Abstract
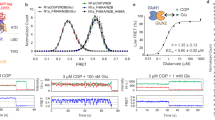
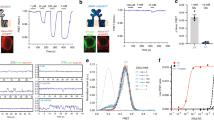
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are highly expressed in the central nervous system and are involved in excitatory synaptic transmission as well as synaptic plasticity. Despite considerable structural and biophysical research, the mechanism behind activation of the NMDA receptor is still poorly understood. By analyzing patch clamp recordings of one channel activated by glutamate, we determined the burst structure and open probability for recombinant rat NR1/NR2B receptors. We used partial agonists at the glutamate and glycine binding sites to show that at least two kinetically distinct subunit-associated conformational changes link co-agonist binding to the opening of the NMDA receptor pore. These data suggest that NR1 and NR2B subunits, respectively, undergo a fast and slow agonist-dependent conformational change that precedes opening of the pore. We propose a new working model of receptor activation that can account for macroscopic as well as microscopic NMDA receptor properties.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dingledine, R., Borges, K., Bowie, D. & Traynelis, S.F. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 51, 7–61 (1999).
Lester, R.A., Clements, J.D., Westbrook, G.L. & Jahr, C.E. Channel kinetics determine the time course of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents. Nature 346, 565–567 (1990).
Jahr, C.E. High-probability opening of NMDA receptor channels by L-glutamate. Science 255, 470–472 (1992).
Edmonds, B. & Colquhoun, D. Rapid decay of averaged single-channel NMDA receptor activations recorded at low agonist concentration. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 250, 279–286 (1992).
Premkumar, L.S., Qin, F. & Auerbach, A. Subconductance states of a mutant NMDA receptor channel kinetics, calcium and voltage dependence. J. Gen. Physiol. 109, 181–189 (1997).
Anson, L.C., Schoepfer, R., Colquhoun, D. & Wyllie, D.J. Single-channel analysis of an NMDA receptor possessing a mutation in the region of the glutamate binding site. J. Physiol. 527, 225–237 (2000).
Gibb, A.J. & Colquhoun, D. Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by L-glutamate in cells dissociated from adult rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 456, 143–179 (1992).
Lester, R.A. & Jahr, C.E. NMDA channel behavior depends on agonist affinity. J. Neurosci. 12, 635–643 (1992).
Schneggenburger, R. & Ascher, P. Coupling of permeation and gating in an NMDA-channel pore mutant. Neuron 18, 167–177 (1997).
Chen, N., Luo, T. & Raymond, L.A. Subtype-dependence of NMDA receptor channel open probability. J. Neurosci. 19, 6844–6854 (1999).
Rosenmund, C., Feltz, A. & Westbrook, G.L. Synaptic NMDA receptor channels have a low open probability. J. Neurosci. 15, 2788–2795 (1995).
Colquhoun, D. & Hawkes, A.G. Stochastic properties of ion channel openings and bursts in a membrane patch that contains two chanels: evidence concerning the number of channels present when a record containing only single openings is observed. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 240, 453–477 (1990).
Horn, R. Estimating the number of channels in patch recording. Biophys. J. 60, 433–439 (1991).
Rosenmund, C., Stern-Bach, Y. & Stevens, C.F. The tetrameric structure of a glutamate receptor channel. Science 280, 1596–1599 (1998).
Perozo, E. New structural perspectives on K+ channel gating. Structure 10, 1027–1029 (2002).
Yellen, G. The voltage-gated potassium channels and their relatives. Nature 419, 35–42 (2002).
Mansour, M., Nagarajan, N., Nehring, R.B., Clements, J.D. & Rosenmund, C. Heteromeric AMPA receptors assemble with a preferred subunit stoichiometry and spatial arrangement. Neuron 32, 841–853 (2001).
Antoine R., Stacey N.I., Hughes, T.E. & Howe, J.R. Subunit interactions and AMPA receptor desensitization. J. Neurosci. 21, 5574–5586 (2001).
