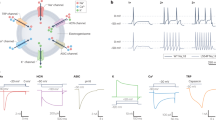
Abstract
The treatment of severe pain with opioids has thus far been limited by their unwanted central side effects. Recent research promises new approaches, including opioid analgesics acting outside the central nervous system, targeting of opioid peptide–containing immune cells to peripheral damaged tissue, and gene transfer to enhance opioid production at sites of injury.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Zeichnung © Christine Voigts-Grafik/UKBF Berlin

Zeichnung © Christine Voigts-Grafik/UKBF Berlin
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kieffer, B.L. & Gaveriaux-Ruff, C. Exploring the opioid system by gene knockout. Prog. Neurobiol. 66, 285–306 (2002).
Brower, V. New paths to pain relief. Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 387–391 (2000).
Machelska, H. & Stein, C. Immune mechanisms in pain control. Anesth. Analg. 95, 1002–1008 (2002).
Pan, Z.Z. Mu-opposing actions of the kappa-opioid receptor. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 19, 94–98 (1998).
Stein, C., Machelska, H. & Schäfer, M. Peripheral analgesic and antiinflammatory effects of opioids. Z. Rheumatol. 60, 416–424 (2001).
Fields, H.L., Emson, P.C., Leigh, B.K., Gilbert, R.F.T. & Iversen, L.L. Multiple opiate receptor sites on primary afferent fibres. Nature 284, 351–353 (1980).
Young, I., W.S., Wamsley, J.K., Zarbin, M.A. & Kuhar, M.J. Opioid receptors undergo axonal flow. Science 210, 76–77 (1980).
Hassan, A.H.S., Ableitner, A., Stein, C. & Herz, A. Inflammation of the rat paw enhances axonal transport of opioid receptors in the sciatic nerve and increases their density in the inflamed tissue. Neuroscience 55, 185–195 (1993).
Mousa, S.A., Zhang, Q., Sitte, N., Ji, R. & Stein, C. Beta-endorphin-containing memory-cells and mu-opioid receptors undergo transport to peripheral inflamed tissue. J. Neuroimmunol. 115, 71–78 (2001).
Truong, W., Cheng, C., Xu, Q.G., Li, X.Q. & Zochodne, D.W. Mu opioid receptors and analgesia at the site of a peripheral nerve injury. Ann. Neurol. 53, 366–375 (2003).
Stein, C. et al. Opioids from immunocytes interact with receptors on sensory nerves to inhibit nociception in inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 5935–5939 (1990).
Coggeshall, R.E., Zhou, S. & Carlton, S.M. Opiate receptors on peripheral sensory axons. Brain Res. 764, 126–132 (1997).
Wenk, H.N. & Honda, C.N. Immunohistochemical localization of delta opioid receptors in peripheral tissues. J. Comp. Neurol. 408, 567–579 (1999).
Stein, C. et al. No tolerance to peripheral morphine analgesia in presence of opioid expression in inflamed synovia. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 793–799 (1996).
Pare, M., Elde, R., Mazurkiewicz, J.E., Smith, A.M. & Rice, F.L. The Meissner corpuscle revised: a multiafferented mechanoreceptor with nociceptor immunochemical properties. J. Neurosci. 21, 7236–7246 (2001).
Poonyachoti, S., Kulkarni-Narla, A. & Brown, D.R. Chemical coding of neurons expressing delta- and kappa-opioid receptor and type I vanilloid receptor immunoreactivities in the porcine ileum. Cell Tissue Res. 307, 23–33 (2002).
Minami, M., Maekawa, K., Yabuuchi, K. & Satoh, M. Double in situ hybridization study on coexistence of mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptor mRNAs with preprotachykinin A mRNA in the rat dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 30, 203–210 (1995).
Borgland, S.L., Connor, M. & Christie, M.J. Nociceptin inhibits calcium channel currents in a subpopulation of small nociceptive trigeminal ganglion neurons in mouse. J. Physiol. 536, 35–47 (2001).
Zhou, L., Zhang, Q., Stein, C. & Schäfer, M. Contribution of opioid receptors on primary afferent versus sympathetic neurons to peripheral opioid analgesia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 286, 1000–1006 (1998).
