Abstract
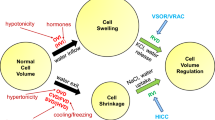
The volume-regulated anion channel (VRAC) is a ubiquitously expressed yet highly enigmatic member of the superfamily of chloride/anion channels. It is activated by cellular swelling and mediates regulatory cell volume decrease in a majority of vertebrate cells, including those in the central nervous system (CNS). In the brain, besides its crucial role in cellular volume regulation, VRAC is thought to play a part in cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and release of physiologically active molecules. Although these roles are not exclusive to the CNS, the relative significance of VRAC in the brain is amplified by several unique aspects of its physiology. One important example is the contribution of VRAC to the release of the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitters glutamate and aspartate. This latter process is thought to have impact on both normal brain functioning (such as astrocyte-neuron signaling) and neuropathology (via promoting the excitotoxic death of neuronal cells in stroke and traumatic brain injury). In spite of much work in the field, the molecular nature of VRAC remained unknown until less than 2 years ago. Two pioneer publications identified VRAC as the heterohexamer formed by the leucine-rich repeat-containing 8 (LRRC8) proteins. These findings galvanized the field and are likely to result in dramatic revisions to our understanding of the place and role of VRAC in the brain, as well as other organs and tissues. The present review briefly recapitulates critical findings in the CNS and focuses on anticipated impact on the LRRC8 discovery on further progress in neuroscience research.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DCPIB:
-
4-[(2-Butyl-6,7-dichloro-2-cyclopentyl-2,3-dihydro-1-oxo-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy]butanoic acid
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- GPCR:
-
G-protein-coupled receptor
- KCC:
-
K+,Cl− cotransporter
- LRRC8:
-
Leucine-rich repeat-containing 8
- NKCC:
-
Na+,K+,2Cl- cotransporter
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- NPPB:
-
5-Nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)benzoic acid
- RVD:
-
Regulatory volume decrease
- RVI:
-
Regulatory volume increase
- VRAC:
-
Volume-regulated anion channel
- VSOAC:
-
Volume-sensitive organic osmolyte-anion channel
- VSOR:
-
Volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying Cl− channel
- YFP:
-
Yellow fluorescent protein
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate
References
Abascal F, Zardoya R (2012) LRRC8 proteins share a common ancestor with pannexins, and may form hexameric channels involved in cell-cell communication. Bioessays 34(7):551–560
Abdullaev IF, Rudkouskaya A, Schools GP, Kimelberg HK, Mongin AA (2006) Pharmacological comparison of swelling-activated excitatory amino acid release and Cl- currents in rat cultured astrocytes. J Physiol 572(Pt. 3):677–689
Adrogue HJ, Madias NE (2000) Hyponatremia. N Engl J Med 342(21):1581–1589
Aitken PG, Borgdorff AJ, Juta AJ, Kiehart DP, Somjen GG, Wadman WJ (1998) Volume changes induced by osmotic stress in freshly isolated rat hippocampal neurons. Pflugers Arch 436(6):991–998
Akita T, Fedorovich SV, Okada Y (2011) Ca2+ nanodomain-mediated component of swelling-induced volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion current triggered by autocrine action of ATP in mouse astrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 28(6):1181–1190
Akita T, Okada Y (2011) Regulation of bradykinin-induced activation of volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion channels by Ca2+ nanodomains in mouse astrocytes. J Physiol 589(Pt 16):3909–3927
Akita T, Okada Y (2014) Characteristics and roles of the volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying (VSOR) anion channel in the central nervous system. Neuroscience 275:211–231
Albrecht J, Norenberg MD (2006) Glutamine: a Trojan horse in ammonia neurotoxicity. Hepatology 44(4):788–794
Allen MC, Newland C, Valverde MA, Hardy SP (1998) Inhibition of ligand-gated cation-selective channels by tamoxifen. Eur J Pharmacol 354(2-3):261–269
Altamirano J, Brodwick MS, Alvarez-Leefmans FJ (1998) Regulatory volume decrease and intracellular Ca2+ in murine neuroblastoma cells studied with fluorescent probes. J Gen Physiol 112(2):145–160
Amzica F, Neckelmann D (1999) Membrane capacitance of cortical neurons and glia during sleep oscillations and spike-wave seizures. J Neurophysiol 82(5):2731–2746
Andrew RD, Labron MW, Boehnke SE, Carnduff L, Kirov SA (2007) Physiological evidence that pyramidal neurons lack functional water channels. Cereb Cortex 17(4):787–802
Andrew RD, Lobinowich ME, Osehobo EP (1997) Evidence against volume regulation by cortical brain cells during acute osmotic stress. Exp Neurol 143(2):300–312
Andrew RD, MacVicar BA (1994) Imaging cell volume changes and neuronal excitation in the hippocampal slice. Neuroscience 62(2):371–383
Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG (1999) Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci 22(5):208–215
Arundine M, Tymianski M (2003) Molecular mechanisms of calcium-dependent neurodegeneration in excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium 34(4-5):325–337
Banderali U, Roy G (1992) Anion channels for amino-acids in Mdck cells. Am J Physiol 263(6):C1200–C1207
