Abstract
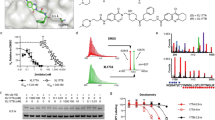
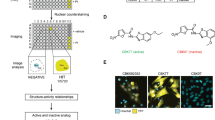
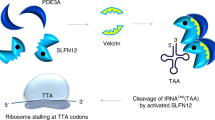
We have previously shown that the clinically relevant polyamine analog N1,N11-diethylnorspermine (DENSPM) causes rapid apoptosis in human melanoma SK-MEL-28 cells via a series of events that include mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and activation of the caspase cascade. Upstream to these events, DENSPM downregulates polyamine biosynthesis and potently upregulates polyamine catabolism at the level of spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase (SSAT). In searching for downstream effectors that either contribute to or abrogate the apoptotic response, we observed that DENSPM treatment of SK-MEL-28 cells for 30 h led to cytosolic release of Smac/Diablo, a mitochondrial protein known to bind and inhibit the function of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs). Subsequently, we found that DENSPM markedly lowered survivin and ML-IAP protein (but not XIAP) levels by 18 h via an apparently Smac/Diablo-independent pathway. Proteasome inhibitors fully prevented survivin and ML-IAP protein loss as well as apoptosis, suggesting that the proteasome-mediated degradation of survivin and ML-IAP is causally linked to the cellular outcome. We also observed that structural analogs of DENSPM which differentially induced SSAT and apoptosis lowered survivin and ML-IAP levels in a manner that correlated with enzyme activity. The linkage between IAPs and SSAT was more directly established by the finding that selective prevention of SSAT induction by small interfering RNA prevented survivin and ML-IAP loss as well as apoptosis during DENSPM treatment. Among the melanoma cell lines (SK-MEL-28, MALME-3M, A375 and LOX), survivin degradation correlated temporally with the onset of DENSPM induced apoptosis or growth inhibition. By contrast, ML-IAP degradation occurred only during rapid apoptosis seen in SK-MEL-28 cells. These data suggest a sequence of events whereby DENSPM induction of SSAT leads to loss of IAP proteins and a more fulminate apoptotic response. The findings implicate survivin and ML-IAP as important determinants of polyamine analog drug action in melanoma cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DENSPM:
-
N1,N11-diethylnorspermine also known as DE-333
- DE-343:
-
N1,N12-diethylspermine
- DE-443:
-
3,7,12,17-tetra-azanonadecane [N1,N13-diethyl(aminopropyl)homospermidine]
- DE-444:
-
N1,N14-diethylhomospermine
- IAP:
-
inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- ML-IAP:
-
melanoma IAP (also known as livin)
- siRNA:
-
small interfering RNA
- Spm:
-
spermine
- SSAT:
-
spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase
- siSSAT:
-
siRNA targeting SSAT
- XIAP:
-
X-chromosome-linked IAP
References
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC . (1997). Nat. Med., 3, 917–921.
Chen Y, Alm K, Vujcic S, Kramer DL, Kee K, Diegelman P and Porter CW (2003) Cancer Res. (In press).
Chen Y, Kramer DL, Diegelman P, Vujcic S and Porter CW . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 6437–6444.
Chen Y, Kramer DL, Vujcic S, Jell J and Porter CW . (Submitted 2003). Mol. Pharm.
Chen Z, Naito M, Hori S, Mashima T, Yamori T and Tsuruo T . (1999). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 264, 847–854.
Creaven PJ, Perez R, Pendyala L, Meropol NJ, Loewen G, Levine E, Berghorn E and Raghavan D . (1997). Invest. New Drugs, 15, 227–234.
Deveraux QL, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Van Arsdale T, Zhou Q, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Salvesen GS and Reed JC . (1998). EMBO J., 17, 2215–2223.
Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS and Reed JC . (1997). Nature, 388, 300–304.
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L and Wang X . (2000). Cell, 102, 33–42.
Duckett CS, Nava VE, Gedrich RW, Clem RJ, Van Dongen JL, Gilfillan MC, Shiels H, Hardwick JM and Thompson CB . (1996). EMBO J., 15, 2685–2694.
Fogel-Petrovic M, Vujcic S, Miller J and Porter CW . (1996). FEBS Lett., 391, 89–94.
Hahm HA, Ettinger DS, Bowling K, Hoker B, Chen TL, Zabelina Y and Casero Jr RA . (2002). Clin. Cancer Res., 8, 684–690.
Hinds MG, Norton RS, Vaux DL and Day CL . (1999). Nat. Struct. Biol., 6, 648–651.
