Abstract
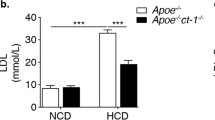
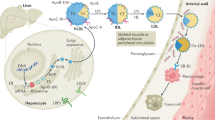
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL surveys have identified a strong inverse relationship between the amount in the plasma of high density lipoproteins (HDL), apolipoprotein Al (ApoA-I), the major protein component of HDL, and the risk for atherosclerosis in humans1,2. It is not known if this relationship arises from a direct antiatherogenic effect of these plasma components or if it is the result of other factors also associated with increases in ApoA-I and HDL levels. Because some strains of mice are susceptible to diet-induced formation of preatherosclerotic fatty streak lesions, and because of available techniques for the genetic manipulation of this organism, the murine system offers a unique setting in which to investigate the process of early atherogenesis. To test the hypothesis that induction of a high plasma concentration of ApoA-I and HDL would inhibit this process, we studied the effects of atherogenic diets on transgenic mice expressing high amounts of human ApoA-I. We report that transgenic mice with high plasma ApoA-I and HDL levels were significantly protected from the development of fatty streak lesions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gordon, D. & Rifkind, B. New Engl. J. Med. 321, 1311–1316 (1989).
Gordon, D. et al. Circulation 79, 8–15 (1989).
Paigen, B., Mitchell, D., Reue, K., Morrow, A. & LeBoeuf, R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 84, 3763–3767 (1987).
Paigen, B., Nesbitt, M. N., Mitchell, D., Albee, D. & LeBoeuf, R. Genetics 122, 163–168 (1989).
Stewart-Philip, J., Lough, J. & Skomene, E. Clin. Invest. Med. 12, 121–126 (1989).
Ishida, B. & Paigen, B. in Genetic Factors and Atherosclerosis: Approaches and Model Systems (eds Lusis, A. J. & Sparkes, R. S.) 198–222 (Karger, Basel, 1989).
Paigen, B., Ishida, B., Verstuyft, J., Winters, R. & Albee, D. Arteriosclerosis 10, 316–323 (1990).
LeBoeuf, R. C. et al. J. Lipid Res. 31, 9–101 (1990).
Rubin, E. M., Ishida, B. Y., Clift, S. M. & Krauss, R. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 88, 434–438 (1991).
Paigen, B., Morrow, A., Holmes, P. A., Mitchel, D. & Williams, R. A. Atherosclerosis 68, 231–240 (1987).
Miller, N. E. Am. Heart J. 113, 589–597 (1987).
Cheung, M., Brown, B., Wolf, J. A. & Albers, J. J. Lipid Res. 32, 383–394 (1991).
Walsh, A., Ito, Y. & Breslow, J. L. J. biol. Chem. 264, 6488–6494 (1989).
Patsch, J., Karlin, J., Scott, L., Smith, L. C. & Gotto, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 1435–1449 (1983).
Brinton, E., Eisenberg, S. & Breslow, J. L. J. Clin. Invest. 87, 536–544 (1991).
Miller, N. E. Lipids 13, 914–919 (1978).
Sorci-Thomas, M. et al. J. biol. Chem. 263, 5183–5189 (1988).
Ross, R. New Engl. J. Med. 314, 488–491 (1986).
McGill, H. C. Arteriosclerosis 4, 443–451 (1984).
Nichols, A. V., Krauss, R. M. & Musliner, T. A. Meth. Enzym. 128, 417–431 (1986).
Nishina, P. M., Verstuyft, J. & Paigen, B. J. Lipid Res. 31, 859–869 (1990).
Rudel, L. L. & Morris, M. D. J. Lipid Res. 14, 364–371 (1973).
Izzo, C., Grillo, F. & Murador, E. Clin. Chem. 27, 371–378 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubin, E., Krauss, R., Spangler, E. et al. Inhibition of early atherogenesis in transgenic mice by human apolipoprotein AI. Nature 353, 265–267 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/353265a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/353265a0
This article is cited by
-
Nanobiotechnology approaches for cardiovascular diseases: site-specific targeting of drugs and nanoparticles for atherothrombosis
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2022)
-
Relationship between lipoprotein concentrations and short-term and 1-year mortality in intensive care unit septic patients: results from the HIGHSEPS study
Annals of Intensive Care (2021)
-
An association of low high-density lipoprotein levels with recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma
Acta Neurochirurgica (2021)
-
APOA1: a Protein with Multiple Therapeutic Functions
Current Atherosclerosis Reports (2021)
-
In vivo estrogenicity of p-phenoxyphenol and p-pentyloxyphenol
Scientific Reports (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.