Pertovaara, A. & Wei, H. Peripheral effects of morphine in neuropathic rats: role of sympathetic postganglionic nerve fibers. Eur. J. Pharmacol 429, 139–145 (2001).
Zöllner, C. et al. Painful inflammation-induced increase in mu-opioid receptor binding and G-protein coupling in primary afferent neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. (in the press).
Lewanowitsch, T. & Irvine, R.J. Naloxone methiodide reverses opioid-induced respiratory depression and analgesia without withdrawal. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 445, 61–67 (2002).
Shannon, H.E. & Lutz, E.A. Comparison of the peripheral and central effects of the opioid agonists loperamide and morphine in the formalin test in rats. Neuropharmacol. 42, 253–261 (2002).
King, M., Su, W., Chang, A., Zuckerman, A. & Pasternak, G.W. Transport of opioids from the brain to the periphery by P-glycoprotein: peripheral actions of central drugs. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 268–274 (2001).
Jiang, M. et al. Multiple neurological abnormalities in mice deficient in the G protein Go . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 3269–3274 (1998).
Taddese, A., Nah, S.-Y. & McCleskey, E.W. Selective opioid inhibition of small nociceptive neurons. Science 270, 1366–1369 (1995).
Akins, P.T. & McCleskey, E.W. Characterization of potassium currents in adult rat sensory neurons and modulation by opioids and cyclic AMP. Neuroscience 56, 759–769 (1993).
Ingram, S.L. & Williams, J.T. Opioid inhibition of Ih via adenylyl cyclase. Neuron 13, 179–186 (1994).
Gold, M.S. & Levine, J.D. DAMGO inhibits prostaglandin E2-induced potentiation of a TTX-resistant Na+ current in rat sensory neurons in vitro. Neurosci. Lett. 212, 83–86 (1996).
Laird, J.M., Souslova, V., Wood, J.N. & Cervero, F. Deficits in visceral pain and referred hyperalgesia in Nav1.8 (SNS/PN3)-null mice. J. Neurosci. 22, 8352–8356 (2002).
Porreca, F. et al. A comparison of the potential role of the tetrodotoxin-insensitive sodium channels, PN3/SNS and NaN/SNS2, in rat models of chronic pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7640–7644 (1999).
Stein, C. Peripheral mechanisms of opioid analgesia. Anesth. Analg. 76, 182–191 (1993).
Walker, J., Catheline, G., Guilbaud, G. & Kayser, V. Lack of cross-tolerance between the antinociceptive effects of systemic morphine and asimadoline, a peripherally-selective kappa-opioid agonist, in CCI-neuropathic rats. Pain 83, 509–516 (1999).
Kalso, E., Smith, L., McQuay, H.J. & Moore, R.A. No pain, no gain: clinical excellence and scientific rigour—lessons learned from IA morphine. Pain 98, 269–275 (2002).
Kraus, J. et al. Regulation of mu-opioid receptor gene transcription by interleukin-4 and influence of an allelic variation within a STAT6 transcription factor binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 43901–43908 (2001).
Borner, C., Höllt, V. & Kraus, J. Involvement of activator protein-1 in transcriptional regulation of the human mu-opioid receptor gene. Mol. Pharmacol. 61, 800–805 (2002).
Ji, R.-R. et al. Expression of μ-, δ-, and κ-opioid receptor-like immunoreactivities in rat dorsal root ganglia after carrageenan-induced inflammation. J. Neurosci. 15, 8156–8166 (1995).
Jeanjean, A.P., Moussaoui, S.M., Maloteaux, J.-M. & Laduron, P.M. Interleukin-1β induces long-term increase of axonally transported opiate receptors and substance P. Neuroscience 68, 151–157 (1995).
Selley, D.E., Breivogel, C.S. & Childers, S.R. Modification of G protein-coupled functions by low pH pretreatment of membranes from NG108-15 cells: increase in opioid agonist efficacy by decreased inactivation of G proteins. Mol. Pharmacol. 44, 731–741 (1993).
Antonijevic, I., Mousa, S.A., Schäfer, M. & Stein, C. Perineurial defect and peripheral opioid analgesia in inflammation. J. Neurosci. 15, 165–172 (1995).
Picard, P.R., Tramer, M.R., McQuay, H.J. & Moore, R.A. Analgesic efficacy of peripheral opioids (all except intra-articular): a qualitative systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Pain 72, 309–318 (1997).
