Abstract
Ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) desensitization can be modulated by mutations that change the stability of a dimer formed by the agonist binding domain. Desensitization of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors can be blocked by a single point mutation (e.g., GluR2 L483Y) that stabilizes this dimer in an active conformation. In contrast, desensitization of kainate receptors can be slowed, but not blocked, by similar dimer interface mutations. Only covalent cross-linking via introduced disulfides has been previously shown to block kainate receptor desensitization completely. We have now identified an apparently nondesensitizing GluR6 point mutant (D776K) located at the apex of the ligand binding (S1S2) domain dimer interface. Asp776 is one of a cluster of four charged residues in this region that together mediate direct dimer interactions and contribute to the binding sites for one chloride and two sodium ions. Despite the localized +4 change in the net charge of the S1S2 dimer, the D776K mutation actually increased the thermodynamic stability of the dimer. Unlike GluR6 wild type, the D776K mutant is insensitive to external cations but retains sensitivity to external anions. We therefore hypothesize that the unexpected phenotype of this charge reversal mutation results from the substitution of the sodium ions bound within the dimer interface by the introduced lysine 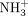 groups. The nondesensitizing D776K mutant provides insights into kainate receptor gating and represents a potentially useful new tool for dissecting kainate receptor function.
groups. The nondesensitizing D776K mutant provides insights into kainate receptor gating and represents a potentially useful new tool for dissecting kainate receptor function.
Footnotes
- Received March 27, 2009.
- Accepted June 25, 2009.
This work was supported by the UK Medical Research Council [Grant G0200084] and by the National Institutes of Health National Institute of General Medical Sciences [Grant T32-GM008704].
N.N. and Y.Z. contributed equally to this work.
ABBREVIATIONS: AMPA, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid; iGluR, ionotropic glutamate receptor; HEK, human embryonic kidney; WT, wild type; GluR, glutamate receptor; KA, kainate; PAGE, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; BN, Blue-Native; Endo H, endoglycosidase H; PNGase F, peptide-N--(N-acetyl-β-glucosaminyl)asparagine amidase; CNQX, 6-cyano-2,3-dihydroxy-7-nitroquinoxaline; ConA, concanavalin A.
↵1 Current affiliation: Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, University of Bristol, Bristol, United Kingdom.
- The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
MolPharm articles become freely available 12 months after publication, and remain freely available for 5 years.Non-open access articles that fall outside this five year window are available only to institutional subscribers and current ASPET members, or through the article purchase feature at the bottom of the page.
|