Abstract
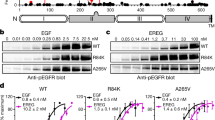
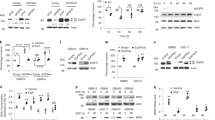
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)vIII is the most common EGFR mutant found in glioblastoma (GBM). EGFRvIII does not bind ligand, is highly oncogenic and is usually coexpressed with EGFR wild type (EGFRwt). EGFRvIII activates Met, and Met contributes to EGFRvIII-mediated oncogenicity and resistance to treatment. Here, we report that addition of EGF results in a rapid loss of EGFRvIII-driven Met phosphorylation in glioma cells. Met is associated with EGFRvIII in a physical complex. Addition of EGF results in a dissociation of the EGFRvIII–Met complex with a concomitant loss of Met phosphorylation. Consistent with the abrogation of Met activation, addition of EGF results in the inhibition of EGFRvIII-mediated resistance to chemotherapy. Thus, our study suggests that ligand in the milieu of EGFRvIII-expressing GBM cells is likely to influence the EGFRvIII–Met interaction and resistance to treatment, and highlights a novel antagonistic interaction between EGFRwt and EGFRvIII in glioma cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang PH, Xu AM, White FM . Oncogenic EGFR signaling networks in glioma. Sci Signal 2009; 2: re6.
Chin L, Meyerson M, Aldape K, Bigner D, Mikkelsen T, VandenBerg S et al. Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 2008; 455: 1061–1068.
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V, Qi Y, Wilkerson MD et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 98–110.
Heimberger AB, Hlatky R, Suki D, Yang D, Weinberg J, Gilbert M et al. Prognostic effect of epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma multiforme patients. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 1462–1466.
Pedersen MW, Meltorn M, Damstrup L, Poulsen HS . The type III epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Biological significance and potential target for anti-cancer therapy. Ann Oncol 2001; 12: 745–760.
Lorimer IA . Mutant epidermal growth factor receptors as targets for cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2002; 2: 91–102.
Hatanpaa KJ, Burma S, Zhao D, Habib AA . Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in glioma: Signal transduction, neuropathology, imaging and radioresistance. Neoplasia 2010; 12: 675–684.
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007; 21: 2683–2710.
Eder JP, Vande Woude GF, Boerner SA, LoRusso PM . Novel therapeutic inhibitors of the c-Met signaling pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 2207–2214.
Abounader R, Lal B, Luddy C, Koe G, Davidson B, Rosen EM et al. In vivo targeting of SF/HGF and c-met expression via U1snRNA/ribozymes inhibits glioma growth and angiogenesis and promotes apoptosis. FASEB J 2002; 16: 108–110.
Zou HY, Li Q, Lee JH, Arango ME, McDonnell SR, Yamazaki S et al. An orally available small-molecule inhibitor of c-Met, PF-2341066, exhibits cytoreductive antitumor efficacy through antiproliferative and antiangiogenic mechanisms. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 4408–4417.
Garnett J, Chumbalkar V, Vaillant B, Gururaj AE, Hill KS, Latha K et al. Regulation of HGF expression by DeltaEGFR-mediated c-Met activation in glioblastoma cells. Neoplasia 2013; 15: 73–84.
Xu L, Nilsson MB, Saintigny P, Cascone T, Herynk MH, Du Z et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor regulates MET levels and invasiveness through hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2616–2627.
Jo M, Stolz DB, Esplen JE, Dorko K, Michalopoulos GK, Strom SC . Cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and c-Met signal pathways in transformed cells. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 8806–8811.
Huang PH, Mukasa A, Bonavia R, Flynn RA, Brewer ZE, Cavenee WK et al. Quantitative analysis of EGFRvIII cellular signaling networks reveals a combinatorial therapeutic strategy for glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 12867–12872.
Chumbalkar V, Latha K, Hwang Y, Maywald R, Hawley L, Sawaya R et al. Analysis of phosphotyrosine signaling in glioblastoma identifies STAT5 as a novel downstream target of DeltaEGFR. J Proteome Res 2011; 10: 1343–1352.
Karpel-Massler G, Schmidt U, Unterberg A, Halatsch ME . Therapeutic inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor in high-grade gliomas: where do we stand? Mol Cancer Res 2009; 7: 1000–1012.
Stommel JM, Kimmelman AC, Ying H, Nabioullin R, Ponugoti AH, Wiedemeyer R et al. Coactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases affects the response of tumor cells to targeted therapies. Science 2007; 318: 287–290.