Murphy, D.B., McCartney, C.J. & Chan, V.W. Novel analgesic adjuncts for brachial plexus block: a systematic review. Anesth. Analg. 90, 1122–1128 (2000).
Schulte-Steinberg, H. et al. Intraperitoneal versus interpleural morphine or bupivacaine for pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesthesiology 82, 634–640 (1995).
Likar, R. et al. Efficacy of peripheral morphine analgesia in inflamed, non-inflamed and perineural tissue of dental surgery patients. J. Pain Symptom Manage. 21, 330–337 (2001).
Aley, K.O., Green, P.G. & Levine, J.D. Opioid and adenosine peripheral antinociception are subject to tolerance and withdrawal. J. Neurosci. 15, 8031–8038 (1995).
Kolesnikov, Y. & Pasternak, G.W. Topical opioids in mice: analgesia and reversal of tolerance by a topical N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 290, 247–252 (1999).
Honore, P., Catheline, G., Le Guen, S. & Besson, J.M. Chronic treatment with systemic morphine induced tolerance to the systemic and peripheral antinociceptive effects of morphine on both carrageenin induced mechanical hyperalgesia and spinal c-Fos expression in awake rats. Pain 71, 99–108 (1997).
Nozaki-Taguchi, N. & Yaksh, T.L. Characterization of the antihyperalgesic action of a novel peripheral mu-opioid receptor agonist-loperamide. Anesthesiology 90, 225–234 (1999).
Ferreira, S.H., Lorenzetti, B.B. & Rae, G.A. Is methylnalorphinium the prototype of an ideal peripheral analgesic. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 99, 23–29 (1984).
Ueda, H. & Inoue, M. Peripheral morphine analgesia resistant to tolerance in chronic morphine-treated mice. Neurosci. Lett. 266, 105–108 (1999).
Kieffer, B.L. & Evans, C.J. Opioid tolerance - in search of the holy grail. Cell 108, 587–590 (2002).
Smith, E.M. Opioid peptides in immune cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 521, 51–68 (2003).
Cabot, P.J. et al. Immune cell-derived β-endorphin: production, release and control of inflammatory pain in rats. J. Clin. Invest. 100, 142–148 (1997).
Cabot, P.J., Carter, L., Schäfer, M. & Stein, C. Methionine-enkephalin- and Dynorphin A-release from immune cells and control of inflammatory pain. Pain 93, 207–212 (2001).
Stein, C., Hassan, A.H.S., Lehrberger, K., Giefing, J. & Yassouridis, A. Local analgesic effect of endogenous opioid peptides. Lancet 342, 321–324 (1993).
Rittner, H.L. et al. Opioid peptide-expressing leukocytes: identification, recruitment, and simultaneously increasing inhibition of inflammatory pain. Anesthesiology 95, 500–508 (2001).
Mousa, S.A., Machelska, H., Schäfer, M. & Stein, C. Immunohistochemical localization of endomorphin-1 and endomorphin-2 in immune cells and spinal cord in a model of inflammatory pain. J. Neuroimmunol. 126, 5–15 (2002).
von Andrian, U.H. & Mackay, C.R. T-cell function and migration. Two sides of the same coin. N. Engl. J. Med. 343, 1020–1034 (2000).
Mousa, S.A., Machelska, H., Schäfer, M. & Stein, C. Co-expression of beta-endorphin with adhesion molecules in a model of inflammatory pain. J. Neuroimmunol. 108, 160–170 (2000).
Machelska, H. et al. Opioid control of inflammatory pain regulated by intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J. Neurosci. 22, 5588–5596 (2002).
Machelska, H., Cabot, P.J., Mousa, S.A., Zhang, Q. & Stein, C. Pain control in inflammation governed by selectins. Nat. Med. 4, 1425–1428 (1998).
Schäfer, M., Carter, L. & Stein, C. Interleukin-1β and corticotropin-releasing-factor inhibit pain by releasing opioids from immune cells in inflamed tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 4219–4223 (1994).
Schäfer, M., Mousa, S.A., Zhang, Q., Carter, L. & Stein, C. Expression of corticotropin-releasing factor in inflamed tissue is required for intrinsic peripheral opioid analgesia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 6096–6100 (1996).
