Abstract
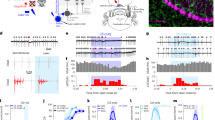
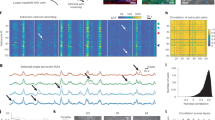
Recent studies suggest that the CREB-CRE transcriptional pathway is pivotal in the formation of some types of long-term memory. However, it has not been demonstrated that stimuli that induce learning and memory activate CRE-mediated gene expression. To address this issue, we used a mouse strain transgenic for a CRE-lac Z reporter to examine the effects of hippocampus-dependent learning on CRE-mediated gene expression in the brain. Training for contextual conditioning or passive avoidance led to significant increases in CRE-dependent gene expression in areas CA1 and CA3 of the hippocampus. Auditory cue fear-conditioning, which is amygdala dependent, was associated with increased CRE-mediated gene expression in the amygdala, but not the hippocampus. These data demonstrate that learning in response to behavioral conditioning activates the CRE transcriptional pathway in specific areas of brain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kandel, E. R. Genes, synapses, and long-term memory. J. Cell. Physiol. 173, 124–125 (1997).
Dubnau, J. & Tully, T. Gene discovery in Drosophila: New insights for learning and memory. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 21, 407–444 (1998).
Collingridge, G. L. & Bliss, T. V. Memories of NMDA receptors and LTP. Trends Neurosci. 18, 54–56 (1995).
Stevens, C. F. A million dollar question: Does LTP = memory? Neuron 20, 1–2 (1998).
Barondes, S. H. & Cohen, H. D. Arousal and the conversion of short-term to long-term memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 61, 923–929 ( 1968).
Goelet, P., Castellucci, V. F., Schacher, S. & Kandel, E. R. The long and short of long-term memory- a molecular framework. Nature 322, 419–422 ( 1986).
Davis, H. P. & Squire, L. R. Protein synthesis and memory: a review. Psychol. Bull. 96, 518– 559 (1984).
Tully, T., Preat, T., Boynton, S. C. & Del Vecchio, M. Genetic disection of consolidated memory in drosophila. Cell 79, 35–47 ( 1994).
Livingston, M. S., Sziber, P. P. & Quinn, W. G. Loss of calcium calmodulin responsiveness in adenylyl cyclase of rutabaga, a Drosophila learning mutant. Cell 37, 205–215 ( 1984).
Yovell, Y., Kandel, E. R., Dudai, Y. & Abrams, T. W. Biochemical correlates of short-term sensitization in Aplysia: temporal analysis of adenylate cyclase stimulation in a perfused-membrane preparation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 9285–9289 (1987).
Silva, A. J., Paylor, R., Wehner, J. M. & Tonegawa, S. Impaired spatial learning in alpha calcium calmodulin kinase II mutant mice. Science 257, 206–210 (1992).
Wu, Z. L. et al. Altered behavior and long-term potentiation in type I adenylyl cyclase mutant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 220–224 (1995).
Abel, T., Nguyen, P. V., Barad, M., Deuel, T. A. S. & Kandel, E. R. Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell 88, 615–626 (1997).
Frey, U., Huang, Y. Y. & Kandel, E. R. Effects of cAMP simulate a late stage of LTP in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Science 260, 1661– 1664 (1993).
Impey, S. et al. Induction of CRE-mediated gene expression by stimuli that generate long-lasting LTP in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Neuron 16, 973–982 ( 1996).
Sheng, M., McFadden, G. & Greenberg, M. E. Membrane depolarization and calcium induce c-fos transcription via phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB. Neuron 4, 571–582 ( 1990).
Impey, S. et al. Crosstalk between ERK and PKA is required for Ca2+ stimulation of CREB-dependent transcription and ERK nuclear translocation. Neuron (in press).
Nguyen, P. V. & Kandel, E. R. A macromolecular synthesis-dependent late phase of long-term potentiation requiring cAMP in the medial perforant pathway of rat hippocampal slices. J. Neurosci. 16, 3189–3198 (1996).
Dash, P. K., Hochner, B. & Kandel, E. R. Injection of the cAMP-responsive element into the nucleus of Aplysia sensory neurons blocks long-term facilitation. Nature 345, 718–721 ( 1990).
Martin, K. C. et al. Synapse-specific, long-form facilitation of Aplysia sensory to motor synapses: A function for local protein synthesis in memory storage. Cell 91, 927–938 (1997).
Yin, J. C. P. et al. Induction of a dominant negative CREB transgene specifically blocks long-term memory in drosophila. Cell 79, 49–58 (1994).
Yin, J. C., Del Vecchio, M., Zhou, H. & Tully, T. CREB as a memory modulator: induced expression of a dCREB2 activator isoform enhances long-term memory in Drosophila. Cell 81, 107–115 (1995).
Bourtchuladze, R. et al. Deficient long-term memory in mice with a targeted mutation of the cAMP-responsive element-binding protein. Cell 79, 59–68 (1994).
Kogan, J. H. et al. Spaced training induces normal long-term memory in CREB mutant mice. Curr. Biol. 7, 1– 11 (1997).
Phillips, R. G. & LeDoux, J. E. Differential contribution of amygdala and hippocampus to cued and contextual fear conditioning. Behav. Neurosci. 106, 274– 285 (1992).
Kim, J. J. & Fanselow, M. S. Modality-specific retrograde amnesia of fear. Science 256, 675– 677 (1992).
Chen, C., Kim, J. J., Thompson, R. F. & Tonegawa, S. Hippocampal lesions impair contextual fear conditioning in two strains of mice. Behav. Neurosci. 110, 1177– 1180 (1996).