Barron KD, Dentinger MP, Kimelberg HK, Nelson LR, Bourke RS, Keegan S, Mankes R, Cragoe EJ Jr (1988) Ultrastructural features of a brain injury model in cat. I. Vascular and neuroglial changes and the prevention of astroglial swelling by a fluorenyl (aryloxy) alkanoic acid derivative (L-644,711). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 75(3):295–307
Basarsky TA, Feighan D, MacVicar BA (1999) Glutamate release through volume-activated channels during spreading depression. J Neurosci 19(15):6439–6445
Basavappa S, Chartouni V, Kirk K, Prpic V, Ellory JC, Mangel AW (1995) Swelling-induced chloride currents in neuroblastoma cells are calcium dependent. J Neurosci 15(5 Pt 1):3662–3666
Benfenati V, Caprini M, Nicchia GP, Rossi A, Dovizio M, Cervetto C, Nobile M, Ferroni S (2009) Carbenoxolone inhibits volume-regulated anion conductance in cultured rat cortical astroglia. Channels (Austin) 3(5):323–336
Benveniste H, Drejer J, Schousboe A, Diemer NH (1984) Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem 43(5):1369–1374
Blei AT, Larsen FS (1999) Pathophysiology of cerebral edema in fulminant hepatic failure. J Hepatol 31(4):771–776
Blum AE, Walsh BC, Dubyak GR (2010) Extracellular osmolarity modulates G protein-coupled receptor dependent ATP release from 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 298:C386–C396
Bortner CD, Cidlowski JA (1998) A necessary role for cell shrinkage in apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 56(12):1549–1559
Bosman DK, Deutz NE, Maas MA, van Eijk HM, Smit JJ, de Haan JG, Chamuleau RA (1992) Amino acid release from cerebral cortex in experimental acute liver failure, studied by in vivo cerebral cortex microdialysis. J Neurochem 59(2):591–599
Boulos AS, Deshaies EM, Dalfino JC, Feustel PJ, Popp AJ, Drazin D (2011) Tamoxifen as an effective neuroprotectant in an endovascular canine model of stroke. J Neurosurg 114(4):1117–1126
Bourque CW (2008) Central mechanisms of osmosensation and systemic osmoregulation. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(7):519–531
Bourque CW, Oliet SH (1997) Osmoreceptors in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol 59:601–619
Bowens NH, Dohare P, Kuo YH, Mongin AA (2013) DCPIB, the proposed selective blocker of volume-regulated anion channels, inhibits several glutamate transport pathways in glial cells. Mol Pharmacol 83(1):22–32
Bres V, Hurbin A, Duvoid A, Orcel H, Moos FC, Rabie A, Hussy N (2000) Pharmacological characterization of volume-sensitive, taurine permeable anion channels in rat supraoptic glial cells. Br J Pharmacol 130(8):1976–1982
Brillault J, Lam TI, Rutkowsky JM, Foroutan S, O'Donnell ME (2008) Hypoxia effects on cell volume and ion uptake of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 294(1):C88–C96
Brusilow SW, Koehler RC, Traystman RJ, Cooper AJ (2010) Astrocyte glutamine synthetase: importance in hyperammonemic syndromes and potential target for therapy. Neurotherapeutics 7(4):452–470
Cahalan MD, Lewis RS (1988) Role of potassium and chloride channels in volume regulation by T lymphocytes. Soc Gen Physiol Ser 43:281–301
Cheema TA, Pettigrew VA, Fisher SK (2007) Receptor regulation of the volume-sensitive efflux of taurine and iodide from human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: differential requirements for Ca2+ and protein kinase C. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320(3):1068–1077
Chen H, Luo J, Kintner DB, Shull GE, Sun D (2005) Na(+)-dependent chloride transporter (NKCC1)-null mice exhibit less gray and white matter damage after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25(1):54–66
Choi DW (1988) Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1(8):623–634
Choi DW (1992) Excitotoxic cell death. J Neurobiol 23(9):1261–1276
Crepel V, Panenka W, Kelly ME, MacVicar BA (1998) Mitogen-activated protein and tyrosine kinases in the activation of astrocyte volume-activated chloride current. J Neurosci 18(4):1196–1206
Custodio JB, Dinis TC, Almeida LM, Madeira VM (1994) Tamoxifen and hydroxytamoxifen as intramembraneous inhibitors of lipid peroxidation. Evidence for peroxyl radical scavenging activity. Biochem Pharmacol 47(11):1989–1998
Dadsetan S, Kukolj E, Bak LK, Sorensen M, Ott P, Vilstrup H, Schousboe A, Keiding S, Waagepetersen HS (2013) Brain alanine formation as an ammonia-scavenging pathway during hyperammonemia: effects of glutamine synthetase inhibition in rats and astrocyte-neuron co-cultures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33(8):1235–1241
Darby M, Kuzmiski JB, Panenka W, Feighan D, MacVicar BA (2003) ATP released from astrocytes during swelling activates chloride channels. J Neurophysiol 89(4):1870–1877
Decher N, Lang HJ, Nilius B, Bruggemann A, Busch AE, Steinmeyer K (2001) DCPIB is a novel selective blocker of I(Cl, swell) and prevents swelling-induced shortening of guinea-pig atrial action potential duration. Br J Pharmacol 134(7):1467–1479
Deleuze C, Duvoid A, Hussy N (1998) Properties and glial origin of osmotic-dependent release of taurine from the rat supraoptic nucleus. J Physiol 507(Pt 2):463–471
Dick GM, Hunter AC, Sanders KM (2002) Ethylbromide tamoxifen, a membrane-impermeant antiestrogen, activates smooth muscle calcium-activated large-conductance potassium channels from the extracellular side. Mol Pharmacol 61(5):1105–1113
Dick GM, Rossow CF, Smirnov S, Horowitz B, Sanders KM (2001) Tamoxifen activates smooth muscle BK channels through the regulatory beta 1 subunit. J Biol Chem 276(37):34594–34599