Schmitt, T.K. et al. Modulation of peripheral endogenous opioid analgesia by central afferent blockade. Anesthesiology 98, 195–202 (2003).
Parsons, C.G., Czlonkowski, A., Stein, C. & Herz, A. Peripheral opioid receptors mediating antinociception in inflammation. Activation by endogenous opioids and role of the pituitary-adrenal axis. Pain 41, 81–93 (1990).
Khodorova, A. et al. Endothelin-B receptor activation triggers an endogenous analgesic cascade at sites of peripheral injury. Nat. Med. 9, 1055–1061 (2003).
Braz, J. et al. Therapeutic efficacy in experimental polyarthritis of viral-driven enkephalin overproduction in sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 21, 7881–7888 (2001).
Barber, A. et al. A pharmacological profile of the novel, peripherally-selective κ-opioid receptor agonist, EMD 61753. Br. J. Pharmacol. 113, 1317–1327 (1994).
Jonker, J.W. et al. Role of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein in limiting brain accumulation and sedative side-effects of asimadoline, a peripherally acting analgaesic drug. Br. J. Pharmacol. 127, 43–50 (1999).
DeHaven-Hudkins, D.L. et al. Loperamide (ADL 2-1294), an opioid antihyperalgesic agent with peripheral selectivity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 289, 494–502 (1999).
Sandner-Kiesling, A. et al. Effect of kappa opioid agonists on visceral nociception induced by uterine cervical distension in rats. Pain 96, 13–22 (2002).
Eisenach, J.C., Carpenter, R. & Curry, R. Analgesia from a peripherally active κ-opioid receptor agonist in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Pain 101, 89–95 (2003).
Binder, W. et al. Analgesic and antiinflammatory effects of two novel kappa opioid peptides. Anesthesiology 94, 1034–1044 (2001).
Stein, C., Millan, M.J., Shippenberg, T.S., Peter, K. & Herz, A. Peripheral opioid receptors mediating antinociception in inflammation. Evidence for involvement of mu, delta and kappa receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 248, 1269–1275 (1989).
Machelska, H. et al. Peripheral effects of the kappa-opioid agonist EMD 61753 on pain and inflammation in rats and humans. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 290, 354–361 (1999).
Averbeck, B., Reeh, P.W. & Michaelis, M. Modulation of CGRP and PGE2 release from isolated rat skin by alpha-adrenoceptors and kappa-opioid-receptors. Neuroreport 12, 2097–2100 (2001).
Yaksh, T.L. Substance P release from knee joint afferent terminals: modulation by opioids. Brain Res. 458, 319–324 (1988).
Chao, C.C., Molitor, T.W., Close, K., Hu, S. & Peterson, P.K. Morphine inhibits the release of tumor necrosis factor in human peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 15, 447–453 (1993).
Wilson, J.L., Walker, J.S., Antoon, J.S. & Perry, M.A. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in adjuvant arthritis in rats: inhibition by kappa-opioid agonist but not by NSAID. J. Rheumatol. 25, 499–505 (1998).
Sengupta, J.N., Snider, A., Su, X. & Gebhart, G.F. Effects of kappa opioids in the inflamed rat colon. Pain 79, 175–185 (1999).
Houghton, A.K., Valdez, J.G. & Westlund, K.N. Peripheral morphine administration blocks the development of hyperalgesia and allodynia after bone damage in the rat. Anesthesiology 89, 190–201 (1998).
Likar, R. et al. Intraarticular morphine analgesia in chronic pain patients with osteoarthritis. Anesth. Analg. 84, 1313–1317 (1997).
Stein, A., Yassouridis, A., Szopko, C., Helmke, K. & Stein, C. Intraarticular morphine versus dexamethasone in chronic arthritis. Pain 83, 525–532 (1999).
Khoury, G.F., Chen, A.C.N., Garland, D.E. & Stein, C. Intraarticular morphine, bupivacaine and morphine/bupivacaine for pain control after knee videoarthroscopy. Anesthesiology 77, 263–266 (1992).
Reuben, S.S. et al. Local administration of morphine for analgesia after iliac bone graft harvest. Anesthesiology 95, 390–394 (2001).
