Abstract
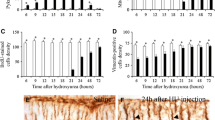
The homozygous (jj) Gunn rat provides a model for hyperbilirubinemia which includes prominent cerebellar hypoplasia. Development of the Gunn rat cerebellum was examined with and without the additional effects of elevating brain bilirubin concentration to still higher levels via sulfadimethoxine (sulfa) administration. Homozygous (jj) Gunn rats and heterozygous (Nj) littermate controls (n = 32 each) were given 100 mg/kg sulfa or saline at postnatal days 3, 7, 17, and 30, and most were sacrificed 24 h later (n = 4 for each genotype at each age). Cerebellar volume, total volume and cell number for each deep cerebellar nucleus, densities for Purkinje and granule cells in the cerebellar cortex of lobules II, VI and IX, and the density of vacuolated Purkinje cells were all measured quantitatively. Cytoplasmic vacuolation provided an indication of bilirubin toxicity and was never observed in the Nj control rats. Vacuolated Purkinje cells were first observed in jj-saline rats at 18 days and were found only in the more anterior lobules of the cerebellum (II and VI). By contrast, vacuolated Purkinje cells were observed in jj-sulfa rats at both 4 and 8 days, but only in the most posterior cerebellar lobule (IX). In all older jj rats, the decline in vacuolation was accompanied by significant necrosis and resorption of the Purkinje cells in the anterior lobules. Since the Purkinje cells in the posterior lobules are the first to differentiate in the cerebellum and are resistant to bilirubin toxicity in jj-saline rats, the results support the presence of a critical period when elevated brain bilirubin may be most toxic to neuronal development. The findings suggest that neurons undergoing differentiation at the time of bilirubin exposure are most susceptible to cell death, while cells that are slightly more or slightly less mature may show only transient changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 March 1996 / Revised, accepted: 16 September 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conlee, J., Shapiro, S. Development of cerebellar hypoplasia in jaundiced Gunn rats: a quantitative light microscopic analysis. Acta Neuropathol 93, 450–460 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010050639
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010050639