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA (1999) Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci 22(9):391–397
Dohare P, Harrigan TJ, Abdullaev IF, Mongin AA (2011) Volume-regulated anion channels mediate glutamate release from migrating microglial cells. Program # PSM03-06 St. Louis, MO, American Society for Neurochemistry. Trans Am Soc Neurochem: CD-ROM
Dreier JP (2011) The role of spreading depression, spreading depolarization and spreading ischemia in neurological disease. Nat Med 17(4):439–447
Dreier JP, Woitzik J, Fabricius M, Bhatia R, Major S, Drenckhahn C, Lehmann TN, Sarrafzadeh A, Willumsen L, Hartings JA, Sakowitz OW, Seemann JH, Thieme A, Lauritzen M, Strong AJ (2006) Delayed ischaemic neurological deficits after subarachnoid haemorrhage are associated with clusters of spreading depolarizations. Brain 129(Pt 12):3224–3237
Droogmans G, Maertens C, Prenen J, Nilius B (1999) Sulphonic acid derivatives as probes of pore properties of volume-regulated anion channels in endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 128(1):35–40
Droogmans G, Prenen J, Eggermont J, Voets T, Nilius B (1998) Voltage-dependent block of endothelial volume-regulated anion channels by calix[4]arenes. Am J Physiol 275(3 Pt 1):C646–C652
Ducharme G, Newell EW, Pinto C, Schlichter LC (2007) Small-conductance Cl(-) channels contribute to volume regulation and phagocytosis in microglia. Eur J Neurosci 26:2119–2130
Eder C, Klee R, Heinemann U (1998) Involvement of stretch-activated Cl- channels in ramification of murine microglia. J Neurosci 18(18):7127–7137
Ellis RJ (2001) Macromolecular crowding: obvious but underappreciated. Trends Biochem Sci 26(10):597–604
Fabene PF, Weiczner R, Marzola P, Nicolato E, Calderan L, Andrioli A, Farkas E, Sule Z, Mihaly A, Sbarbati A (2006) Structural and functional MRI following 4-aminopyridine-induced seizures: a comparative imaging and anatomical study. Neurobiol Dis 21(1):80–89
Fan HT, Morishima S, Kida H, Okada Y (2001) Phloretin differentially inhibits volume-sensitive and cyclic AMP-activated, but not Ca-activated, Cl(-) channels. Br J Pharmacol 133(7):1096–1106
Felipo V (2013) Hepatic encephalopathy: effects of liver failure on brain function. Nat Rev Neurosci 14(12):851–858
Felipo V, Butterworth RF (2002) Neurobiology of ammonia. Prog Neurobiol 67(4):259–279
Feustel PJ, Jin Y, Kimelberg HK (2004) Volume-regulated anion channels are the predominant contributors to release of excitatory amino acids in the ischemic cortical penumbra. Stroke 35(5):1164–1168
Fiacco TA, Agulhon C, McCarthy KD (2009) Sorting out astrocyte physiology from pharmacology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49:151–174
Fields RD (2011) Signaling by neuronal swelling. Sci Signal 4(155):tr1
Fields RD, Ni Y (2010) Nonsynaptic communication through ATP release from volume-activated anion channels in axons. Sci Signal 3(142):ra73
Fisher SK, Cheema TA, Foster DJ, Heacock AM (2008) Volume-dependent osmolyte efflux from neural tissues: regulation by G-protein-coupled receptors. J Neurochem 106(5):1998–2014
Fisher SK, Heacock AM, Keep RF, Foster DJ (2010) Receptor regulation of osmolyte homeostasis in neural cells. J Physiol 588(18):3355–3364
Franco R, Panayiotidis MI, de La Paz LD (2008) Autocrine signaling involved in cell volume regulation: the role of released transmitters and plasma membrane receptors. J Cell Physiol 216(1):14–28
Fraser CL, Arieff AI (1997) Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management of hyponatremic encephalopathy. Am J Med 102(1):67–77
Furtner T, Zierler S, Kerschbaum HH (2007) Blockade of chloride channels suppresses engulfment of microspheres in the microglial cell line, BV-2. Brain Res 1184:1–9
Gorg B, Morwinsky A, Keitel V, Qvartskhava N, Schror K, Haussinger D (2010) Ammonia triggers exocytotic release of L-glutamate from cultured rat astrocytes. Glia 58(6):691–705
Grinstein S, Clarke CA, Dupre A, Rothstein A (1982) Volume-induced increase of anion permeability in human lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol 80(6):801–823
Haj-Yasein NN, Jensen V, Ostby I, Omholt SW, Voipio J, Kaila K, Ottersen OP, Hvalby O, Nagelhus EA (2012) Aquaporin-4 regulates extracellular space volume dynamics during high-frequency synaptic stimulation: a gene deletion study in mouse hippocampus. Glia 60(6):867–874
Hamilton NB, Attwell D (2010) Do astrocytes really exocytose neurotransmitters? Nat Rev Neurosci 11(4):227–238
Hardy SP, deFelipe C, Valverde MA (1998) Inhibition of voltage-gated cationic channels in rat embryonic hypothalamic neurones and C1300 neuroblastoma cells by triphenylethylene antioestrogens. FEBS Lett 434(3):236–240
Harrigan TJ, Abdullaev IF, Jourd’heuil D, Mongin AA (2008) Activation of microglia with zymosan promotes excitatory amino acid release via volume-regulated anion channels: the role of NADPH oxidases. J Neurochem 106(6):2449–2462
Haskew-Layton RE, Rudkouskaya A, Jin Y, Feustel PJ, Kimelberg HK, Mongin AA (2008) Two distinct modes of hypoosmotic medium-induced release of excitatory amino acids and taurine in the rat brain in vivo. PLoS ONE 3(10):e3543
Haussinger D, Kircheis G, Fischer R, Schliess F, Vom DS (2000) Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: a clinical manifestation of astrocyte swelling and low-grade cerebral edema? J Hepatol 32(6):1035–1038
Hawkins BT, Davis TP (2005) The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 57(2):173–185