Holcik M and Korneluk RG . (2001). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2, 550–556.
Kasof GM and Gomes BC . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 3238–3246.
Kramer DL, Chang BD, Chen Y, Diegelman P, Alm K, Black AR, Roninson IB and Porter CW . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 7754–7762.
Kramer DL, Vujcic S, Diegelman P, Alderfer J, Miller JT, Black JD, Bergeron RJ and Porter CW . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 1278–1286.
LaCasse EC, Baird S, Korneluk RG and MacKenzie AE . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 3247–3259.
Liston P, Roy N, Tamai K, Lefebvre C, Baird S, Cherton-Horvat G, Farahani R, McLean M, Ikeda JE, MacKenzie A and Korneluk RG . (1996). Nature, 379, 349–353.
Olie RA, Simoes-Wust AP, Baumann B, Leech SH, Fabbro D, Stahel RA and Zangemeister-Wittke U . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 2805–2809.
Porter CW and Bergeron RJ . (1988). Adv. Enzyme Regul., 27, 57–79.
Porter CW, Ganis B, Libby PR and Bergeron RJ . (1991). Cancer Res., 51, 3715–3720.
Reed JC and Bischoff JR . (2000). Cell, 102, 545–548.
Rothe M, Pan MG, Henzel WJ, Ayres TM and Goeddel DV . (1995). Cell, 83, 1243–1252.
Salvesen GS and Duckett CS . (2002). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 3, 401–410.
Shappell NW, Miller JT, Bergeron RJ and Porter CW . (1992). Anticancer Res., 12, 1083–1089.
Shin S, Sung BJ, Cho YS, Kim HJ, Ha NC, Hwang JI, Chung CW, Jung YK and Oh BH . (2001). Biochemistry, 40, 1117–1123.
Streiff RR and Bender JF . (2001). Invest. New Drugs, 19, 29–39.
Suzuki A, Hayashida M, Ito T, Kawano H, Nakano T, Miura M, Akahane K and Shiraki K . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 3225–3234.
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, Scudiero DA, Vigna N, Oltersdorf T and Reed JC . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 5315–5320.
Tanaka K, Iwamoto S, Gon G, Nohara T, Iwamoto M and Tanigawa N . (2000). Clin. Cancer Res., 6, 127–134.
van Loo G, Saelens X, van Gurp M, MacFarlane M, Martin SJ and Vandenabeele P . (2002). Cell Death Differ., 9, 1031–1042.
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly LM, Reid GE, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ and Vaux DL . (2000). Cell, 102, 43–53.
Vucic D, Deshayes K, Ackerly H, Pisabarro MT, Kadkhodayan S, Fairbrother WJ and Dixit VM . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 12275–12279.
Vucic D, Stennicke HR, Pisabarro MT, Salvesen GS and Dixit VM . (2000). Curr. Biol., 10, 1359–1366.
Vujcic S, Diegelman P, Bacchi CJ, Kramer DL and Porter CW . (2002). Biochem. J., 367, 665–675.
Vujcic S, Liang P, Diegelman P, Kramer DL and Porter CW . (2003). Biochem. J., 370, 19–28.
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP and Wang X . (1997). Science, 275, 1129–1132.
Zhao J, Tenev T, Martins LM, Downward J and Lemoine NR . (2000). J. Cell Sci., 113, (Part 23) 4363–4371.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the skilled technical assistance of Nicholas D Kisiel and Paula Diegelman and helpful discussions with Slavoljub Vujcic. This work was supported in part by Grant NCI RO1 CA-22153 and Institute Core Grant CA-16056.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Kramer, D., Li, F. et al. Loss of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins as a determinant of polyamine analog-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Oncogene 22, 4964–4972 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206725
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206725
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of autophagy enhances DENSpm-induced apoptosis in human colon cancer cells in a p53 independent manner
Cellular Oncology (2018)
-
Significant correlation between urinary N1, N12-diacetylspermine and tumor invasiveness in patients with clinical stage IA non-small cell lung cancer
BMC Cancer (2015)
-
Lack of functional p53 renders DENSpm-induced autophagy and apoptosis in time dependent manner in colon cancer cells
Amino Acids (2015)
-
Targeting polyamine metabolism and function in cancer and other hyperproliferative diseases
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2007)
-
Platinum drug effects on the expression of genes in the polyamine pathway: time-course and concentration-effect analysis based on Affymetrix gene expression profiling of A2780 ovarian carcinoma cells
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2007)