Li L, Chakraborty S, Yang C–R, Hatanpaa KJ, Cipher DJ, Puliyappadamba VT et al. An EGFR wild type–EGFRvIII-HB-EGF feed-forward loop regulates the activation of EGFRvIII. Oncogene 2014; 33: 4253–4264..
Mishima K, Higashiyama S, Asai A, Yamaoka K, Nagashima Y, Taniguchi N et al. Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor stimulates mitogenic signaling and is highly expressed in human malignant gliomas. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1998; 96: 322–328.
Tang P, Steck PA, Yung WK . The autocrine loop of TGF-alpha/EGFR and brain tumors. J Neurooncol 1997; 35: 303–314.
Ramnarain DB, Park S, Lee DY, Hatanpaa KJ, Scoggin SO, Otu H et al. Differential gene expression analysis reveals generation of an autocrine loop by a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor in glioma cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 867–874.
Biernat W, Huang H, Yokoo H, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H . Predominant expression of mutant EGFR (EGFRvIII) is rare in primary glioblastomas. Brain Pathol 2004; 14: 131–136.
Nishikawa R, Sugiyama T, Narita Y, Furnari F, Cavenee WK, Matsutani M . Immunohistochemical analysis of the mutant epidermal growth factor, deltaEGFR, in glioblastoma. Brain Tumor Pathol 2004; 21: 53–56.
Puliyappadamba VT, Chakraborty S, Chauncey SS, Li L, Hatanpaa KJ, Mickey B et al. Opposing Effect of EGFRWT on EGFRvIII-Mediated NF-kappaB Activation with RIP1 as a Cell Death Switch. Cell Rep 2013; 4: 764–775.
Dulak AM, Gubish CT, Stabile LP, Henry C, Siegfried JM . HGF-independent potentiation of EGFR action by c-Met. Oncogene 2011; 30: 3625–3635.
Wang X, Dong Y, Jiwani AJ, Zou Y, Pastor J, Kuro OM et al. Improved protein arrays for quantitative systems analysis of the dynamics of signaling pathway interactions. Proteome Sci 2011; 9: 53.
Inda MD, Bonavia R, Mukasa A, Narita Y, Sah DW, Vandenberg S et al. Tumor heterogeneity is an active process maintained by a mutant EGFR-induced cytokine circuit in glioblastoma. Genes Dev 2010; 24: 1731–1745.
Luwor RB, Zhu HJ, Walker F, Vitali AA, Perera RM, Burgess AW et al. The tumor-specific de2-7 epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) promotes cells survival and heterodimerizes with the wild-type EGFR. Oncogene 2004; 23: 6095–6104.
Hwang Y, Chumbalkar V, Latha K, Bogler O . Forced dimerization increases the activity of DeltaEGFR/EGFRvIII and enhances its oncogenicity. Mol Cancer Res 2011; 9: 1199–1208.
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 987–996.
Zhang Y, Farenholtz KE, Yang Y, Guessous F, Dipierro CG, Calvert VS et al. Hepatocyte growth factor sensitizes brain tumors to c-MET kinase inhibition. Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 1433–1444.
Li B, Yuan M, Kim IA, Chang CM, Bernhard EJ, Shu HK . Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor displays increased signaling through the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/AKT pathway and promotes radioresistance in cells of astrocytic origin. Oncogene 2004; 23: 4594–4602.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by NIH grant RO1NS062080 to AAH and by RO1 CA139217 to DAB. SB is supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (RO1 CA149461), National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NNX13AI13G) and the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (RP100644). This work was also supported by the Office of Medical Research, Departments of Veterans Affairs (RFS) and the National Institutes of Health (R01-DK63621, R01-CA134571 to RFS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Puliyappadamba, V., Chakraborty, S. et al. EGFR wild type antagonizes EGFRvIII-mediated activation of Met in glioblastoma. Oncogene 34, 129–134 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.534
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.534
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Poly(p-phenylenevinylene) nanoparticles modified with antiEGFRvIII for specific glioblastoma therapy
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
EGFR‐vIII downregulated H2AZK4/7AC though the PI3K/AKT‐HDAC2 axis to regulate cell cycle progression
Clinical and Translational Medicine (2020)
-
MET in glioma: signaling pathways and targeted therapies
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
The third-generation EGFR inhibitor AZD9291 overcomes primary resistance by continuously blocking ERK signaling in glioblastoma
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
FHL2 interacts with EGFR to promote glioblastoma growth
Oncogene (2018)