Hawkins EG, Dewey WL, Anitha M, Srinivasan S, Grider JR, Akbarali HI (2013) Electrophysiological characteristics of enteric neurons isolated from the immortomouse. Dig Dis Sci 58(6):1516–1527
Hayashi T, Nozaki Y, Nishizuka M, Ikawa M, Osada S, Imagawa M (2011) Factor for adipocyte differentiation 158 gene disruption prevents the body weight gain and insulin resistance induced by a high-fat diet. Biol Pharm Bull 34(8):1257–1263
Haydon PG, Carmignoto G (2006) Astrocyte control of synaptic transmission and neurovascular coupling. Physiol Rev 86(3):1009–1031
Hazama A, Okada Y (1988) Ca2+ sensitivity of volume-regulatory K+ and Cl- channels in cultured human epithelial cells. J Physiol 402:687–702
He J, Kargacin ME, Kargacin GJ, Ward CA (2003) Tamoxifen inhibits Na+ and K+ currents in rat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285(2):H661–H668
Hermenegildo C, Marcaida G, Montoliu C, Grisolia S, Minana MD, Felipo V (1996) NMDA receptor antagonists prevent acute ammonia toxicity in mice. Neurochem Res 21(10):1237–1244
Hines DJ, Hines RM, Mulligan SJ, MacVicar BA (2009) Microglia processes block the spread of damage in the brain and require functional chloride channels. Glia 57(15):1610–1618
Hisadome K, Koyama T, Kimura C, Droogmans G, Ito Y, Oike M (2002) Volume-regulated anion channels serve as an auto/paracrine nucleotide release pathway in aortic endothelial cells. J Gen Physiol 119(6):511–520
Hoffmann EK (1978) Regulation of cell volume by selective changes in the leak permeabilities of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Alfred Benzon Symp XI:397–417
Hoffmann EK, Lambert IH, Pedersen SF (2009) Physiology of cell volume regulation in vertebrates. Physiol Rev 89(1):193–277
Hoffmann EK, Simonsen LO, Lambert IH (1984) Volume-induced increase of K+ and Cl- permeabilities in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Role of internal Ca2+. J Membr Biol 78(3):211–222
Holthoff K, Witte OW (1996) Intrinsic optical signals in rat neocortical slices measured with near-infrared dark-field microscopy reveal changes in extracellular space. J Neurosci 16(8):2740–2749
Hussy N, Deleuze C, Desarmenien MG, Moos FC (2000) Osmotic regulation of neuronal activity: a new role for taurine and glial cells in a hypothalamic neuroendocrine structure. Prog Neurobiol 62(2):113–134
Hussy N, Deleuze C, Pantaloni A, Desarmenien MG, Moos F (1997) Agonist action of taurine on glycine receptors in rat supraoptic magnocellular neurones: possible role in osmoregulation. J Physiol 502(Pt 3):609–621
Hyzinski-Garcia MC, Rudkouskaya A, Mongin AA (2014) LRRC8A protein is indispensable for swelling-activated and ATP-induced release of excitatory amino acids in rat astrocytes. J Physiol 592(22):4855–4862
Hyzinski-Garcia MC, Vincent MY, Haskew-Layton RE, Dohare P, Keller RW Jr, Mongin AA (2011) Hypoosmotic swelling modifies glutamate-glutamine cycle in the cerebral cortex and in astrocyte cultures. J Neurochem 118(1):140–152
Ichikawa M, Okamura-Oho Y, Shimokawa K, Kondo S, Nakamura S, Yokota H, Himeno R, Lesch KP, Hayashizaki Y (2008) Expression analysis for inverted effects of serotonin transporter inactivation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 368(1):43–49
Inoue H, Mori S, Morishima S, Okada Y (2005) Volume-sensitive chloride channels in mouse cortical neurons: characterization and role in volume regulation. Eur J Neurosci 21(6):1648–1658
Inoue H, Okada Y (2007) Roles of volume-sensitive chloride channel in excitotoxic neuronal injury. J Neurosci 27(6):1445–1455
Jackson PS, Morrison R, Strange K (1994) The volume-sensitive organic osmolyte-anion channel VSOAC is regulated by nonhydrolytic ATP binding. Am J Physiol 267(5 Pt 1):C1203–C1209
Jackson PS, Strange K (1993) Volume-sensitive anion channels mediate swelling-activated inositol and taurine efflux. Am J Physiol 265(6 Pt 1):C1489–C1500
Jayakumar AR, Panickar KS, Curtis KM, Tong XY, Moriyama M, Norenberg MD (2011) Na-K-Cl cotransporter-1 in the mechanism of cell swelling in cultured astrocytes after fluid percussion injury. J Neurochem 117(3):437–448
Jayakumar AR, Valdes V, Norenberg MD (2011) The Na-K-Cl cotransporter in the brain edema of acute liver failure. J Hepatol 54(2):272–278
Kahle KT, Khanna AR, Alper SL, Adragna NC, Lauf PK, Sun D, Delpire E (2015) K-Cl cotransporters, cell volume homeostasis, and neurological disease. Trends Mol Med 21(8):513–523
Kato M, Hughes RD, Keays RT, Williams R (1992) Electron microscopic study of brain capillaries in cerebral edema from fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology 15(6):1060–1066
Kimelberg HK (1995) Current concepts of brain edema. Review of laboratory investigations. J Neurosurg 83(6):1051–1059
Kimelberg HK (2005) Astrocytic swelling in cerebral ischemia as a possible cause of injury and target for therapy. Glia 50(4):389–397
Kimelberg HK, Feustel PJ, Jin Y, Paquette J, Boulos A, Keller RW Jr, Tranmer BI (2000) Acute treatment with tamoxifen reduces ischemic damage following middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neuroreport 11(12):2675–2679
Kimelberg HK, Goderie SK, Higman S, Pang S, Waniewski RA (1990) Swelling-induced release of glutamate, aspartate, and taurine from astrocyte cultures. J Neurosci 10(5):1583–1591
Kimelberg HK, Jin Y, Charniga C, Feustel PJ (2003) Neuroprotective activity of tamoxifen in permanent focal ischemia. J Neurosurg 99(1):138–142
Kubota K, Kim JY, Sawada A, Tokimasa S, Fujisaki H, Matsuda-Hashii Y, Ozono K, Hara J (2004) LRRC8 involved in B cell development belongs to a novel family of leucine-rich repeat proteins. FEBS Lett 564(1-2):147–152