Sobolevsky, A.I., Beck, C. & Wollmuth, L.P. Molecular rearrangements of the extracellular vestibule in NMDAR channels during gating. Neuron 33, 75–85 (2002).
Jones, K.S., VanDongen, H.M.A. & VanDongen, A.M.J. The NMDA receptor M3 segment is a conserved transduction element coupling ligand binding to channel opening. J. Neurosci. 22, 2044–2053 (2002).
Benveniste, M. & Mayer, M.L. Trapping of glutamate and glycine during open channel block of rat hippocampal neuron NMDA receptors by 9-aminoacridine. J. Physiol. 483, 367–385 (1995).
Sun, Y. et al. Mechanism of glutamate receptor desensitization. Nature 417, 245–253 (2002).
Careaga, C.L., Sutherland, J., Sabeti, J. & Falke, J.J. Large-amplitude twisting motions of an interdomain hinge: a disulfide trapping study of the galactose–glucose binding protein. Biochemistry 34, 3048–3055 (1995).
Sobolevsky, A.I., Rooney, L. & Wollmuth, L.P. Staggering of subunits in NMDAR channels. Biophysical. J. 83, 3304–3314 (2002).
Traynelis, S.F. & Wahl, P. Control of rat GluR6 glutamate receptor open probability by protein kinase A and calcineurin. J. Physiol. 503, 513–531 (1997).
Chen, C. & Okayama, H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 2745–2752 (1987).
Banke, T.G. et al. Control of GluR1 AMPA receptor function by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Neurosci. 20, 89–102 (2000).
Colquhoun, D. & Sigworth, F.J. Fitting and statistical analysis of single-channel records. in Single-channel Recording 2nd edn. (eds. Sakmann, B. & Neher, E.) 483–585 (Plenum Press, New York, 1995).
Qin, F., Auerbach, A. & Sachs, F. Estimating single-channel kinetic parameters from idealized patch clamp data containing missed events. Biophysical J. 70, 264–280 (1996).
Qin, F., Auerbach, A. & Sachs, F. Maximum likelihood estimation of aggregated Markov processes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 264, 375–383 (1997).
Perozo, E., Cortes, D.M. & Cuello, L.G. Structural rearrangements underlying K+-channel activation gating. Science 285, 73–78 (1999).
Jiang, Y. et al. The open pore conformation of potassium channels. Nature 417, 523–526 (2002).
Armstrong, N. & Gouaux, E. Mechanisms for activation and antagonism of an AMPA-sensitive glutamate receptor: crystal structures of the gluR2 ligand binding core. Neuron 28, 165–181 (2000).
Akk, G., Zhou, M. & Auerbach, A. A mutational analysis of the acetylcholine receptor channel transmitter binding site. Biophys. J. 76, 207–218 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Heinemann for sharing NMDA receptor cDNAs and D. Colquhoun for helpful discussions and sharing of software. In addition, we thank T. Auerbach for helpful discussions, critical comments on the manuscript and for suggesting the experiments with partial agonists. We also thank K. Erreger, A. Gibb and S. Cull-Candy for providing helpful comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by an Alfred Benzon Foundation grant (T.B.), a Danish Medical Research Fellowship (T.B.) and the National Institutes of Health (NS36654, S.F.T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banke, T., Traynelis, S. Activation of NR1/NR2B NMDA receptors. Nat Neurosci 6, 144–152 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1000
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1000
This article is cited by
-
Two gates mediate NMDA receptor activity and are under subunit-specific regulation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
A conserved glycine harboring disease-associated mutations permits NMDA receptor slow deactivation and high Ca2+ permeability
Nature Communications (2018)
-
NMDA receptors: linking physiological output to biophysical operation
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2017)
-
The structure–energy landscape of NMDA receptor gating
Nature Chemical Biology (2017)
-
A single-channel mechanism for pharmacological potentiation of GluN1/GluN2A NMDA receptors
Scientific Reports (2017)