daud A., Perez-Reyes E., Bayliss D.A. 1999. Differential distribution of three members of a gene family encoding low voltage-activated (T-type) calcium channels. J. Neurosci. 19:1895–1911
Tang S., Mikala G., Bahinski A., Yatani A., Varadi G., Schwartz A. 1993. Molecular localization of ion selectivity sites within the pore of a human L-type cardiac calcium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 268:13026–13029
Thevenod F., Jones S.W. 1992. Cadmium block of calcium current in frog sympathetic neurons. Biophys. J. 63:162–168
Todorovic S.M., Jevtovic-Todorovic V., Mennerick S., Perez-Reyes E., Zorumski C.F. 2001a. Ca(v)3.2 channel is a molecular substrate for inhibition of T-type calcium currents in rat sensory neurons by nitrous oxide. Mol Pharmacol. 60:603–610
Todorovic S.M., Jevtovic-Todorovic V., Meyenburg A., Mennerick S., Perez-Reyes E., Romano C., Olney J.W., Zorumski C.F. 2001b. Redox modulation of T-type calcium channels in rat peripheral nociceptors. Neuron 31:75–85
Wakamori M., Strobeck M., Niidome T., Teramoto T., Imoto K., Mori Y. 1998. Functional characterization of ion permeation pathway in the N-type Ca2+ channel. J. Neurophysiol. 79:622–634
Wu J.Y., Lipsius S.L. 1990. Effects of extracellular Mg2+ on T- and L-type Ca2+ currents in single atrial myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 259:H1842–H1850
Yang J., Ellinor P.T., Sather W.A., Zhang J.F., Tsien R.W. 1993. Molecular determinants of Ca2+ selectivity and ion permeation in L-type Ca2+ channels. Nature 366:158–161
Zamponi G.W., Bourinet E., Snutch T.P. 1996. Nickel block of a family of neuronal calcium channels: subtype- and subunit-dependent action at multiple sites. J. Membrane Biol. 151:77–90
Acknowledgement
We are deeply grateful to Dr. Edward Perez-Reyes (University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA) for his enormous contribution providing cell lines stably expressing Cav3 channels, and his comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by the following grants: CONACyT (Mexico) I37976-B and J-40693-Q to J.C. Gomora, and DGAPA-UNAM (Mexico) IN201602 to J.C. Gomora.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz, D., Bartolo, R., Delgadillo, D. et al. Contrasting Effects of Cd2+ and Co2+ on the Blocking/Unblocking of Human Cav3 Channels. J Membrane Biol 207, 91–105 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0804-1
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0804-1