Kumar L, Chou J, Yee CS, Borzutzky A, Vollmann EH, von Andrian UH, Park SY, Hollander G, Manis JP, Poliani PL, Geha RS (2014) Leucine-rich repeat containing 8A (LRRC8A) is essential for T lymphocyte development and function. J Exp Med 211(5):929–942
Lang F, Busch GL, Ritter M, Volkl H, Waldegger S, Gulbins E, Haussinger D (1998) Functional significance of cell volume regulatory mechanisms. Physiol Rev 78(1):247–306
Lauf PK, Bauer J, Adragna NC, Fujise H, Zade-Oppen AM, Ryu KH, Delpire E (1992) Erythrocyte K-Cl cotransport: properties and regulation. Am J Physiol 263(5 Pt 1):C917–C932
Leaney JL, Marsh SJ, Brown DA (1997) A swelling-activated chloride current in rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol-London 501(3):555–564
Lee EL, Shimizu T, Ise T, Numata T, Kohno K, Okada Y (2007) Impaired activity of volume-sensitive Cl(-) channel is involved in cisplatin resistance of cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 211(2):513–521
Lee S, Yoon BE, Berglund K, Oh SJ, Park H, Shin HS, Augustine GJ, Lee CJ (2010) Channel-mediated tonic GABA release from glia. Science 330(6005):790–796
Lepple-Wienhues A, Szabo I, Laun T, Kaba NK, Gulbins E, Lang F (1998) The tyrosine kinase p56lck mediates activation of swelling-induced chloride channels in lymphocytes. J Cell Biol 141(1):281–286
Lippmann BJ, Yang R, Barnett DW, Misler S (1995) Pharmacology of volume regulation following hypotonicity-induced cell swelling in clonal N1E115 neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res 686(1):29–36
Lipton P (1999) Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol Rev 79(4):1431–1568
Liu HT, Akita T, Shimizu T, Sabirov RZ, Okada Y (2009) Bradykinin-induced astrocyte-neuron signalling: glutamate release is mediated by ROS-activated volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion channels. J Physiol 587(Pt 10):2197–2209
Liu HT, Tashmukhamedov BA, Inoue H, Okada Y, Sabirov RZ (2006) Roles of two types of anion channels in glutamate release from mouse astrocytes under ischemic or osmotic stress. Glia 54(5):343–357
Lo EH, Dalkara T, Moskowitz MA (2003) Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(5):399–415
Luckl J, Dreier JP, Szabados T, Wiesenthal D, Bari F, Greenberg JH (2012) Peri-infarct flow transients predict outcome in rat focal brain ischemia. Neuroscience 226:197–207
MacVicar BA, Feighan D, Brown A, Ransom B (2002) Intrinsic optical signals in the rat optic nerve: role for K(+) uptake via NKCC1 and swelling of astrocytes. Glia 37(2):114–123
Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS (2000) Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med 6(2):159–163
Manolopoulos VG, Voets T, Declercq PE, Droogmans G, Nilius B (1997) Swelling-activated efflux of taurine and other organic osmolytes in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol 273(1 Pt 1):C214–C222
Martin DL, Madelian V, Seligmann B, Shain W (1990) The role of osmotic pressure and membrane potential in K(+)-stimulated taurine release from cultured astrocytes and LRM55 cells. J Neurosci 10(2):571–577
Medina I, Friedel P, Rivera C, Kahle KT, Kourdougli N, Uvarov P, Pellegrino C (2014) Current view on the functional regulation of the neuronal K(+)-Cl(-) cotransporter KCC2. Front Cell Neurosci 8:27
Milenkovic A, Brandl C, Milenkovic VM, Jendryke T, Sirianant L, Wanitchakool P, Zimmermann S, Reiff CM, Horling F, Schrewe H, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K, Wetzel CH, Weber BH (2015) Bestrophin 1 is indispensable for volume regulation in human retinal pigment epithelium cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(20):E2630–E2639
Minieri L, Pivonkova H, Caprini M, Harantova L, Anderova M, Ferroni S (2013) The inhibitor of volume-regulated anion channels DCPIB activates TREK potassium channels in cultured astrocytes. Br J Pharmacol 168(5):1240–1254
Mongin AA (2007) Disruption of ionic and cell volume homeostasis in cerebral ischemia: the perfect storm. Pathophysiology 14(3-4):183–193
Mongin AA, Aksentsev SL, Orlov SN, Kvacheva ZB, Mezen NI, Fedulov AS, Konev SV (1996) Swelling-induced activation of Na+,K+,2Cl− cotransport in C6 glioma cells: kinetic properties and intracellular signalling mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 1285(2):229–236
Mongin AA, Aksentsev SL, Orlov SN, Slepko NG, Kozlova MV, Maximov GV, Konev SV (1994) Swelling-induced K+ influx in cultured primary astrocytes. Brain Res 655(1-2):110–114
Mongin AA, Kimelberg HK (2002) ATP potently modulates anion channel-mediated excitatory amino acid release from cultured astrocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283(2):C569–C578
Mongin AA, Kimelberg HK (2003) Is autocrine ATP release required for activation of volume-sensitive chloride channels? J Neurophysiol 90(4):2791–2792
Mongin AA, Kimelberg HK (2005) Astrocytic swelling in neuropathology. In: Kettenmann H, Ransom BR (eds) Neuroglia, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford/New York
Mongin AA, Kimelberg HK (2005) ATP regulates anion channel-mediated organic osmolyte release from cultured rat astrocytes via multiple Ca2+-sensitive mechanisms. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288(1):C204–C213
Mongin AA, Orlov SN (2001) Mechanisms of cell volume regulation and possible nature of the cell volume sensor. Pathophysiology 8(2):77–88
Montana V, Verkhratsky A, Parpura V (2014) Pathological role for exocytotic glutamate release from astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy. Curr Neuropharmacol 12(4):324–333