Logue, S. F., Paylor, R. & Wehner, J. M. Hippocampal lesions cause learning deficits in inbred mice in the Morris water maze and conditioned-fear task. Behav. Neurosci. 111, 104–113 ( 1997).
Fanselow, M. S. Conditioned and unconditional components of post-shock freezing. Pavlov. J. Biol. Sci. 15, 177–182 (1980).
Paylor, R., Tracy, R., Wehner, J. & Rudy, J. W. DBA/2 and C57BL/6 mice differ in contextual fear but not auditory fear conditioning. Behav. Neurosci. 108, 810–817 (1994).
Brindle, P., Nakajima, T. & Montminy, M. Multiple protein kinase A-regulated events are required for transcriptional induction by cAMP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 10521–10525 ( 1995).
Bito, H., Deisseroth, K. & Tsien, R. W. CREB phosphorylation and dephosphorylation: a Ca(2+)- and stimulus duration-dependent switch for hippocampal gene expression. Cell 87, 1203–1214 ( 1996).
Davis, M. The role of the amygdala in fear and anxiety. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 15, 353–375 ( 1992).
Maren, S., Aharonov, G. & Fanselow, M. S. Retrograde abolition of conditional fear after excitotoxic lesions in the basolateral amygdala of rats: absence of a temporal gradient. Behav. Neurosci. 110, 718– 726 (1996).
Rogan, M. T., Staubli, U. V. & LeDoux, J. E. Fear conditioning induces associative long-term potentiation in the amygdala. Nature 390, 604– 607 (1997).
Campeau, S. & Davis, M. The amygdala and fear conditioning: has the nut been cracked? Involvement of the central nucleus and basolateral complex of the amygdala in fear conditioning measured with fear-potentiated startle in rats trained concurrently with auditory and visual conditioned stimuli. Neuron 16, 237– 240 (1996).
Helmstetter, F. J. & Bellgowan, P. S. Effects of muscimol applied to the basolateral amygdala on acquisition and expression of contextual fear conditioning in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 108, 1005–1009 (1994).
Stubley Weatherly, L., Harding, J. W. & Wright, J. W. Effects of discrete kainic acid-induced hippocampal lesions on spatial and contextual learning and memory in rats. Brain Res. 716, 29–38 ( 1996).
Lubow, R. E. Latent inhibition. Psychol. Bull. 79, 398 –407 (1973).
Phillips, R. G. & LeDoux, J. E. Lesions of the fornix but not the entorhinal or perirhinal cortex interfere with contextual fear conditioning. J. Neurosci. 15, 5308 –5315 (1995).
Good, M. & Honey, R. C. Dissociable effects of selective lesions to hippocampal subsystems on exploratory behavior, contextual learning, and spatial learning. Behav. Neurosci. 111, 487–493 (1997).
Yeckel, M. F. & Berger, T. W. Monosynaptic excitation of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells by afferents from the entorhinal cortex. Hippocampus 5, 108–114 ( 1995).
Moore, R.Y. & Bloom, F.E. Central catecholamine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of the norepinephrine and epinephrine systems. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 113–168 (1979).
Dutar, P., Bassant, M. H., Senut, M. C. & Lamour, Y. The septohippocampal pathway: structure and function of a central cholinergic system. Physiol. Rev. 75, 393– 427 (1995).
English, J. D. & Sweatt, J. D. A requirement for the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in hippocampal long term potentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 19103– 19106 (1997).
Brambilla, R. et al. A role for the Ras signalling pathway in synaptic transmission and long-term memory. Nature 390, 281– 286 (1997).
Shieh, P. B., Hu, S. C., Bobb, K., Timmusk, T. & Ghosh, A. Identification of a signaling pathway involved in calcium regulation of BDNF expression. Neuron 20, 727–740 (1998).
Tao, X., Finkbeiner, S., Arnold, D. B., Shaywitz, A. J. & Greenberg, M. E. Ca2+ influx regulates BDNF transcription by a CREB family transcription factor-dependent mechanism. Neuron 20, 709–726 ( 1998).
Alberini, C. M., Ghirardi, M., Metz, R. & Kandel, E. R. C/EBP is an immediate-early gene required for the consolidation of long-term facilitation in Aplysia. Cell 76, 1099– 1114 (1994).
Huang, Y. Y. et al. Mice lacking the gene encoding tissue-type plasminogen activator show a selective interference with late-phase long-term potentiation in both Schaffer collateral and mossy fiber pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 8699–8704 ( 1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank Lauren Baker and Zhengui Xia for reading the manuscript. Microscopy and image analysis was done in the W. M. Keck Center for Neural Signaling, University of Washington. This research was supported by National Institutes of Health grant NS 20498.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Impey, S., Smith, D., Obrietan, K. et al. Stimulation of cAMP response element (CRE)-mediated transcription during contextual learning. Nat Neurosci 1, 595–601 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/2830
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2830
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of ERK/CREB signaling contributes to postoperative learning and memory dysfunction in neonatal rats
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
Bioinformatics Analysis of miR-181a and Its Role in Adipogenesis, Obesity, and Lipid Metabolism Through Review of Literature
Molecular Biotechnology (2023)
-
Climate-driven flyway changes and memory-based long-distance migration
Nature (2021)
-
Lacidipine Prevents Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment by Reducing Brain Oxido-nitrosative Stress in Mice
Neurotoxicity Research (2021)
-
Genetic and metabolic links between the murine microbiome and memory
Microbiome (2020)