Abstract
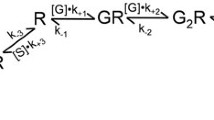
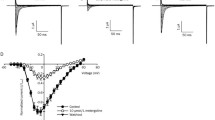
Effects and the mechanism of action of quaternary amine local anesthetics on ligand- and voltage-activated ion currents were studied using voltage-clamped ovarian follicles and oocytes from Xenopus laevis. The fast inward and slow outward currents in response to acetylcholine were unaltered by procaine, whereas the oscillatory and smooth inward chloride currents (I Cl) were abolished. Potassium currents (I K) elicited by norepinephrine and oscillatory I Cl elicited by lysophosphatidic acid were blocked. Procaine caused a noncompetitive inhibition of oscillatory I Cl mediated by heterologously expressed neurotransmitter receptors from the rat brain. Threefold differences were found in the procaine sensitivity of the 5-HT2a and 5-HT2c receptors. The rank order of intrinsic inhibitory activity of local anesthetics was: procaine > lidocaine > dibucaine > tetracaine. Extra- or intracellular application of procaine did not alter the Ca2+-activated Cl–current, indicating that neither the endogenous voltage-gated Ca2+ nor the Ca2+-activated Cl–channels account for the inhibition. Procaine caused only a slight reduction in I Cl elicited by photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP 3) and did not abolish I Cl triggered by GTP[γ-S]-induced direct activation of G proteins. For receptors coupling to the phosphoinositide/Ca2+ signal transduction pathway, the primary and physiologically relevant site of procaine action appears to be on the extracellular surface, upstream from the G protein, presumably on the receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 July 1996 / Received after revision and accepted: 9 October 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tigyi, J., Tigyi, G., Liliom, K. et al. Local anesthetics inhibit receptors coupled to phosphoinositide signaling in Xenopus oocytes. Pfluegers Arch 433, 478–487 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050303
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050303