Moran J, Morales-Mulia S, Hernandez-Cruz A, Pasantes-Morales H (1997) Regulatory volume decrease and associated osmolyte fluxes in cerebellar granule neurons are calcium independent. J Neurosci Res 47(2):144–154
Nakajima K, Kohsaka S (2001) Microglia: activation and their significance in the central nervous system. J Biochem (Tokyo) 130(2):169–175
Nilius B (2004) Is the volume-regulated anion channel VRAC a “water-permeable” channel? Neurochem Res 29(1):3–8
Nilius B, Droogmans G (2003) Amazing chloride channels: an overview. Acta Physiol Scand 177(2):119–147
Nilius B, Eggermont J, Voets T, Buyse G, Manolopoulos V, Droogmans G (1997) Properties of volume-regulated anion channels in mammalian cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 68(1):69–119
Norenberg MD (1977) A light and electron microscopic study of experimental portal-systemic (ammonia) encephalopathy. Progression and reversal of the disorder. Lab Invest 36(6):618–627
Norenberg MD, Rao KV, Jayakumar AR (2005) Mechanisms of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Metab Brain Dis 20(4):303–318
O’Donnell ME (2014) Blood-brain barrier Na transporters in ischemic stroke. Adv Pharmacol 71:113–146
O’Donnell ME, Tran L, Lam TI, Liu XB, Anderson SE (2004) Bumetanide inhibition of the blood-brain barrier Na-K-Cl cotransporter reduces edema formation in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24(9):1046–1056
Oh SJ, Han KS, Park H, Woo DH, Kim HY, Traynelis SF, Lee CJ (2012) Protease activated receptor 1-induced glutamate release in cultured astrocytes is mediated by bestrophin-1 channel but not by vesicular exocytosis. Mol Brain 5:38
Okada Y (1997) Volume expansion-sensing outward-rectifier Cl- channel: fresh start to the molecular identity and volume sensor. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 273(3 Pt 1):C755–C789
Okada Y, Maeno E, Shimizu T, Dezaki K, Wang J, Morishima S (2001) Receptor-mediated control of regulatory volume decrease (RVD) and apoptotic volume decrease (AVD). J Physiol 532(Pt 1):3–16
Olson JE, Li GZ (1997) Increased potassium, chloride, and taurine conductances in astrocytes during hypoosmotic swelling. Glia 20(3):254–261
Osuka K, Feustel PJ, Mongin AA, Tranmer BI, Kimelberg HK (2001) Tamoxifen inhibits nitrotyrosine formation after reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Neurochem 76(6):1842–1850
Parpura V, Heneka MT, Montana V, Oliet SH, Schousboe A, Haydon PG, Stout RF Jr, Spray DC, Reichenbach A, Pannicke T, Pekny M, Pekna M, Zorec R, Verkhratsky A (2012) Glial cells in (patho)physiology. J Neurochem 121(1):4–27
Pasantes-Morales H, Moran J, Schousboe A (1990) Volume-sensitive release of taurine from cultured astrocytes: properties and mechanism. Glia 3(5):427–432
Pasantes-Morales H, Schousboe A (1989) Release of taurine from astrocytes during potassium-evoked swelling. Glia 2(1):45–50
Patel AJ, Lauritzen I, Lazdunski M, Honore E (1998) Disruption of mitochondrial respiration inhibits volume-regulated anion channels and provokes neuronal cell swelling. J Neurosci 18(9):3117–3123
Pedersen SF, Kapus A, Hoffmann EK (2011) Osmosensory mechanisms in cellular and systemic volume regulation. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(9):1587–1597
Pedersen SF, Klausen TK, Nilius B (2015) The identification of a volume-regulated anion channel: an amazing Odyssey. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 213(4):868–881
Phillis JW, O’Regan MH (1996) Mechanisms of glutamate and aspartate release in the ischemic rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res 730(1-2):150–164
Phillis JW, Song D, O’Regan MH (1997) Inhibition by anion channel blockers of ischemia-evoked release of excitotoxic and other amino acids from rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res 758(1-2):9–16
Phillis JW, Song D, O’Regan MH (1998) Tamoxifen, a chloride channel blocker, reduces glutamate and aspartate release from the ischemic cerebral cortex. Brain Res 780(2):352–355
Planells-Cases R, Lutter D, Guyader C et al. (2015) Subunit composition of VRAC channels determines substrate specificity and cellular resistance to Pt-based anti-cancer drugs. EMBO J. doi:10.15252/embj.201592409
Podesta MA, Faravelli I, Cucchiari D, Reggiani F, Oldani S, Fedeli C, Graziani G (2015) Neurological counterparts of hyponatremia: pathological mechanisms and clinical manifestations. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 15(4):536
Poulsen KA, Andersen EC, Hansen CF, Klausen TK, Hougaard C, Lambert IH, Hoffmann EK (2010) Deregulation of apoptotic volume decrease and ionic movements in multidrug-resistant tumor cells: role of chloride channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 298(1):C14–C25
Qiu Z, Dubin AE, Mathur J, Tu B, Reddy K, Miraglia LJ, Reinhardt J, Orth AP, Patapoutian A (2014) SWELL1, a plasma membrane protein, is an essential component of volume-regulated anion channel. Cell 157(2):447–458
Rappert A, Biber K, Nolte C, Lipp M, Schubel A, Lu B, Gerard NP, Gerard C, Boddeke HW, Kettenmann H (2002) Secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine (CCL21) activates CXCR3 to trigger a Cl- current and chemotaxis in murine microglia. J Immunol 168(7):3221–3226
Rasmusson RL, Davis DG, Lieberman M (1993) Amino acid loss during volume regulatory decrease in cultured chick heart cells. Am J Physiol 264(1 Pt 1):C136–C145