Peyman, G.A., Rahimy, M.H. & Fernandes, M.L. Effects of morphine on corneal sensitivity and epithelial wound healing: implications for topical ophthalmic analgesia. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 78, 138–141 (1994).
Duckett, J.W., Cangiano, T., Cubina, M., Howe, C. & Cohen, D. Intravesical morphine analgesia after bladder surgery. J. Urol. 157, 1407–1409 (1997).
Rorarius, M. et al. Peripherally administered sufentanil inhibits pain perception after postpartum tubal ligation. Pain 79, 83–88 (1999).
Rosseland, L.A., Stubhaug, A., Skoglund, A. & Breivik, H. Intra-articular morphine for pain relief after knee arthroscopy. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 43, 252–257 (1999).
Bickel, A. et al. Effects of antihyperalgesic drugs on experimentally induced hyperalgesia in man. Pain 76, 317–325 (1998).
Polydefkis, M. et al. Reduced intraepidermal nerve fiber density in HIV-associated sensory neuropathy. Neurology 58, 115–119 (2002).
Lu, C.Y. et al. Gene-gun particle with pro-opiomelanocortin cDNA produces analgesia against formalin-induced pain in rats. Gene Ther. 9, 1008–1014 (2002).
Taguchi, A. et al. Selective postoperative inhibition of gastrointestinal opioid receptors. N. Engl. J. Med. 345, 935–940 (2001).
Simonin, F. & Kieffer, B.L. Two faces for an opioid peptide - and more receptors for pain research. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 185–186 (2002).
Stein, C., Millan, M.J., Shippenberg, T.S. & Herz, A. Peripheral effect of fentanyl upon nociception in inflamed tissue of the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 84, 225–228 (1988).
Stein, C. et al. Analgesic effect of intraarticular morphine after arthroscopic knee surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 325, 1123–1126 (1991).
Joris, J.L., Dubner, R. & Hargreaves, K.M. Opioid analgesia at peripheral sites: a target for opioids released during stress and inflammation? Anesth. Analg. 66, 1277–1281 (1987).
Koppert, W. et al. Peripheral antihyperalgesic effect of morphine to heat, but not mechanical, stimulation in healthy volunteers after ultraviolet-B irradiation. Anesth. Analg. 88, 117–122 (1999).
Likar, R., Kapral, S., Steinkellner, H., Stein, C. & Schäfer, M. Dose-dependency of intra-articular morphine analgesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 83, 241–244 (1999).
Dionne, R.A. et al. Analgesic effects of peripherally administered opioids in clinical models of acute and chronic inflammation. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 70, 66–73 (2001).
Moiniche, S., Dahl, J.B. & Kehlet, H. Peripheral antinociceptive effects of morphine after burn injury. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 37, 710–712 (1993).
Binder, W., Carmody, J. & Walker, J. Effect of gender on anti-inflammatory and analgesic actions of two kappa-opioids. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 292, 303–309 (2000).
Krajnik, M., Zylicz, Z., Finlay, I., Luczak, J. & van Sorge, A.A. Potential uses of topical opioids in palliative care—report of 6 cases. Pain 80, 121–125 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Voigts for the preparation of the illustrations, and B. Oldörp and C. Wiegand-Löhnert for their critical comments on the manuscript. The authors are supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (KFO 100, GRK 276, STE 477), the International Anesthesia Research Society (Frontiers in Anesthesia Research Program), the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (01GZ0311) and the Freie Universität Berlin (Research Program Inflammatory Diseases).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stein, C., Schäfer, M. & Machelska, H. Attacking pain at its source: new perspectives on opioids. Nat Med 9, 1003–1008 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm908
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm908
This article is cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory activities of several diterpenoids isolated from Hemionitis albofusca
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2024)
-
Dermorphin [D-Arg2, Lys4] (1-4) Amide Alleviates Frostbite-Induced Pain by Regulating TRP Channel-Mediated Microglial Activation and Neuroinflammation
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)
-
Dual Enkephalinase Inhibitors and Their Role in Chronic Pain Management
Current Pain and Headache Reports (2021)
-
Recent Advances in Peripheral Opioid Receptor Therapeutics
Current Pain and Headache Reports (2021)
-
Signaling mechanisms of μ-opioid receptor (MOR) in the hippocampus: disinhibition versus astrocytic glutamate regulation
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)