Abstract
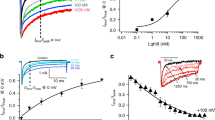
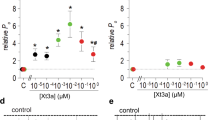
NEUROTOXINS that selectively block Na+, K+ or Ca2+ channels have provided valuable information about the functional diversity of the voltage-gated channel superfamily1. For Ca2+ channels, a variety of toxins have been found to block individual channel types2,3. The best-known example is ω-conotoxin-GVIA, a member of a large family of peptide toxins derived from venomous cone snails2,3, which potently and selectively blocks N-type Ca2+ channels4–9, allowing their purification10,11, cellular localization12,13, and the elucidation of their roles in Ca2+ entry14, neurotransmitter release15,16 and neuronal migration17. In contrast to Na+ and K+ channels, little is known about the molecular features that underlie Ca2+-channel susceptibility to toxin block; it is also unknown whether block occurs by direct physical occlusion3 or an action on channel gating18. Here we describe structural determinants of the N-type Ca2+ channel's interaction with ω-conotoxin-GVIA. When chimaeras combining individual motifs from the N-type channel and from a channel insensitive to ω-conotoxin-GVIA were expressed in Xenopus oocytes, each of the four motifs appeared to contribute to interaction with the toxin. The most dramatic effects on toxin interactions were seen at a single cluster of residues in the large putative extracellular loopbetween IIIS5 and IIIH5, consistent with a direct pore-blocking mechanism. These results provide a starting point for delineating the architecture of the outer vestibule of the Ca2+ channel.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hille, B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes (Sinauer, Sutherland, Massachusetts, 1992).
Olivera, B. M. et al. Biochemistry 23, 5087 (1984).
Olivera, B. M., Miljanich, G., Ramachandran, J. & Adams, M. E. A. Rev. Biochem. (in the press).
McCleskey, E. W. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 4327–4331 (1987).
Aosaki, T. & Kasai, H. Pflugers Arch. 414, 150–156 (1989).
Boland, L. M., Morill, J. A. & Bean, B. P. J. Neurosci. (in the press).
Regan, L. J., Sah, D. W. Y. & Bean, B. P. Neuron 6, 269–280 (1991).
Tsien, R. W., Ellinor, P. & Horne, W. A. Trends Pharmac. Sci. 12, 349–354 (1991).
Zhang, J.-F. et al. Neuropharmacology 32, 1075–1088 (1993).
McEnery, M. W., Snowman, A. M., Sharp, A. H., Adams, M. E. & Snyder, S. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 11095 (1991).
Witcher, D. R. et al. Science 261, 486–489 (1993).
Robitaille, R., Adler, E. M. & Charlton, M. P. Neuron 5, 773–779 (1990).
Westenbroek, R. E. et al. Neuron 9, 1099–1115 (1992).
Nowycky, M. C., Fox, A. P. & Tsien, R. W. Nature 316, 440–443 (1985).
Hirning, L. D. et al. Science 239, 57–61 (1988).
Stanley, E. & Goping, G. J. Neurosci. 11, 985–993 (1991).
Komoru, H. & Rakic, P. Science 257, 806–809 (1992).
Witcher, D. R., DeWaard, M. & Campbell, K. P. Neuropharmacology 32, 1127–1139 (1993).
Williams, M. E. et al. Science 257, 389–395 (1992).
Dubel, S. J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 5058–5062 (1992).
Fujita, Y. et al. Neuron 10, 585 (1993).
Mori, Y. et al. Nature 350, 398–402 (1991).
Starr, T. V. B., Prystay, W. & Snutch, T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 5621–5625 (1991).
Plummer, M. R., Logothetis, D. E. & Hess, P. Neuron 2, 1453–1463 (1989).
Yang, J., Ellinor, P. T., Sather, W. A., Zhang, J.-F. & Tsien, R. W. Nature 366, 158–161 (1993).
Kim, M.-K., Morii, T., Sun, L.-X., Imoto, K. & Mori, Y. FEBS Lett. 318, 145–148 (1993).
Yoshikami, D., Bagabaldo, Z. & Olivera, B. M. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 560, 230–248 (1989).
MacKinnon, R. Nature 350, 232–235 (1991).
Miller, C., Stocker, M. & Goldstein, S. A. N. Biophysical J. 66, A23 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellinor, P., Zhang, JF., Horne, W. et al. Structural determinants of the blockade of N-type calcium channels by a peptide neurotoxin. Nature 372, 272–275 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/372272a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/372272a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.