Risher WC, Andrew RD, Kirov SA (2009) Real-time passive volume responses of astrocytes to acute osmotic and ischemic stress in cortical slices and in vivo revealed by two-photon microscopy. Glia 57(2):207–221
Rosell A, Vilalta A, Garcia-Berrocoso T, Fernandez-Cadenas I, Domingues-Montanari S, Cuadrado E, Delgado P, Ribo M, Martinez-Saez E, Ortega-Aznar A, Montaner J (2011) Brain perihematoma genomic profile following spontaneous human intracerebral hemorrhage. PLoS ONE 6(2):e16750
Rossi DJ, Oshima T, Attwell D (2000) Glutamate release in severe brain ischaemia is mainly by reversed uptake. Nature 403(6767):316–321
Rosso L, Peteri-Brunback B, Poujeol P, Hussy N, Mienville JM (2004) Vasopressin-induced taurine efflux from rat pituicytes: a potential negative feedback for hormone secretion. J Physiol 554(Pt 3):731–742
Roth RB, Hevezi P, Lee J, Willhite D, Lechner SM, Foster AC, Zlotnik A (2006) Gene expression analyses reveal molecular relationships among 20 regions of the human CNS. Neurogenetics 7(2):67–80
Rothman SM (1985) The neurotoxicity of excitatory amino acids is produced by passive chloride influx. J Neurosci 5(6):1483–1489
Roy G, Malo C (1992) Activation of amino acid diffusion by a volume increase in cultured kidney (MDCK) cells. J Membr Biol 130(1):83–90
Roy G, Sauve R (1987) Effect of anisotonic media on volume, ion and amino-acid content and membrane potential of kidney cells (MDCK) in culture. J Membr Biol 100(1):83–96
Rudkouskaya A, Chernoguz A, Haskew-Layton RE, Mongin AA (2008) Two conventional protein kinase C isoforms, alpha and betaI, are involved in the ATP-induced activation of volume-regulated anion channel and glutamate release in cultured astrocytes. J Neurochem 105(6):2260–2270
Russell JM (2000) Sodium-potassium-chloride cotransport. Physiol Rev 80(1):211–276
Rutledge EM, Kimelberg HK (1996) Release of [3H]-D-aspartate from primary astrocyte cultures in response to raised external potassium. J Neurosci 16(24):7803–7811
Sabirov RZ, Kurbannazarova RS, Melanova NR, Okada Y (2013) Volume-sensitive anion channels mediate osmosensitive glutathione release from rat thymocytes. PLoS ONE 8(1):e55646
Sahagian BM (1965) Active glucose uptake by strips of guinea pig intestine; competitive inhibition by phlorhizin and phloretin. Can J Biochem 43(7):851–858
Sanchez-Olea R, Pena C, Moran J, Pasantes-Morales H (1993) Inhibition of volume regulation and efflux of osmoregulatory amino acids by blockers of Cl- transport in cultured astrocytes. Neurosci Lett 156(1-2):141–144
Sarkadi B, Mack E, Rothstein A (1984) Ionic events during the volume response of human peripheral blood lymphocytes to hypotonic media. I. Distinctions between volume-activated Cl- and K+ conductance pathways. J Gen Physiol 83(4):497–512
Sarkadi B, Mack E, Rothstein A (1984) Ionic events during the volume response of human peripheral blood lymphocytes to hypotonic media. II. Volume- and time-dependent activation and inactivation of ion transport pathways. J Gen Physiol 83(4):513–527
Sato K, Numata T, Saito T, Ueta Y, Okada Y (2011) V(2) receptor-mediated autocrine role of somatodendritic release of AVP in rat vasopressin neurons under hypo-osmotic conditions. Sci Signal 4(157):ra5
Sawada A, Takihara Y, Kim JY, Matsuda-Hashii Y, Tokimasa S, Fujisaki H, Kubota K, Endo H, Onodera T, Ohta H, Ozono K, Hara J (2003) A congenital mutation of the novel gene LRRC8 causes agammaglobulinemia in humans. J Clin Invest 112(11):1707–1713
Schlichter LC, Mertens T, Liu B (2011) Swelling activated Cl- channels in microglia: biophysics, pharmacology and role in glutamate release. Channels (Austin) 5(2):128–137
Schlichter LC, Sakellaropoulos G, Ballyk B, Pennefather PS, Phipps DJ (1996) Properties of K+ and Cl- channels and their involvement in proliferation of rat microglial cells. Glia 17(3):225–236
Schober AL, Mongin AA (2015) Intracellular levels of glutamate in swollen astrocytes are preserved via neurotransmitter reuptake and de novo synthesis: implications for hyponatremia. J Neurochem 135(1):176–185
Schousboe A, Moran J, Pasantes-Morales H (1990) Potassium-stimulated release of taurine from cultured cerebellar granule neurons is associated with cell swelling. J Neurosci Res 27(1):71–77
Schousboe A, Sanchez OR, Moran J, Pasantes-Morales H (1991) Hyposmolarity-induced taurine release in cerebellar granule cells is associated with diffusion and not with high-affinity transport. J Neurosci Res 30(4):661–665
Seki Y, Feustel PJ, Keller RW Jr, Tranmer BI, Kimelberg HK (1999) Inhibition of ischemia-induced glutamate release in rat striatum by dihydrokinate and an anion channel blocker. Stroke 30(2):433–440
Stauber T (2015) The volume-regulated anion channel is formed by LRRC8 heteromers—molecular identification and roles in membrane transport and physiology. Biol Chem 396(9-10):975–990
Steffensen AB, Sword J, Croom D, Kirov SA, MacAulay N (2015) Chloride cotransporters as a molecular mechanism underlying spreading depolarization-induced dendritic beading. J Neurosci 35(35):12172–12187
Strange K, Emma F, Jackson PS (1996) Cellular and molecular physiology of volume-sensitive anion channels. Am J Physiol 270(3 Pt 1):C711–C730
Stutzin A, Hoffmann EK (2006) Swelling-activated ion channels: functional regulation in cell-swelling, proliferation and apoptosis. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 187(1-2):27–42
Su G, Kintner DB, Flagella M, Shull GE, Sun D (2002) Astrocytes from Na(+)-K(+)-Cl(-) cotransporter-null mice exhibit absence of swelling and decrease in EAA release. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282(5):C1147–C1160
Su G, Kintner DB, Sun D (2002) Contribution of Na(+)-K(+)-Cl(-) cotransporter to high-[K(+)](o)-induced swelling and EAA release in astrocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282(5):C1136–C1146
Sykova E (2004) Extrasynaptic volume transmission and diffusion parameters of the extracellular space. Neuroscience 129(4):861–876
Szatkowski M, Barbour B, Attwell D (1990) Non-vesicular release of glutamate from glial cells by reversed electrogenic glutamate uptake. Nature 348(6300):443–446
Takano T, Kang J, Jaiswal JK, Simon SM, Lin JH, Yu Y, Li Y, Yang J, Dienel G, Zielke HR, Nedergaard M (2005) Receptor-mediated glutamate release from volume sensitive channels in astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(45):16466–16471
Ternovsky VI, Okada Y, Sabirov RZ (2004) Sizing the pore of the volume-sensitive anion channel by differential polymer partitioning. FEBS Lett 576(3):433–436
Tofteng F, Hauerberg J, Hansen BA, Pedersen CB, Jorgensen L, Larsen FS (2006) Persistent arterial hyperammonemia increases the concentration of glutamine and alanine in the brain and correlates with intracranial pressure in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26(1):21–27
Tominaga K, Kondo C, Kagata T, Hishida T, Nishizuka M, Imagawa M (2004) The novel gene fad158, having a transmembrane domain and leucine-rich repeat, stimulates adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 279(33):34840–34848
Uckermann O, Vargova L, Ulbricht E, Klaus C, Weick M, Rillich K, Wiedemann P, Reichenbach A, Sykova E, Bringmann A (2004) Glutamate-evoked alterations of glial and neuronal cell morphology in the guinea pig retina. J Neurosci 24(45):10149–10158
Upadhyay A, Jaber BL, Madias NE (2006) Incidence and prevalence of hyponatremia. Am J Med 119(7 Suppl 1):S30–S35
Verkman AS, Galietta LJ (2009) Chloride channels as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8(2):153–171
Voss FK, Ullrich F, Munch J, Lazarow K, Lutter D, Mah N, Andrade-Navarro MA, von Kries JP, Stauber T, Jentsch TJ (2014) Identification of LRRC8 heteromers as an essential component of the volume-regulated anion channel VRAC. Science 344(6184):634–638
Wang Y, Roman R, Lidofsky SD, Fitz JG (1996) Autocrine signaling through ATP release represents a novel mechanism for cell volume regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(21):12020–12025
Wasterlain CG, Torack RM (1968) Cerebral edema in water intoxication. II. An ultrastructural study. Arch Neurol 19(1):79–87
Wehner F, Olsen H, Tinel H, Kinne-Saffran E, Kinne RKH (2003) Cell volume regulation: osmolytes, osmolyte transport, and signal transduction. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 148:1–80
Woitzik J, Hecht N, Pinczolits A, Sandow N, Major S, Winkler MK, Weber-Carstens S, Dohmen C, Graf R, Strong AJ, Dreier JP, Vajkoczy P (2013) Propagation of cortical spreading depolarization in the human cortex after malignant stroke. Neurology 80(12):1095–1102
Woo DH, Han KS, Shim JW, Yoon BE, Kim E, Bae JY, Oh SJ, Hwang EM, Marmorstein AD, Bae YC, Park JY, Lee CJ (2012) TREK-1 and Best1 channels mediate fast and slow glutamate release in astrocytes upon GPCR activation. Cell 151(1):25–40
Yan Y, Dempsey RJ, Sun D (2001) Na+-K+-Cl- cotransporter in rat focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21(6):711–721
Ye ZC, Oberheim N, Kettenmann H, Ransom BR (2009) Pharmacological “cross-inhibition” of connexin hemichannels and swelling activated anion channels. Glia 57(3):258–269
Zhang Z, Bourque CW (2003) Osmometry in osmosensory neurons. Nat Neurosci 6(10):1021–1022
Zhang H, Cao HJ, Kimelberg HK, Zhou M (2011) Volume regulated anion channel currents of rat hippocampal neurons and their contribution to oxygen-and-glucose deprivation induced neuronal death. PLoS ONE 6(2):e16803
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Feustel PJ, Kimelberg HK (2008) DCPIB, a specific inhibitor of volume regulated anion channels (VRACs), reduces infarct size in MCAo and the release of glutamate in the ischemic cortical penumbra. Exp Neurol 210(2):514–520
Zierler S, Frei E, Grissmer S, Kerschbaum HH (2008) Chloride influx provokes lamellipodium formation in microglial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 21(1-3):55–62
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to my colleagues, Dr. Richard W. Keller, Jr., and Alexandra L. Schober, for critical reading and helpful suggestions on the manuscript, as well as for help with figure preparation. The work in the author’s laboratory was supported by a grant from the National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NS061953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Frenemy (n.) is a portmanteau of “friend” and “enemy” that refers to one who pretends to be a friend but is actually an enemy. Frenemy may also denote the one who really is a friend but also a rival (Merriam-Webster Dictionary online accessed on 04/07/2015).
This article is published as a part of the special issue on “Molecular physiology of anion channels: dual function proteins and new structural motifs.”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mongin, A.A. Volume-regulated anion channel—a frenemy within the brain. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 468, 421–441 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-015-1765-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-015-1765-6